Sustainable development is an approach to growth and human development that aims to meet the needs of the present without compromising the ability of future generations to meet their own needs. The aim is to have a society where living conditions and resources meet human needs without undermining planetary integrity. Sustainable development aims to balance the needs of the economy, environment, and social well-being. The Brundtland Report in 1987 helped to make the concept of sustainable development better known.
Overconsumption describes a situation where a consumer overuses their available goods and services to where they can't, or don't want to, replenish or reuse them. In microeconomics, this may be described as the point where the marginal cost of a consumer is greater than their marginal utility. The term overconsumption is quite controversial in use and does not necessarily have a single unifying definition. When used to refer to natural resources to the point where the environment is negatively affected, it is synonymous with the term overexploitation. However, when used in the broader economic sense, overconsumption can refer to all types of goods and services, including manmade ones, e.g. "the overconsumption of alcohol can lead to alcohol poisoning". Overconsumption is driven by several factors of the current global economy, including forces like consumerism, planned obsolescence, economic materialism, and other unsustainable business models and can be contrasted with sustainable consumption.
The phrase sustainable industries is related to the development of industrial processes in a sustainable way. The phrase refers to greening of energy intensive industries such as the textiles, steel, cement, and paper industries.
The Wuppertal Institute for Climate, Environment and Energy is a German research institution for sustainability research, focusing on impacts and practical application. It explores and develops models, strategies, and instruments to support sustainable development at local, national, and international levels. Research at the Wuppertal Institute focuses on ecology and its relation to economy and society. Special emphasis is put on analyzing and supporting technological and social innovations that decouple the prosperity of economic growth from the use of natural resources. The organization's activities focus on developing transformation processes aimed at shaping a climate-friendly and resource-efficient world.

The Brundtland Commission, formerly the World Commission on Environment and Development, was a sub-organization of the United Nations (UN) that aimed to unite countries in pursuit of sustainable development. It was founded in 1983 when Javier Pérez de Cuéllar, the Secretary-General of the United Nations, appointed Gro Harlem Brundtland, former Prime Minister of Norway, as chairperson of the commission. Brundtland was chosen due to her strong background in the sciences and public health.
Eco-capitalism, also known as environmental capitalism or (sometimes) green capitalism, is the view that capital exists in nature as "natural capital" on which all wealth depends. Therefore, governments should use market-based policy-instruments to resolve environmental problems.
Eco-efficiency refers to the delivery of goods and services to meet human needs and improve quality of life while progressively reducing their environmental impacts of goods and resource intensity during their life-cycle.

In economics, the Jevons paradox occurs when technological progress increases the efficiency with which a resource is used, but the falling cost of use induces increases in demand enough that resource use is increased, rather than reduced. Governments, both historical and modern, typically expect that energy efficiency gains will lower energy consumption, rather than expecting the Jevons paradox.
A green economy is an economy that aims at reducing environmental risks and ecological scarcities, and that aims for sustainable development without degrading the environment. It is closely related with ecological economics, but has a more politically applied focus. The 2011 UNEP Green Economy Report argues "that to be green, an economy must not only be efficient, but also fair. Fairness implies recognizing global and country level equity dimensions, particularly in assuring a Just Transition to an economy that is low-carbon, resource efficient, and socially inclusive."

