
The Upper Peninsulaof Michigan—also known as Upper Michigan or colloquially the U.P.—is the northern and more elevated of the two major landmasses that make up the U.S. state of Michigan; it is separated from the Lower Peninsula by the Straits of Mackinac. It is bounded primarily by Lake Superior to the north, separated from the Canadian province of Ontario at the east end by the St. Marys River, and flanked by Lake Huron and Lake Michigan along much of its south. Although the peninsula extends as a geographic feature into the state of Wisconsin, the state boundary follows the Montreal and Menominee rivers and a line connecting them.

Copper Island is a local name given to the northern part of the Keweenaw Peninsula, separated from the rest of the Keweenaw Peninsula by Portage Lake and the Keweenaw Waterway.

Hancock is a city in the Upper Peninsula of the U.S. state of Michigan. The population of Hancock was 4,501 at the 2020 census. The city is located within Houghton County, and is situated upon the Keweenaw Waterway, a channel of Lake Superior that cuts across the Keweenaw Peninsula. Hancock is located across the Keweenaw Waterway from the city of Houghton, and is connected to that city by the Portage Lake Lift Bridge. The city is located within Michigan's Copper Country region.

Ontonagon County is a county in the Upper Peninsula of the U.S. state of Michigan. As of the 2020 census, the population was 5,816, making it Michigan's third-least populous county. The county seat is Ontonagon. The county was set off in 1843, and organized in 1848. Its territory had been organized as part of Chippewa and Mackinac counties. With increasing population in the area, more counties were organized. After Ontonagon was organized, it was split to create Gogebic County. It is also the westernmost county in United States that lies within the Eastern Time Zone.

Keweenaw County is a county in the western Upper Peninsula of the U.S. state of Michigan. As of the 2020 census, the county's population was 2,046, making it Michigan's least populous county. It is also the state's largest county by total area, including the waters of Lake Superior, as well as the state's northernmost county. The county seat is Eagle River.

Houghton County is a county in the Upper Peninsula in the U.S. state of Michigan. As of the 2020 census, the population was 37,361. The county seat and largest city is Houghton. Both the county and the city were named for Michigan State geologist and Detroit Mayor Douglass Houghton.

Calumet is a village in the Upper Peninsula of the U.S. state of Michigan. The village is located within Calumet Township, Houghton County, and had a population of 621 at the 2020 census.

L'Anse Township is a civil township of Baraga County in the U.S. state of Michigan. As of the 2020 census, the township population was 3,551. The township contains Mount Arvon and Mount Curwood, Michigans highest and second-highest points, as well as the village of L'Anse.
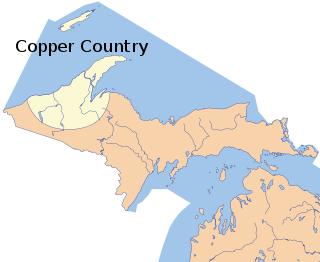
The Copper Country is an area in the Upper Peninsula of Michigan in the United States, including Keweenaw County, Michigan, Houghton, Baraga and Ontonagon counties as well as part of Marquette County. The area is so named as copper mining was prevalent there from 1845 until the late 1960s, with one mine continuing through 1995. In its heyday in the latter half of the 19th century and the early 20th century, the area was the world's greatest producer of copper.

M-26 is a 96.355-mile-long (155.068 km) state trunkline highway in the U.S. state of Michigan, running from two miles (3.2 km) east of Rockland to its junction with US Highway 41 (US 41) in Copper Harbor. It generally runs southwest-to-northeast in the western half or Michigan's Upper Peninsula. The northernmost segment, which closely parallels the shore of Lake Superior on the west side of the Keweenaw Peninsula, is highly scenic.

Douglass Houghton was an American geologist and physician, primarily known for his exploration of the Keweenaw Peninsula of Michigan. It was the site of a copper boom and extensive copper mining beginning in the 19th century. He was appointed in 1839 as the first state geologist of Michigan, after it was admitted to the union, and served in that position for the rest of his life.

