
Aetosaurs were heavily armored reptiles belonging to the extinct order Aetosauria. They were medium- to large-sized omnivorous or herbivorous pseudosuchians, part of the branch of archosaurs more closely related to crocodilians than to birds and other dinosaurs. All known aetosaurs are restricted to the Late Triassic, and in some strata from this time they are among the most abundant fossil vertebrates. They have small heads, upturned snouts, erect limbs, and a body ornamented with four rows of plate-like osteoderms. Aetosaur fossil remains are known from Europe, North and South America, parts of Africa, and India. Since their armoured plates are often preserved and are abundant in certain localities, aetosaurs serve as important Late Triassic tetrapod index fossils. Many aetosaurs had wide geographic ranges, but their stratigraphic ranges were relatively short. Therefore, the presence of particular aetosaurs can accurately date a site that they are found in.
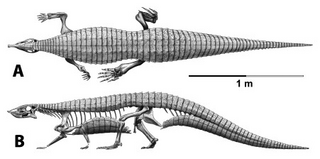
Stagonolepis is an extinct genus of stagonolepidid aetosaur known from the Late Triassic Hassberge Formation of Germany, the Drawno Beds of Poland, the Lossiemouth Sandstone of Scotland, the Chinle Formation of Arizona and Utah and the Bluewater Creek Formation of New Mexico.

Desmatosuchus is an extinct genus of archosaur belonging to the Order Aetosauria. It lived during the Late Triassic.

Mahajangasuchus is an extinct genus of crocodyliform which had blunt, conical teeth. The type species, M. insignis, lived during the Late Cretaceous; its fossils have been found in the Maevarano Formation in northern Madagascar. It was a fairly large predator, measuring up to 3 m (9.8 ft) with a weight up to 360 kg (790 lb).

Qianosuchus is an extinct genus of aquatic poposauroid archosaur from the middle Triassic (Anisian) Guanling Formation of Pan County, China. It is represented by two nearly complete skeletons and a crushed skull preserved in the limestone. Qianosuchus was at least 3 metres long, and had several skeletal adaptations which indicate a semi-marine lifestyle, similar to modern-day saltwater crocodiles. These adaptations have not been seen in any other archosaur from the Triassic.

Typothorax is an extinct genus of typothoracine aetosaur that lived in the Late Triassic. Its remains have been found in North America. Two species are known: T. coccinarum, the type species, and T. antiquum.

Polonosuchus is a genus of rauisuchid known from the late Triassic of Poland. It was a huge predator about 5–6 metres in length and, like all rauisuchians, was equipped with a large head of long sharp teeth. The legs were placed almost underneath the body, unlike most reptiles, which would have made it quite fast and a powerful runner. The appearance was very similar to that of the more known Postosuchus, of North America, and shared with the latter the ecological niche of the apex predator.

Paratypothorax is an extinct genus of aetosaur, known from a single species, Paratypothorax andressi. It was a broadly distributed member of the group found in Germany, North America, and possibly parts of Gondwana. The best specimens come from Germany, though for more than a century they were mistakenly considered phytosaur armor. Paratypothorax was a large and wide-bodied typothoracine aetosaur, as well as the namesake of the tribe Paratypothoracisini.

Typothoracinae is a clade of aetosaurs within the subfamily Aetosaurinae. It was originally defined as a stem-based taxon including all aetosaurs closer to Typothorax than to Stagonolepis or Desmatosuchus. This definition was later expanded to specifically exclude Aetosaurus; as of 2016, Typothoracinae is defined as the least inclusive clade containing Typothorax and Paratypothorax, but not Aetosaurus,Stagonolepis, or Desmatosuchus. The clade was first named in 2007 under the spelling Typothoracisinae, after its namesake Typothorax. However, this spelling was based on incorrect taxonomic nomenclature, and the clade's name was corrected to Typothoracinae in 2016.

Aetosaurinae is one of the two main clades of aetosaurs, the other being Desmatosuchia. It is a stem-based taxon defined as all aetosaurs more closely related to Aetosaurus than Desmatosuchus. Aetosaurinae currently comprises Aetosaurus, similar forms such as Coahomasuchus and Stenomyti, and the widespread and successful aetosaur clade Typothoracinae.

Paratypothoracini is a clade of aetosaurs within the group Typothoracinae. It is a node-based taxon that includes Rioarribasuchus (=Heliocanthus), Paratypothorax, Tecovasuchus, and all descendants of their most recent common ancestor. The clade was first named in 2007 under the spelling Paraypothoracisini, after its namesake Paratypothorax. However, this spelling was based on incorrect taxonomic nomenclature, and the clade's name was corrected to Paratypothoracinae in 2016.

Desmatosuchinae is a major subfamily of aetosaurs within the clade Desmatosuchia. It is a stem-based taxon defined as all aetosaurs more closely related to Desmatosuchus than to Stagonolepis,Aetosaurus, or Paratypothorax.