Environmental resource management or environmental management is the management of the interaction and impact of human societies on the environment. It is not, as the phrase might suggest, the management of the environment itself. Environmental resources management aims to ensure that ecosystem services are protected and maintained for future human generations, and also maintain ecosystem integrity through considering ethical, economic, and scientific (ecological) variables. Environmental resource management tries to identify factors between meeting needs and protecting resources. It is thus linked to environmental protection, resource management, sustainability, integrated landscape management, natural resource management, fisheries management, forest management, wildlife management, environmental management systems, and others.
Sustainable urban infrastructure expands on the concept of urban infrastructure by adding the sustainability element with the expectation of improved and more resilient urban development. In the construction and physical and organizational structures that enable cities to function, sustainability also aims to meet the needs of the present generation without compromising the capabilities of the future generations.
A sustainable business, or a green business, is an enterprise that has a minimal negative impact or potentially a positive effect on the global or local environment, community, society, or economy—a business that attempts to meet the triple bottom line. They cluster under different groupings and the whole is sometimes referred to as "green capitalism". Often, sustainable businesses have progressive environmental and human rights policies. In general, a business is described as green if it matches the following four criteria:
- It incorporates principles of sustainability into each of its business decisions.
- It supplies environmentally friendly products or services that replace demand for nongreen products and/or services.
- It is greener than traditional competition.
- It has made an enduring commitment to environmental principles in its business operations.
Material flow analysis (MFA), also referred to as substance flow analysis (SFA), is an analytical method to quantify flows and stocks of materials or substances in a well-defined system. MFA is an important tool to study the bio-physical aspects of human activity on different spatial and temporal scales. It is considered a core method of industrial ecology or anthropogenic, urban, social and industrial metabolism. MFA is used to study material, substance, or product flows across different industrial sectors or within ecosystems. MFA can also be applied to a single industrial installation, for example, for tracking nutrient flows through a waste water treatment plant. When combined with an assessment of the costs associated with material flows this business-oriented application of MFA is called material flow cost accounting. MFA is an important tool to study the circular economy and to devise material flow management. Since the 1990s, the number of publications related to material flow analysis has grown steadily. Peer-reviewed journals that publish MFA-related work include the Journal of Industrial Ecology, Ecological Economics, Environmental Science and Technology, and Resources, Conservation, and Recycling.
Sustainability metrics and indices are measures of sustainability, using numbers to quantify environmental, social and economic aspects of the world. There are multiple perspectives on how to measure sustainability as there is no universal standard. Intead, different disciplines and international organizations have offered measures or indicators of how to measure the concept.
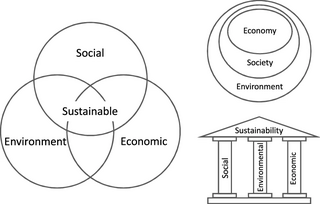
Sustainability is a social goal for people to co-exist on Earth over a long period of time. Definitions of this term are disputed and have varied with literature, context, and time. Sustainability usually has three dimensions : environmental, economic, and social. Many definitions emphasize the environmental dimension. This can include addressing key environmental problems, including climate change and biodiversity loss. The idea of sustainability can guide decisions at the global, national, organizational, and individual levels. A related concept is that of sustainable development, and the terms are often used to mean the same thing. UNESCO distinguishes the two like this: "Sustainability is often thought of as a long-term goal, while sustainable development refers to the many processes and pathways to achieve it."
Material input per unit of service (MIPS) is an economic concept, originally developed at the Wuppertal Institute, Germany in the 1990s. The MIPS concept can be used to measure eco-efficiency of a product or service and applied in all scales from a single product to complex systems. The calculation takes into account materials required to produce a product or service. The total material input (MI) is divided by the number of service units (S). For example, in case of a passenger car, the number of service units is the total number of passenger kilometres during the whole life span of the vehicle. The lower the material input per kilometre, the more eco-efficient is the vehicle. The whole life-cycle of a product or service is measured when MIPS values are calculated. This allows comparisons of resource consumption of different solutions to produce the same service. When a single product is examined, the MIPS calculations reveal the magnitude of resource use along the life-cycle and help to focus efforts on the most significant phases to reduce environmental burden of the product.

Green growth is a concept in economic theory and policymaking used to describe paths of economic growth that are environmentally sustainable. It is based on the understanding that as long as economic growth remains a predominant goal, a decoupling of economic growth from resource use and adverse environmental impacts is required. As such, green growth is closely related to the concepts of green economy and low-carbon or sustainable development. A main driver for green growth is the transition towards sustainable energy systems. Advocates of green growth policies argue that well-implemented green policies can create opportunities for employment in sectors such as renewable energy, green agriculture, or sustainable forestry.
A sustainability organization is (1) an organized group of people that aims to advance sustainability and/or (2) those actions of organizing something sustainably. Unlike many business organizations, sustainability organizations are not limited to implementing sustainability strategies which provide them with economic and cultural benefits attained through environmental responsibility. For sustainability organizations, sustainability can also be an end in itself without further justifications.

In economic and environmental fields, decoupling refers to an economy that would be able to grow without corresponding increases in environmental pressure. In many economies, increasing production (GDP) raises pressure on the environment. An economy that would be able to sustain economic growth while reducing the amount of resources such as water or fossil fuels used and delink environmental deterioration at the same time would be said to be decoupled. Environmental pressure is often measured using emissions of pollutants, and decoupling is often measured by the emission intensity of economic output.
Dematerialization is a term in economics and the social sciences that describes the process of making more goods with less material. The term itself possesses multi-accentuality, which allows it to be diversely explained by different fields of social science, such as Mainstream economics, which puts focus on the aspects of technological evolution and market demand shifts, and Ecological economics, which emphasizes the effect of dematerialization on the natural environment.






