Related Research Articles

A pet, or companion animal, is an animal kept primarily for a person's company or entertainment rather than as a working animal, livestock, or a laboratory animal. Popular pets are often considered to have attractive/cute appearances, intelligence, and relatable personalities, but some pets may be taken in on an altruistic basis and accepted by the owner regardless of these characteristics.

An animal shelter or pound is a place where stray, lost, abandoned or surrendered animals – mostly dogs and cats – are housed. The word "pound" has its origins in the animal pounds of the agricultural communities, where stray livestock would be penned or impounded until they were claimed by their owners.
The Vinča symbols are a set of undeciphered symbols found on artifacts from the Neolithic Vinča culture and other "Old European" cultures of Central and Southeast Europe. They have sometimes been described as an example of proto-writing. The symbols went out of use around 3500 BC. Many scholars agree that the "writing" itself is not based on any language whatsoever and it is mostly symbolic.
Animal euthanasia is the act of killing an animal humanely, most commonly with injectable drugs. Reasons for euthanasia include incurable conditions or diseases, lack of resources to continue supporting the animal, or laboratory test procedures. Euthanasia methods are designed to cause minimal pain and distress. Euthanasia is distinct from animal slaughter and pest control.

Avala is a mountain in Serbia, overlooking Belgrade. It is situated in the south-eastern corner of the city and provides a great panoramic view of Belgrade, Vojvodina and Šumadija, as the surrounding area on all sides is mostly lowlands. It stands at 511 metres (1,677 ft) above sea level, which means that it enters the locally defined mountain category just by 11 m (36 ft).

The kallikantzaros is a malevolent creature in Southeast European and Anatolian folklore. Stories about the kallikantzaros or its equivalents can typically be found in Greece, Bulgaria, Turkey, Serbia, Albania, Bosnia, and Cyprus. Kallikantzaroi are believed to dwell underground but come to the surface during the twelve days of Christmas, from 25 December to 6 January.

Livestock branding is a technique for marking livestock so as to identify the owner. Originally, livestock branding only referred to hot branding large stock with a branding iron, though the term now includes alternative techniques. Other forms of livestock identification include freeze branding, inner lip or ear tattoos, earmarking, ear tagging, and radio-frequency identification (RFID), which is tagging with a microchip implant. The semi-permanent paint markings used to identify sheep are called a paint or color brand. In the American West, branding evolved into a complex marking system still in use today.
A breed registry, also known as a herdbook, studbook or register, in animal husbandry, the hobby of animal fancy, is an official list of animals within a specific breed whose parents are known. Animals are usually registered by their breeders while they are young. The terms studbook and register are also used to refer to lists of male animals "standing at stud", that is, those animals actively breeding, as opposed to every known specimen of that breed. Such registries usually issue certificates for each recorded animal, called a pedigree, pedigreed animal documentation, or most commonly, an animal's "papers". Registration papers may consist of a simple certificate or a listing of ancestors in the animal's background, sometimes with a chart showing the lineage.

Đerdap National Park stretches along the right bank of the Danube River from the Golubac Fortress to the dam near Novi Sip, Serbia. It was established in 1974 and spreads on 63,786.5 ha. The park management office is in the town of Donji Milanovac on the Danube. Across the river is the Parcul Natural Porțile de Fier in Romania.

Tara is a mountain in western Serbia. It is part of the Dinaric Alps and stands at 1,000 to 1,590 m above sea level. The mountain's slopes are clad in dense forests with numerous high-elevation clearings and meadows, steep cliffs, deep ravines carved by the nearby Drina River, and many karst caves. The mountain is a popular tourist centre. Tara National Park encompasses a large part of the mountain. The highest peak is Zborište, at 1,544 m (5,066 ft).

The Bosnian Crisis, also known as the Annexation Crisis or the First Balkan Crisis, erupted on 5 October 1908 when Austria-Hungary announced the annexation of Bosnia and Herzegovina, territories formerly within the sovereignty of the Ottoman Empire but under Austro-Hungarian administration since 1878.