Vancleavea is a genus of extinct, armoured, non-archosaurian archosauriforms from the Late Triassic of western North America. The type and only known species is V. campi, named by Robert Long & Phillip A Murry in 1995. At that time, the genus was only known from fragmentary bones including osteoderms and vertebrae. However, since then many more fossils have been found, including a pair of nearly complete skeletons discovered in 2002. These finds have shown that members of the genus were bizarre semiaquatic reptiles. Vancleavea individuals had short snouts with large, fang-like teeth, and long bodies with small limbs. They were completely covered with bony plates known as osteoderms, which came in several different varieties distributed around the body. Phylogenetic analyses by professional paleontologists have shown that Vancleavea was an archosauriform, part of the lineage of reptiles that would lead to archosaurs such as dinosaurs and crocodilians. Vancleavea lacks certain traits which are present in most other archosauriforms, most notably the antorbital, mandibular and supratemporal fenestrae, which are weight-saving holes in the skulls of other taxa. However, other features clearly support its archosauriform identity, including a lack of intercentra, the presence of osteoderms, an ossified laterosphenoid, and several adaptations of the femur and ankle bones. In 2016, a new genus of archosauriform, Litorosuchus, was described. This genus resembled both Vancleavea and more typical archosauriforms in different respects, allowing Litorosuchus to act as a transitional fossil linking Vancleavea to less aberrant archosauriforms.

Parringtonia is an extinct genus of Triassic archosaur within the family Erpetosuchidae, known from the type species Parringtonia gracilis. It is known from a single specimen, NHMUK R8646, found from the Anisian-age Manda Formation of Tanzania. This specimen, like most archosaur material from the Manda Formation, is fragmentary, including only a maxilla and a few postcranial bones. They show similarities with those of another archosaur called Erpetosuchus, known from the Middle Triassic of Scotland and the eastern United States. The phylogenetic placement of Parringtonia and Erpetosuchus are uncertain; some studies placed them close to the group Crocodylomorpha, which includes all modern crocodylians and many extinct forms that diversified after the Triassic, but this relationship has more recently been questioned.
Redondasuchus is an extinct genus of aetosaur. It may be a junior synonym of Typothorax coccinarum, another aetosaur. Redondasuchus is a member of the clade Typothoracisinae within the subfamily Aetosaurinae, and lived during the middle Norian stage of the Late Triassic. Material belonging to the genus has been found from the Redonda Formation in east-central New Mexico. The type species, R. reseri, was named in 1991 after having been referred to as a species of Typothorax since 1985. A second species, R. rineharti, was described in 2006.
Tarjadia is an extinct genus of erpetosuchid pseudosuchian, distantly related to modern crocodilians. It is known from a single species, T. ruthae, first described in 1998 from the Middle Triassic Chañares Formation in Argentina. Partial remains have been found from deposits that are Anisian-Ladinian in age. Long known mostly from osteoderms, vertebrae, and fragments of the skull, specimens described in 2017 provided much more anatomical details and showed that it was a fairly large predator. Tarjadia predates known species of aetosaurs and phytosaurs, two Late Triassic groups of crurotarsans with heavy plating, making it one of the first heavily armored archosaurs. Prior to 2017, most studies placed it outside Archosauria as a member of Doswelliidae, a family of heavily armored and crocodile-like archosauriforms. The 2017 specimens instead show that it belonged to the Erpetosuchidae.

Erpetosuchidae is an extinct family of pseudosuchian archosaurs. Erpetosuchidae was named by D. M. S. Watson in 1917 to include Erpetosuchus. It includes the type species Erpetosuchus granti from the Late Triassic of Scotland, Erpetosuchus sp. from the Late Triassic of eastern United States and Parringtonia gracilis from the middle Middle Triassic of Tanzania; the group might also include Dyoplax arenaceus from the Late Triassic of Germany, Archeopelta arborensis and Pagosvenator candelariensis from Brazil and Tarjadia ruthae from Argentina.
Jaxtasuchus is an extinct genus of armored doswelliid archosauriform reptile known from the Middle Triassic of the Erfurt Formation in Germany. The type species, Jaxtasuchus salomoni, was named in 2013 on the basis of several incomplete skeletons and other isolated remains. Like other doswelliids, members of the genus were heavily armored, with four longitudinal rows of bony plates called osteoderms covering the body. Jaxtasuchus is the first doswelliid known from Europe and is most closely related to Doswellia from the Late Triassic of the eastern United States. However, it was not as specialized as Doswellia, retaining several generalized archosauriform characteristics and having less armor. Jaxtasuchus fossils have been found in aquatic mudstones alongside fossils of temnospondyl amphibians, crustaceans, and mollusks, suggesting that Jaxtasuchus was semiaquatic like modern crocodilians.
Polesinesuchus is an extinct genus of stagonolepidid aetosaur known from the Late Triassic of southern Brazil. Fossils have been found from the Santa Maria Supersequence of the late Carnian and early Norian stages, making Polesinesuchus one of the oldest aetosaurs. It contains a single species, Polesinesuchus aurelioi, the fifth aetosaur species known from South America to date. Anatomical evidence suggests that Polesinesuchus likely represents a juvenile individual of the contemporary Aetosauroides.
Gorgetosuchus is an extinct genus of aetosaur from the Late Triassic of the North Carolina, represented by the type species Gorgetosuchus pekinensis. It is mainly known from osteoderms, including the front half of an articulated carapace. Gorgotesuchus is typically considered a basal desmatosuchin, though alternative interpretations exist.












