Related Research Articles

The national flag of the Russian Federation is a tricolour of three equal horizontal bands: white on the top, blue in the middle, and red on the bottom.
Mat Zemlya is the Moist Earth Mother and is probably the oldest deity in Slavic mythology besides Marzanna. She is also called Mati Syra Zemlya meaning Mother Damp Earth or Mother Moist Earth. Her identity later blended into that of Mokosh.
Ruthenian is an exonymic linguonym for a closely related group of East Slavic linguistic varieties, particularly those spoken from the 15th to 18th centuries in the Grand Duchy of Lithuania and in East Slavic regions of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth. Regional distribution of those varieties, both in their literary and vernacular forms, corresponded approximately to the territories of the modern states of Belarus and Ukraine. By the end of the 18th century, they gradually diverged into regional variants, which subsequently developed into the modern Belarusian, Ukrainian, and Rusyn languages.

In the Slavic religious tradition, Domovoy (Russian: Домовой, literally "[the one] of the household"; also spelled Domovoi, Domovoj, and known as Polish: Domowik, Serbian: Домовик, Ukrainian: Домовик and Belarusian: Дамавік is the household spirit of a given kin. They are deified progenitors, that is to say the fountainhead ancestors of the kin. According to the Russian folklorist E. G. Kagarov, the Domovoy is a personification of the supreme Rod in the microcosm of kinship. Sometimes he has a female counterpart, Domania, the goddess of the household, though he is most often a single god. The Domovoy expresses himself as a number of other spirits of the household in its different functions.

A Slavic dragon is any dragon in Slavic mythology, including the Russian zmei, Ukrainian zmiy, and its counterparts in other Slavic cultures: the Bulgarian zmey, the Slovak drak and šarkan, Czech drak, Polish żmij, the Serbo-Croatian zmaj, the Macedonian zmej (змеј) and the Slovene zmaj. The Romanian zmeu could also be deemed a "Slavic" dragon, but a non-cognate etymology has been proposed.

The Ovinnik, Joŭnik or Jownik is a malevolent spirit of the threshing house in Slavic folklore whose name derived from ovin 'barn'. He is prone to burning down the threshing houses by setting fire to the grain. To placate him, peasants would offer him roosters and bliny. On New Year's Eve, the touch of an Ovinnik would determine their fortune for the New Year. A warm touch meant good luck and fortune, while a cold touch meant unhappiness.

Prince Pyotr Andreyevich Vyazemsky was a Russian Imperial poet, a leading personality of the Golden Age of Russian poetry.

Merefa is a city in Kharkiv Raion, Kharkiv Oblast, Ukraine. Merefa hosts the administration of Merefa urban hromada, one of the hromadas of Ukraine. Population: 21,202.
Boris Sokolov, is a historian and a Russian literature researcher. In 1979 he graduated from the department of geography of the Moscow State University, specialising in economic geography. His works have been translated into Japanese, Polish, Latvian and Estonian. He has also translated literary works from various languages.
Oleg Nikolayevich Trubachyov was a Russian linguist. A researcher of the etymology of Slavic languages and Slavic onomastics, he was considered a specialist in historical linguistics and lexicography. He was a Doctor of Sciences in Philological Sciences, an academician of the Russian Academy of Sciences and served as the editor-in-chief of the Etimologiya yearbook. His works are on the etymology of Slavic languages and on East Slavic onomastics.
The word Rus' referred initially to a group of Scandinavian Vikings, also known as Varangians, who founded the medieval state of Kievan Rus' in Eastern Europe in the 10th century. The term gradually acquired the meaning of the aforementioned dynastic polity itself, and also the geographic region of its heartlands Kiev, Pereiaslavl' and Chernihiv. Russia is a Hellenized rendition of the same word, and Ruthenia is its Latinized form.
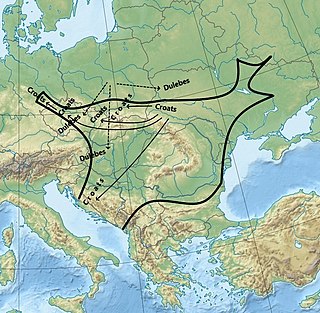
The Dulebes, Dulebs, Dudlebi or Dulibyh were one of the tribal unions of Early Slavs between the 6th and the 10th centuries. According to medieval sources they lived in Western Volhynia, as well as southern parts of the Duchy of Bohemia and the Middle Danube between Lake Balaton and the Mur River in the Principality of Hungary, probably implying migrations from a single region.

Alex Battler, known in Russia under the pen name Oleg Alekseyevich Arin, is a Soviet-born Russian-Canadian scholar and political writer. He is a member of the organization «Defend Science» (US).

A Fiery Serpent is an evil entity common to Slavic mythology, which presents itself as an anthropomorphic snake demon.

Slavic fantasy is a sub-genre of contemporary art that developed in the late 90s and early 2000s. Slavic fantasy is distinguished by the incorporation of Slavic folklore, legends, bylinas, and myths into the general canons of fantasy literature. However, its genre boundaries remain indistinct.

The Etymological Dictionary of Slavic Languages: Proto-Slavic Lexical Stock is an etymological dictionary of the reconstructed Proto-Slavic lexicon. It has been continuously published since 1974 until present, in 43 volumes, making it one of the most comprehensive in the world.

The Rus' chronicle, Russian chronicle or Rus' letopis was the primary Rus' historical literature. Chronicles were composed from the 11th to the 18th centuries, generally written in Old East Slavic, about Kievan Rus' and subsequent Rus' principalities and history. They were one of the leading genres of Old Rus' literature in medieval and early modern Eastern and Central Europe.

Vladimir Petrukhin is a Russian historian, archaeologist and ethnographer, Doctor of Historical Sciences, chief research fellow of the Medieval Section in the Institute of Slavic Studies in the Russian Academy of Sciences, professor of Higher School of Economics.

The Alatyr in East Slavic legends and folklore is a sacred stone, the "father to all stones", the navel of the earth, containing sacred letters and endowed with healing properties. Although the name Alatyr appears only in East Slavic sources, the awareness of the existence of such a stone exists in various parts of the Slavdom. It is often mentioned in stories and referred to in love spells as "a mighty force that has no end."

The Circle of Veles is an association of neo-pagan communities dedicated to the revival and promotion of Slavic native spirituality. The association venerates Veles, the Slavic god of wisdom, and regards Rod as the supreme deity, aligning itself with the Rodnovery tradition.
References
- 1 2 Dixon-kennedy, Mike (1998). Encyclopedia of Russian & Slavic myth and legend. ABC-CLIO. p. 78. ISBN 978-1-57607-130-4.
- 1 2 Parker, Janet; Mills, Alice; Stanton, Julie (2007). Mythology: Myths, Legends and Fantasies. Struik. p. 262. ISBN 978-1-77007-453-8.