The Soo Line Railroad is one of the primary United States railroad subsidiaries for the CPKC Railway, one of six U.S. Class I railroads, controlled through the Soo Line Corporation. Although it is named for the Minneapolis, St. Paul and Sault Ste. Marie Railroad (MStP&SSM), which was commonly known as the Soo Line after the phonetic spelling of Sault, it was formed in 1961 by the consolidation of that company with two other CPKC subsidiaries: The Duluth, South Shore and Atlantic Railway, and the Wisconsin Central Railway. It is also the successor to other Class I railroads, including the Minneapolis, Northfield and Southern Railway and the Chicago, Milwaukee, St. Paul and Pacific Railroad. On the other hand, a large amount of mileage was spun off in 1987 to Wisconsin Central Ltd., now part of the Canadian National Railway. The Soo Line Railroad and the Delaware and Hudson Railway, CPKC's other major subsidiary, presently do business as the Canadian Pacific Railway (CP). Most equipment has been repainted into the CP scheme, but the U.S. Surface Transportation Board groups all of the company's U.S. subsidiaries under the Soo Line name for reporting purposes. The Minneapolis headquarters are in the Canadian Pacific Plaza building, having moved from the nearby Soo Line Building.

Keweenaw National Historical Park is a unit of the U.S. National Park Service. Established in 1992, the park celebrates the life and history of the Keweenaw Peninsula in the Upper Peninsula of the U.S. state of Michigan. It is a federal-local cooperative park made up of two primary units, the Calumet Unit and the Quincy Unit, and almost two dozen cooperating "Heritage Sites" located on federal, state, and privately owned land in and around the Keweenaw Peninsula. The National Park Service owns approximately 1,700 acres (690 ha) in the Calumet and Quincy Units. Units are located in Baraga, Houghton, Keweenaw, and Ontonagon counties.

The Duluth, South Shore and Atlantic Railway (DSS&A) was an American railroad serving the Upper Peninsula of Michigan and the Lake Superior shoreline of Wisconsin. It provided service from Sault Ste. Marie, Michigan, and St. Ignace, Michigan, westward through Marquette, Michigan, to Superior, Wisconsin, and Duluth, Minnesota. A branchline stretched northward from Nestoria, Michigan, up to the Keweenaw Peninsula and terminating at Houghton, Michigan, with two branches extending further to Calumet, Michigan, and Lake Linden, Michigan.

Freda is an unincorporated community fifteen miles west of Houghton, United States in the Stanton Township.

In Michigan, copper mining became an important industry in the 19th and early 20th centuries. Its rise marked the start of copper mining as a major industry in the United States.

US Highway 41 (US 41) is a part of the United States Numbered Highway System that runs from Miami, Florida, to the Upper Peninsula of the US state of Michigan. In Michigan, it is a state trunkline highway that enters the state via the Interstate Bridge between Marinette, Wisconsin, and Menominee, Michigan. The 278.769 miles (448.635 km) of US 41 that lie within Michigan serve as a major conduit. Most of the highway is listed on the National Highway System. Various sections are rural two-lane highway, urbanized four-lane divided expressway and the Copper Country Trail National Scenic Byway. The northernmost community along the highway is Copper Harbor at the tip of the Keweenaw Peninsula. The trunkline ends at a cul-de-sac east of Fort Wilkins State Park after serving the Central Upper Peninsula and Copper Country regions of Michigan.
The Lac La Belle and Calumet Railroad was an American, 3 ft narrow gauge railroad that operated in the Keweenaw Peninsula, or the extreme northern Upper Peninsula of Michigan. The line was owned by the Conglomerate Mining Company and ran between a stamp mill at Lac La Belle and the Delaware copper mine from 1883 to 1888, when poor economic conditions forced the line's closure.

Copper Range Railroad No. 29 is the sole survivor of the C-2 class 2-8-0 "Consolidation" type steam locomotives. Built by ALCO in 1907, No. 29 was primarily used to pull loaded copper trains out of copper mines in the Upper Peninsula of Michigan, as well as occasional passenger trains between Houghton and McKeever, until it was removed from service in 1953. In 1967, it was leased to the Keweenaw Central Railroad, who used it to pull excursion trains between Calumet and Lake Linden, until 1971. For thirty years, the locomotive was stored outside the abandoned Quincy Smelter plant in Hancock under the ownership of Mineral Range Inc.. In 2003, No. 29 was purchased by the Mid-Continent Railway Museum for static display purposes, and the locomotive's move to North Freedom, Wisconsin was funded and financed by the museum the following year. As of 2023, No. 29 remains on static display in front of two passenger cars on the museum's grounds, slowly undergoing a cosmetic stabilization.

Chicago and North Western 175 is a preserved R-1 class 4-6-0 "Ten-Wheeler" steam locomotive built by the American Locomotive Company (ALCO) in December 1908. The locomotive was used for pulling various passenger and freight trains throughout Wisconsin, until the Chicago and North Western (C&NW) Railroad ended commercial steam operations in 1956.




