Blic is a Serbian web portal covering politics, economy, entertainment, and current events. The first printed edition of Blic was published in 1996, its online portal was launched in 1998, and Blic TV began broadcasting in 2022. Blic is part of Ringier Serbia's portfolio, which belongs to the international media company Ringier, headquartered in Switzerland. According to Gemius Audience research, Blic has been Serbia's most visited news portal since 2012.

In property law, lost, mislaid, and abandoned property are categories of the common law of property which deals with personal property or chattel which has left the possession of its rightful owner without having directly entered the possession of another person. Property can be considered lost, mislaid, or abandoned depending on the circumstances under which it is found by the next party who obtains its possession.

Deliblato Sands is a large sand area covering around 300 km2 (120 sq mi) of ground in Vojvodina province, Serbia. It is located in southern Banat, situated between the river Danube and the southwestern slopes of the Carpathian Mountains. The sands are named after the village of Deliblato, in the municipality of Kovin. Its main masses are elliptical shaped hills with steppe grassland plains and steppe forests.

In Slavic folklore, the raskovnik or razkovniche is a magical herb. According to lore, the raskovnik has the magical property to unlock or uncover anything that is locked or closed. However, legends claim it is notoriously difficult to recognize the herb, and reputedly only certain chthonic animals are able to identify it.

A zduhać and vetrovnjak in Serbian tradition, and a dragon man in Bulgarian, Macedonian and southern Serbian traditions, were men believed to have an inborn supernatural ability to protect their estate, village, or region against destructive weather conditions, such as storms, hail, or torrential rains. It was believed that the souls of these men could leave their bodies in sleep, to intercept and fight with demonic beings imagined as bringers of bad weather. Having defeated the demons and taken away the stormy clouds they brought, the protectors would return into their bodies and wake up tired.

An ala or hala is a female mythological creature recorded in the folklore of Bulgarians, Macedonians, and Serbs. Ale are considered demons of bad weather whose main purpose is to lead hail-producing thunderclouds in the direction of fields, vineyards, or orchards to destroy the crops, or loot and take them away. Extremely voracious, ale particularly like to eat children, though their gluttony is not limited to Earth. It is believed they sometimes try devouring the Sun or the Moon, causing eclipses, and that it would mean the end of the world should they succeed. When people encounter an ala, their mental or physical health, or even life, are in peril; however, her favor can be gained by approaching her with respect and trust. Being in a good relationship with an ala is very beneficial, because she makes her favorites rich and saves their lives in times of trouble.
Serbian Christmas traditions are customs and practices of the Serbs associated with Christmas and a period encompassing it, between the third Sunday before Christmas Day and Epiphany. Serbian Christmas is celebrated on January 7th. There are many, complex traditions connected with this period. They vary from place to place, and in many areas have been updated or watered down to suit modern living. The Serbian name for Christmas is Božić, which is the diminutive form of the word bog ("god"), and can be translated as "young god". Christmas is celebrated for three consecutive days, starting with Christmas Day, which the Serbs call the first day of Christmas. On these days, one is to greet another person by saying "Christ is Born," which should be responded to with "Truly He is Born," or in Serbian: "Hristos se rodi" – "Vaistinu se rodi".
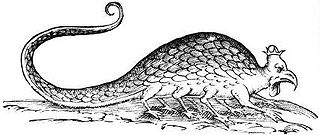
In European bestiaries and legends, a basilisk is a legendary reptile reputed to be a serpent king, who causes death to those who look into its eyes. According to the Naturalis Historia of Pliny the Elder, the basilisk of Cyrene is a small snake, "being not more than twelve inches in length", that is so venomous, it leaves a wide trail of deadly venom in its path, and its gaze is likewise lethal.

Pešturina is a cave in the municipality of Niška Banja in southeast Serbia. It is located southwest of Jelašnica and 20 km (12 mi) southeast of Niš. Artifacts from the Middle and Upper Paleolithic periods were discovered since the archaeological excavations began in 2006. The remains, identified as the Mousterian culture, were dated from 111,000 BP+ 5,000 to 39,000 BP + 3,000, which makes Pešturina one of the latest surviving Neanderthal habitats. The cave has been nicknamed the "Serbian Atapuerca".