| Copalis National Wildlife Refuge | |
|---|---|
IUCN category IV (habitat/species management area) | |
View of Copalis Rock from Roosevelt Beach | |
| Location | Grays Harbor County, Washington |
| Nearest city | Aberdeen |
| Coordinates | 47°23′59″N124°19′50″W / 47.3998039°N 124.3304646°W [1] Coordinates: 47°23′59″N124°19′50″W / 47.3998039°N 124.3304646°W [1] |
| Area | 60.8 acres (24.6 ha) [2] |
| Established | 1907 |
| Governing body | U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service |
| Website | Copalis National Wildlife Refuge |
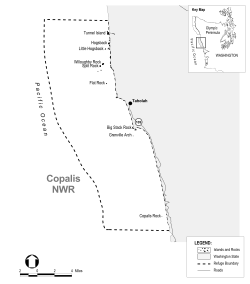
Copalis National Wildlife Refuge is the southernmost of the three refuges (along with Flattery Rocks and Quillayute Needles) which make up the Washington Maritime National Wildlife Refuge Complex, a group of 870 islands, rocks, and reefs extending for more than 100 miles along Washington's coast from Cape Flattery to Copalis Beach. These islands are protected from human disturbance, yet are close to abundant ocean food sources. [3]

Flattery Rocks National Wildlife Refuge is the northernmost of the three refuges which make up the Washington Maritime National Wildlife Refuge Complex, a group of 870 islands, rocks, and reefs extending for more than 100 miles along Washington's coast from Cape Flattery to Copalis Beach. These islands are protected from human disturbance, yet are close to abundant ocean food sources. They are closed to the public, with wildlife observation only from boats and the mainland, and a 200-yard buffer zone surrounding each island.

Quillayute Needles National Wildlife Refuge is the central refuge of the three which make up the Washington Maritime National Wildlife Refuge Complex, a group of 870 islands, rocks, and reefs extending for more than 100 miles along Washington's coast from Cape Flattery to Copalis Beach. These islands are protected from human disturbance, yet are close to abundant ocean food sources.

An island or isle is any piece of sub-continental land that is surrounded by water. Very small islands such as emergent land features on atolls can be called islets, skerries, cays or keys. An island in a river or a lake island may be called an eyot or ait, and a small island off the coast may be called a holm. A grouping of geographically or geologically related islands is called an archipelago, such as the Philippines.
Contents
They are a vital sanctuary where 14 species of seabirds nest and raise their young. During migration the total populations of seabirds, waterfowl, and shorebirds may exceed a million birds. Sea lions, harbor seals, sea otters, and whales may also be seen around the islands. [3]

Seabirds are birds that are adapted to life within the marine environment. While seabirds vary greatly in lifestyle, behaviour and physiology, they often exhibit striking convergent evolution, as the same environmental problems and feeding niches have resulted in similar adaptations. The first seabirds evolved in the Cretaceous period, and modern seabird families emerged in the Paleogene.

Sea lions are sea mammals characterized by external ear flaps, long foreflippers, the ability to walk on all fours, short, thick hair, and a big chest and belly. Together with the fur seals, they comprise the family Otariidae, eared seals, which contains six extant and one extinct species in five genera. Their range extends from the subarctic to tropical waters of the global ocean in both the Northern and Southern Hemispheres, with the notable exception of the northern Atlantic Ocean. They have an average lifespan of 20–30 years. A male California sea lion weighs on average about 300 kg (660 lb) and is about 8 ft (2.4 m) long, while the female sea lion weighs 100 kg (220 lb) and is 6 ft (1.8 m) long. The largest sea lion is Steller's sea lion, which can weigh 1,000 kg (2,200 lb) and grow to a length of 10 ft (3.0 m). Sea lions consume large quantities of food at a time and are known to eat about 5–8% of their body weight at a single feeding. Sea lions can go around 16 knots in water and at their fastest they can go up to 30 knots. Three species, the Australian sea lion, the Galápagos sea lion and the New Zealand sea lion are listed as Endangered.

The harborseal, also known as the common seal, is a true seal found along temperate and Arctic marine coastlines of the Northern Hemisphere. The most widely distributed species of pinniped, they are found in coastal waters of the northern Atlantic and Pacific Oceans and the Baltic and North Seas.
The refuge is within the boundary of Olympic Coast National Marine Sanctuary and Olympic National Park and is also incorporated into the Washington Islands Wilderness. The three agencies cooperate on research programs and other issues that may have impacts on the resources. [3]

The Olympic Coast National Marine Sanctuary is one of 14 marine sanctuaries administered by the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA), an agency of the U.S. Department of Commerce. It is located along the Olympic Peninsula of Washington state. The sanctuary was declared in 1994 and encompasses 3,189 square miles (8,260 km2) of the Pacific Ocean from Cape Flattery in the north, to the mouth of the Copalis River, a distance of about 162.5 miles (261.5 km). Extending 25 to 40 miles from the shore, it includes most of the continental shelf, as well as parts of three important submarine canyons, the Nitinat Canyon, the Quinault Canyon and the Juan de Fuca Canyon. For 64 miles (103 km) along the coast, the sanctuary shares stewardship with the Olympic National Park. The sanctuary overlays the Flattery Rocks, Quillayute Needles, and Copalis Rock National Wildlife Refuges.

Olympic National Park is an American national park located in the State of Washington, on the Olympic Peninsula. The park has four regions: the Pacific coastline, alpine areas, the west side temperate rainforest and the forests of the drier east side. Within the park there are three distinct ecosystems which are subalpine forest and wildflower meadow, temperate forest, and the rugged Pacific coast.

Washington Islands Wilderness is a protected area consisting of more than 600 islands, rocks, and reefs belonging to the three Washington Islands National Wildlife Refuges in Washington state. Although the land base is only about 1.8 square kilometres (0.69 sq mi), the total protected area covers over 780 square kilometres (300 sq mi).



















