In human anatomy, the arm refers to the upper limb in common usage, although academically the term specifically means the upper arm between the glenohumeral joint and the elbow joint. The distal part of the upper limb between the elbow and the radiocarpal joint is known as the forearm or "lower" arm, and the extremity beyond the wrist is the hand.

The scapula, also known as the shoulder blade, is the bone that connects the humerus with the clavicle. Like their connected bones, the scapulae are paired, with each scapula on either side of the body being roughly a mirror image of the other. The name derives from the Classical Latin word for trowel or small shovel, which it was thought to resemble.

The humerus is a long bone in the arm that runs from the shoulder to the elbow. It connects the scapula and the two bones of the lower arm, the radius and ulna, and consists of three sections. The humeral upper extremity consists of a rounded head, a narrow neck, and two short processes. The body is cylindrical in its upper portion, and more prismatic below. The lower extremity consists of 2 epicondyles, 2 processes, and 3 fossae. As well as its true anatomical neck, the constriction below the greater and lesser tubercles of the humerus is referred to as its surgical neck due to its tendency to fracture, thus often becoming the focus of surgeons.

The radial nerve is a nerve in the human body that supplies the posterior portion of the upper limb. It innervates the medial and lateral heads of the triceps brachii muscle of the arm, as well as all 12 muscles in the posterior osteofascial compartment of the forearm and the associated joints and overlying skin.

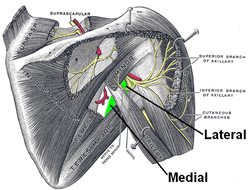
The axillary nerve or the circumflex nerve is a nerve of the human body, that originates from the brachial plexus at the level of the axilla (armpit) and carries nerve fibers from C5 and C6. The axillary nerve travels through the quadrangular space with the posterior circumflex humeral artery and vein to innervate the deltoid and teres minor.

The deltoid muscle is the muscle forming the rounded contour of the human shoulder. It is also known as the 'common shoulder muscle', particularly in other animals such as the domestic cat. Anatomically, the deltoid muscle is made up of three distinct sets of muscle fibers, namely the
- anterior or clavicular part
- posterior or scapular part
- intermediate or acromial part

The upper limbs or upper extremities are the forelimbs of an upright-postured tetrapod vertebrate, extending from the scapulae and clavicles down to and including the digits, including all the musculatures and ligaments involved with the shoulder, elbow, wrist and knuckle joints. In humans, each upper limb is divided into the shoulder, arm, elbow, forearm, wrist and hand, and is primarily used for climbing, lifting and manipulating objects. In anatomy, just as arm refers to the upper arm, leg refers to the lower leg.

The teres minor is a narrow, elongated muscle of the rotator cuff. The muscle originates from the lateral border and adjacent posterior surface of the corresponding right or left scapula and inserts at both the greater tubercle of the humerus and the posterior surface of the joint capsule.

The triceps, or triceps brachii, is a large muscle on the back of the upper limb of many vertebrates. It consists of three parts: the medial, lateral, and long head. It is the muscle principally responsible for extension of the elbow joint.
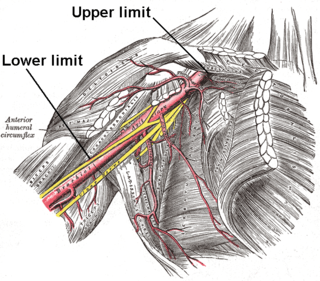
In human anatomy, the axillary artery is a large blood vessel that conveys oxygenated blood to the lateral aspect of the thorax, the axilla (armpit) and the upper limb. Its origin is at the lateral margin of the first rib, before which it is called the subclavian artery.

The shoulder joint is structurally classified as a synovial ball-and-socket joint and functionally as a diarthrosis and multiaxial joint. It involves an articulation between the glenoid fossa of the scapula and the head of the humerus. Due to the very loose joint capsule, it gives a limited interface of the humerus and scapula, it is the most mobile joint of the human body.

The teres major muscle is a muscle of the upper limb. It attaches to the scapula and the humerus and is one of the seven scapulohumeral muscles. It is a thick but somewhat flattened muscle.
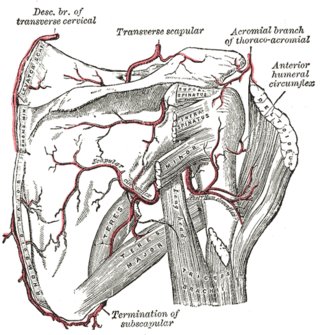
The circumflex scapular artery is a branch of the subscapular artery and part of the scapular anastomoses.

The deep artery of arm is a large artery of the arm which arises from the brachial artery. It descends in the arm before ending by anastomosing with the radial recurrent artery.

The posterior humeral circumflex artery arises from the third part of the axillary artery at the distal border of the subscapularis.

The fascial compartments of arm refers to the specific anatomical term of the compartments within the upper segment of the upper limb of the body. The upper limb is divided into two segments, the arm and the forearm. Each of these segments is further divided into two compartments which are formed by deep fascia – tough connective tissue septa (walls). Each compartment encloses specific muscles and nerves.
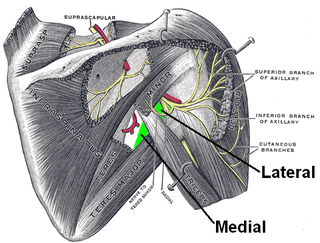
The quadrangular space, also known as the quadrilateral space (of Velpeau) and the foramen humerotricipitale, is one of the three spaces in the axillary space. The other two spaces are: triangular space and triangular interval.

The triangular space is one of the three spaces found at the axillary space. The other two spaces are the quadrangular space and the triangular interval.

The triangular interval is a space found in the axilla. It is one of the three intermuscular spaces found in the axillary space. The other two spaces are: quadrangular space and triangular space.

The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to human anatomy: