
Mount Rainier National Park is a national park of the United States located in southeast Pierce County and northeast Lewis County in Washington state. The park was established on March 2, 1899, as the fourth national park in the United States, preserving 236,381 acres including all of Mount Rainier, a 14,410-foot (4,390 m) stratovolcano. The mountain rises abruptly from the surrounding land with elevations in the park ranging from 1,600 feet to over 14,000 feet (490–4,300 m). The highest point in the Cascade Range, Mount Rainier is surrounded by valleys, waterfalls, subalpine meadows, and 91,000 acres of old-growth forest. More than 25 glaciers descend the flanks of the volcano, which is often shrouded in clouds that dump enormous amounts of rain and snow.

The Continental Divide National Scenic Trail is a United States National Scenic Trail with a length measured by the Continental Divide Trail Coalition of 3,028 miles (4,873 km) between the U.S. border with Chihuahua, Mexico and the border with Alberta, Canada. Frequent route changes and a large number of alternate routes result in an actual hiking distance of 2,700 miles (4,300 km) to 3,150 miles (5,070 km). The CDT follows the Continental Divide of the Americas along the Rocky Mountains and traverses five U.S. states — Montana, Idaho, Wyoming, Colorado, and New Mexico. In Montana near the Canadian border the trail crosses Triple Divide Pass.

The Wonderland Trail is an approximately 93-mile (150 km) hiking trail that circumnavigates Mount Rainier in Mount Rainier National Park, Washington, United States. The trail goes over many ridges of Mount Rainier for a cumulative 22,000 feet (6,700 m) of elevation gain. The trail was built in 1915. In 1981, it was designated a National Recreation Trail. An estimated 200 to 250 people a year complete the entire trail with several thousand others doing shorter sections of it. The average time taken to complete the entire trip is 10 to 14 days.

Newberry National Volcanic Monument was designated on November 5, 1990, to protect the area around the Newberry Volcano in the U.S. state of Oregon. The monument was created within the boundaries of the Deschutes National Forest, which is managed by the U.S. Forest Service, and includes 54,822 acres of lakes, lava flows, and geologic features in central Oregon.

The Mount Baker–Snoqualmie National Forest in Washington is a National Forest extending more than 140 miles (230 km) along the western slopes of the Cascade Range from the Canada–US border to the northern boundary of Mount Rainier National Park. Administered by the United States Forest Service, the forest is headquartered in Everett. There are local ranger district offices in North Bend and Skykomish.

El Yunque National Forest, formerly known as the Caribbean National Forest, is a forest located in northeastern Puerto Rico. While there are both temperate and tropical rainforests in other states and territories, it is the only tropical rainforest in the United States National Forest System and the United States Forest Service. El Yunque National Forest is located on the slopes of the Sierra de Luquillo mountains, encompassing more than 28,000 acres of land, making it the largest block of public land in Puerto Rico.

Kisatchie National Forest, the only National forest in Louisiana, United States, is located in the forested piney hills and hardwood bottoms of seven central and northern parishes. It is part of the Cenozoic uplands and has large areas of longleaf pine forests. It is one of the largest pieces of natural landscape in Louisiana, with some 604,000 acres (2,440 km2) of public land, more than half of which is vital longleaf pine and flatwoods vegetation. These support many rare plant and animal species. There are also rare habitats, such as hillside seepage bogs and calcareous prairies. The forest also contains and provides a buffer for the Kisatchie Hills Wilderness, a nationally designated wilderness area that contributes to protecting biodiversity of the coastal plain region of the United States.

Tahoe National Forest is a United States National Forest located in California, northwest of Lake Tahoe. It includes the 8,587-foot (2,617 m) peak of Sierra Buttes, near Sierra City, which has views of Mount Lassen and Mount Shasta. It is located in parts of six counties: Sierra, Placer, Nevada, Yuba, Plumas and El Dorado. The forest has a total area of 871,495 acres. Its headquarters is in Nevada City, California. There are local ranger district offices in Camptonville, Foresthill, Sierraville and Truckee.

Chippewa National Forest is a National Forest located in north central Minnesota, United States, in the counties of Itasca, Cass and Beltrami. Forest headquarters are located in Cass Lake, Minnesota. There are local ranger district offices in Blackduck, Deer River and Walker.

Lincoln National Forest is a unit of the U.S. Forest Service located in southern New Mexico. The Lincoln National Forest covers an extensive 1.1 million acres in southeastern New Mexico. Established by Presidential Proclamation in 1902 as the Lincoln Forest Reserve, the 1,103,897 acres (4,467.31 km2) forest begins near the Texas border and contains lands in parts of Chaves, Eddy, Lincoln, and Otero counties. The Lincoln National Forest is home to three major mountain ranges: Sacramento, Guadalupe and Capitan. The three Ranger Districts within the forest contain all or part of a total of four mountain ranges, and include a variety of different environmental areas, from desert to heavily forested mountains and sub-alpine grasslands. Clean air, water, and soil are necessary elements that the National Forests contribute to the environment. Established to balance conservation, resource management, and recreation, the lands of the Lincoln National Forest include important local timber resources, protected wilderness areas, and popular recreation and winter sports areas. The forest headquarters is located in Alamogordo, N.M. with local offices in Carlsbad, Cloudcroft, and Ruidoso.

Ouachita National Recreation Trail is a 223-mile (359 km) long, continuous hiking trail through the Ouachita Mountains of Oklahoma and Arkansas. It is the longest backpacking trail in the Ouachita National Forest, spanning 192 miles across its length. Approximately 177 miles of the trail is in Arkansas and 46 miles of the trail is in Oklahoma. The trail is used by hikers, backpackers, hunters, and mountain bikers. It is a non-motorized single track trail open only to foot traffic and partially open to mountain bicycles. Segments opened to mountain bikes are from the western terminus of the Ouachita Trail at Talimena State Park to the Big Cedar trailhead on US Highway 259 at approximately Mile Marker (MM) 30.5 in Oklahoma, and from the Talimena Scenic Drive Trailhead at MM 54.1, east to Highway 7 at mile 160.4, north of Jessieville, Arkansas.
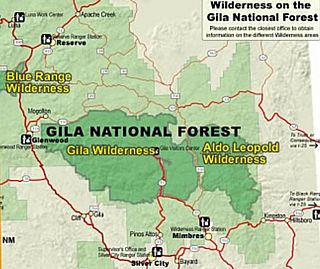
Gila Wilderness was designated the world's first wilderness area on June 3, 1924. Along with Aldo Leopold Wilderness and Blue Range Wilderness, the 558,014 acre wilderness is part of New Mexico's Gila National Forest. The wilderness is approximately 27 miles (43 km) from north to south and 39 miles (63 km) east to west.

The Yolla Bolly–Middle Eel Wilderness is a federally designated wilderness area in the Yolla Bolly Range of the southern Klamath Mountains and the Inner Northern California Coast Ranges, in Northern California.

The Eagles Nest Wilderness is a U.S. Wilderness Area located in the Gore Range near Vail, Copper Mountain, Frisco, Silverthorne, and Heeney, in Summit and Eagle Counties, Colorado. Eagles Nest Wilderness falls within the jurisdiction of Dillon Ranger District and Holy Cross Ranger District, White River National Forest. The 135,114-acre (546.79 km2) wilderness with 180 miles (290 km) of trails was established in 1976. In 2010, additional lands were proposed for wilderness protection under the Hidden Gems proposal, affecting Elliot Ridge, Tenmile, and Lower Piney areas of Summit and Eagle Counties.

The White Mountain Wilderness is a 46,963 acre designated wilderness area managed by the United States Forest Service. Located in the Smokey Bear Ranger District of the Lincoln National Forest, the White Mountain Wilderness lies in the Sierra Blanca mountains of south central New Mexico, approximately 15 miles (24 km) north northwest of the town of Ruidoso.

Wells Gray Provincial Park is a large wilderness park located in east-central British Columbia, Canada. The park protects most of the southern, and highest, regions of the Cariboo Mountains and covers 5,415 square kilometres. It is British Columbia's fifth largest provincial park, after Tweedsmuir, Tatshenshini, Spatsizi and Northern Rocky Mountains.

The Lone Star Hiking Trail (LSHT) is a 96 mile long hiking trail with an additional 32 miles of loop and crossover trails of footpath-only trails. Connecting public lands of the Sam Houston National Forest and private lands it is the longest continuous hiking trail in the State of Texas. The trail starts just South of Richards, Texas and ends North-West of Cleveland, Texas.

The Oregon Skyline Trail is a long-distance trail in the Cascade Mountains of Oregon. The trail extends 428 miles (689 km) from Cascade Locks on the Columbia River south to Siskiyou Summit near the Oregon-California border. The century-old trail is a foot and equestrian path that passes through nine wilderness areas, Crater Lake National Park, and Cascade-Siskiyou National Monument. Historically known as the Oregon Skyline Trail or Skyline Trail, the entire length of the trail was incorporated into the Pacific Crest National Scenic Trail in 1968.
Big Heart Lake is the most remote and highest-elevation on-trail lake in the West Fork Foss River system. It is a 14.6-mile (23.5 km) round-trip hike from the trailhead, just off of the Foss River Road. The lake is located at the eastern base of Camp Robber Peak in the Alpine Lakes Wilderness Area, within King County, Washington.
The protected areas of the Sierra Nevada, a major mountain range located in the U.S. states of California and Nevada, are numerous and highly diverse. Like the mountain range itself, these areas span hundreds of miles along the length of the range, and over 14,000 feet of elevation from the lowest foothills to the summit of Mount Whitney.




















