
A scanning electron microscope (SEM) is a type of electron microscope that produces images of a sample by scanning the surface with a focused beam of electrons. The electrons interact with atoms in the sample, producing various signals that contain information about the surface topography and composition of the sample. The electron beam is scanned in a raster scan pattern, and the position of the beam is combined with the intensity of the detected signal to produce an image. In the most common SEM mode, secondary electrons emitted by atoms excited by the electron beam are detected using a secondary electron detector. The number of secondary electrons that can be detected, and thus the signal intensity, depends, among other things, on specimen topography. Some SEMs can achieve resolutions better than 1 nanometer.

A diatom is any member of a large group comprising several genera of algae, specifically microalgae, found in the oceans, waterways and soils of the world. Living diatoms make up a significant portion of the Earth's biomass: they generate about 20 to 50 percent of the oxygen produced on the planet each year, take in over 6.7 billion tonnes of silicon each year from the waters in which they live, and constitute nearly half of the organic material found in the oceans. The shells of dead diatoms can reach as much as a half-mile deep on the ocean floor, and the entire Amazon basin is fertilized annually by 27 million tons of diatom shell dust transported by transatlantic winds from the African Sahara, much of it from the Bodélé Depression, which was once made up of a system of fresh-water lakes.

A high-voltage direct current (HVDC) electric power transmission system uses direct current (DC) for electric power transmission, in contrast with the more common alternating current (AC) transmission systems.

Bivalvia, in previous centuries referred to as the Lamellibranchiata and Pelecypoda, is a class of marine and freshwater molluscs that have laterally compressed bodies enclosed by a shell consisting of two hinged parts. As a group, bivalves have no head and they lack some usual molluscan organs, like the radula and the odontophore. The class includes the clams, oysters, cockles, mussels, scallops, and numerous other families that live in saltwater, as well as a number of families that live in freshwater. The majority are filter feeders. The gills have evolved into ctenidia, specialised organs for feeding and breathing. Most bivalves bury themselves in sediment, where they are relatively safe from predation. Others lie on the sea floor or attach themselves to rocks or other hard surfaces. Some bivalves, such as the scallops and file shells, can swim. Shipworms bore into wood, clay, or stone and live inside these substances.

The following are examples of orders of magnitude for different lengths.

Chitons are marine molluscs of varying size in the class Polyplacophora, formerly known as Amphineura. About 940 extant and 430 fossil species are recognized.
Rotational–vibrational spectroscopy is a branch of molecular spectroscopy that is concerned with infrared and Raman spectra of molecules in the gas phase. Transitions involving changes in both vibrational and rotational states can be abbreviated as rovibrational transitions. When such transitions emit or absorb photons, the frequency is proportional to the difference in energy levels and can be detected by certain kinds of spectroscopy. Since changes in rotational energy levels are typically much smaller than changes in vibrational energy levels, changes in rotational state are said to give fine structure to the vibrational spectrum. For a given vibrational transition, the same theoretical treatment as for pure rotational spectroscopy gives the rotational quantum numbers, energy levels, and selection rules. In linear and spherical top molecules, rotational lines are found as simple progressions at both higher and lower frequencies relative to the pure vibration frequency. In symmetric top molecules the transitions are classified as parallel when the dipole moment change is parallel to the principal axis of rotation, and perpendicular when the change is perpendicular to that axis. The ro-vibrational spectrum of the asymmetric rotor water is important because of the presence of water vapor in the atmosphere.

A lenticular lens is an array of lenses, designed so that when viewed from slightly different angles, different parts of the image underneath are shown. The most common example is the lenses used in lenticular printing, where the technology is used to give an illusion of depth, or to make images that appear to change or move as the image is viewed from different angles.

The operculum is a corneous or calcareous anatomical structure like a trapdoor that exists in many groups of sea snails and freshwater snails, and also in a few groups of land snails; the structure is found in some marine and freshwater gastropods, and in a minority of terrestrial gastropods, including the families Helicinidae, Cyclophoridae, Aciculidae, Maizaniidae, Pomatiidae, etc.

The environmental scanning electron microscope (ESEM) is a scanning electron microscope (SEM) that allows for the option of collecting electron micrographs of specimens that are wet, uncoated, or both by allowing for a gaseous environment in the specimen chamber. Although there were earlier successes at viewing wet specimens in internal chambers in modified SEMs, the ESEM with its specialized electron detectors and its differential pumping systems, to allow for the transfer of the electron beam from the high vacuum in the gun area to the high pressure attainable in its specimen chamber, make it a complete and unique instrument designed for the purpose of imaging specimens in their natural state. The instrument was designed originally by Gerasimos Danilatos while working at the University of New South Wales.

Sphaerium corneum, also known as the European fingernailclam, is a very small freshwater clam, an aquatic bivalve mollusk in the family Sphaeriidae, the fingernail clams.

Lingula is a genus of brachiopods within the class Lingulata. Lingula or forms very close in appearance have existed possibly since the Cambrian. Like its relatives, it has two unadorned organo-phosphatic valves and a long fleshy stalk. Lingula lives in burrows in barren sandy coastal seafloor and feeds by filtering detritus from the water. It can be detected by a short row of three openings through which it takes in water (sides) and expels it again (middle).
Craticula is a genus of diatom that lies on or in the top layers of sediments in the freshwater to brackish water environments it inhabits. In addition to frustule morphology the genus differs from closely related species by its sexual reproduction and movement in response to light.

Amphora is a major genus of marine and freshwater diatoms. With over 1000 species, it is one of the largest genera of diatoms. These diatoms are recognized by their strongly dorsiventral frustules, which means that their ridges lie close to the ventral margin of the valve, and their girdle is much wider on the dorsal side.

Bacillaria is a diatom genus in the family Bacillariaceae.

Fragilaria is a genus of freshwater and saltwater diatoms. It is usually a colonial diatom, forming filaments of cells mechanically joined by protrusions on the face and in the center of their valves. The individual diatoms appear swollen in their centers where they are joined to the colonial ribbon. the genus grows as both plankton and benthic species, free living in colonies or epiphytic. Some species are bloom forming diatoms in eutrophic lakes. The type species is Fragilaria pectinalis Lyngbye from designating a lectotype from Conferva pectinalis O.F.Müller. The taxonomy of the genus is still uncertain.

DNA barcoding of algae is commonly used for species identification and phylogenetic studies. Algae form a phylogenetically heterogeneous group, meaning that the application of a single universal barcode/marker for species delimitation is unfeasible, thus different markers/barcodes are applied for this aim in different algal groups.
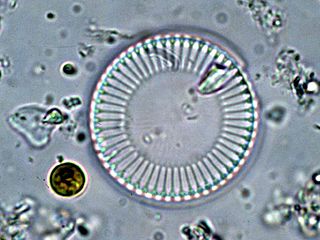
Cyclotella is a genus of diatoms often found in oligotrophic environments, both marine and fresh water. It is in the family Stephanodiscaceae and the order Thalassiosirales. The genus was first discovered in the mid-1800s and since then has become an umbrella genus for nearly 100 different species, the most well-studied and the best known being Cyclotella meneghiniana. Despite being among the most dominant genera in low-productivity environments, it is relatively understudied.
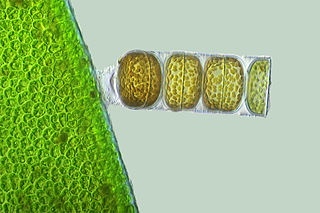
Melosira is a genus of diatoms belonging to the family Melosiraceae.
Stauroneis is a genus of diatoms (Bacillariophyta) with species that occur in fresh and marine water.


















