Related Research Articles
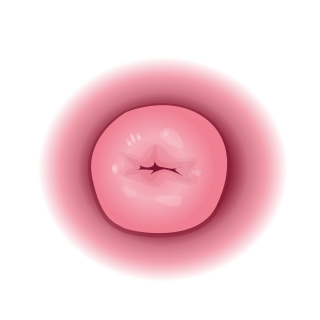
The cervix or cervix uteri is a dynamic fibromuscular organ of the female reproductive system that connects the vagina with the uterine cavity. The human cervix has been documented anatomically since at least the time of Hippocrates, over 2,000 years ago. The cervix is approximately 4 cm long with a diameter of approximately 3 cm and tends to be described as a cylindrical shape, although the front and back walls of the cervix are contiguous. The size of the cervix changes throughout a women's life cycle. For example, during their fertile years of the reproductive cycle, females tend to have a larger cervix vis á vis postmenopausal females; likewise, females who have produced offspring have a larger sized cervix than females who have not produced offspring.

The ovary is a gonad in the female reproductive system that produces ova. When an ovum is released, this travels through the fallopian tube/oviduct into the uterus. There is an ovary found on the left and the right side of the body. The ovaries also secrete hormones that play a role in the menstrual cycle and fertility. The ovary progresses through many stages beginning in the prenatal period through menopause. It is also an endocrine gland because of the various hormones that it secretes.

The uterus or womb is the organ in the reproductive system of most female mammals, including humans, that accommodates the embryonic and fetal development of one or more embryos until birth. The uterus is a hormone-responsive sex organ that contains glands in its lining that secrete uterine milk for embryonic nourishment.

The Bartholin's glands are two pea-sized compound alveolar glands located slightly posterior and to the left and right of the opening of the vagina. They secrete mucus to lubricate the vagina.

The mesonephric duct, also known as the Wolffian duct, archinephric duct, Leydig's duct or nephric duct, is a paired organ that develops in the early stages of embryonic development in humans and other mammals. It is an important structure that plays a critical role in the formation of male reproductive organs. The duct is named after Caspar Friedrich Wolff, a German physiologist and embryologist who first described it in 1759.

The female reproductive system is made up of the internal and external sex organs that function in the reproduction of new offspring. The human female reproductive system is immature at birth and develops to maturity at puberty to be able to produce gametes, and to carry a fetus to full term. The internal sex organs are the vagina, uterus, fallopian tubes, and ovaries. The female reproductive tract includes the vagina, uterus, and fallopian tubes and is prone to infections. The vagina allows for sexual intercourse and childbirth, and is connected to the uterus at the cervix. The uterus or womb accommodates the embryo, which develops into the fetus. The uterus also produces secretions, which help the transit of sperm to the fallopian tubes, where sperm fertilize ova produced by the ovaries. The external sex organs are also known as the genitals and these are the organs of the vulva including the labia, clitoris, and vaginal opening.

The paramesonephric ducts are paired ducts of the embryo in the reproductive system of humans and other mammals that run down the lateral sides of the genital ridge and terminate at the sinus tubercle in the primitive urogenital sinus. In the female, they will develop to form the fallopian tubes/oviducts, uterus, cervix, and the upper one-third of the vagina.

Persistent Müllerian duct syndrome (PMDS) is the presence of Müllerian duct derivatives in what would be considered a genetically and otherwise physically normal male animal by typical human based standards. In humans, PMDS typically is due to an autosomal recessive congenital disorder and is considered by some to be a form of pseudohermaphroditism due to the presence of Müllerian derivatives. PMDS can also present in non-human animals.

The human reproductive system includes the male reproductive system, which functions to produce and deposit sperm, and the female reproductive system, which functions to produce egg cells and to protect and nourish the fetus until birth. Humans have a high level of sexual differentiation. In addition to differences in nearly every reproductive organ, there are numerous differences in typical secondary sex characteristics.

The epoophoron or epoöphoron is a remnant of the mesonephric duct that can be found next to the ovary and fallopian tube.

A unicornuate uterus represents a uterine malformation where the uterus is formed from one only of the paired Müllerian ducts while the other Müllerian duct does not develop or only in a rudimentary fashion. The sometimes called hemi-uterus has a single horn linked to the ipsilateral fallopian tube that faces its ovary.

A bicornuate uterus or bicornate uterus, is a type of Müllerian anomaly in the human uterus, where there is a deep indentation at the fundus (top) of the uterus.

Sexual differentiation in humans is the process of development of sex differences in humans. It is defined as the development of phenotypic structures consequent to the action of hormones produced following gonadal determination. Sexual differentiation includes development of different genitalia and the internal genital tracts and body hair plays a role in sex identification.

The cardinal ligament is a major ligament of the uterus formed as a thickening of connective tissue of the base of the broad ligament of the uterus. It extends laterally from the cervix and vaginal fornix to attach onto the lateral wall of the pelvis. The female ureter, uterine artery, and inferior hypogastric (nervous) plexus course within the cardinal ligament. The cardinal ligament supports the uterus.
The development of the reproductive system is the part of embryonic growth that results in the sex organs and contributes to sexual differentiation. Due to its large overlap with development of the urinary system, the two systems are typically described together as the genitourinary system.

The fallopian tubes, also known as uterine tubes, oviducts or salpinges, are paired tubes in the human female body that stretch from the ovaries to the uterus. The fallopian tubes are part of the female reproductive system. In other vertebrates, they are only called oviducts.
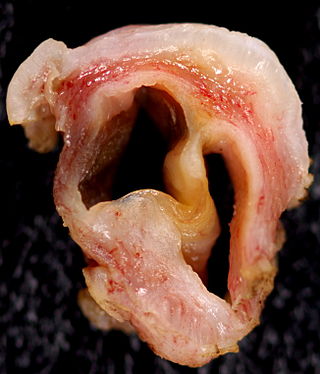
A Gartner's duct cyst is a benign vaginal cyst that originates from the Gartner's duct, which is a vestigial remnant of the mesonephric duct in females. Persistent Wolffian duct syndrome (PWDS) in individuals with XX chromosomes is the inverse disorder of Persistent Müllerian duct syndrome (PMDS) in individuals with XY chromosomes. They are typically small asymptomatic cysts that occur along the lateral walls of the vagina, following the course of the duct. They can present in adolescence with painful menstruation (dysmenorrhea) or difficulty inserting a tampon. They can also enlarge to substantial proportions and be mistaken for urethral diverticulum or cystocele. In some rare instances, they can be congenital.
Müllerian duct anomalies are those structural anomalies caused by errors in Müllerian duct development as an embryo forms. Factors contributing to them include genetics and maternal exposure to substances that interfere with fetal development.

Vaginal anomalies are abnormal structures that are formed during the prenatal development of the female reproductive system and are rare congenital defects that result in an abnormal or absent vagina.

Vaginal cysts are uncommon benign cysts that develop in the vaginal wall. The type of epithelial tissue lining a cyst is used to classify these growths. They can be congenital. They can present in childhood and adulthood. The most common type is the squamous inclusion cyst. It develops within vaginal tissue present at the site of an episiotomy or other vaginal surgical sites. In most instances they do not cause symptoms and present with few or no complications. A vaginal cyst can develop on the surface of the vaginal epithelium or in deeper layers. Often, they are found by the woman herself and as an incidental finding during a routine pelvic examination. Vaginal cysts can mimic other structures that protrude from the vagina such as a rectocele and cystocele. Some cysts can be distinguished visually but most will need a biopsy to determine the type. Vaginal cysts can vary in size and can grow as large as 7 cm. Other cysts can be present on the vaginal wall though mostly these can be differentiated. Vaginal cysts can often be palpated (felt) by a clinician. Vaginal cysts are one type of vaginal mass, others include cancers and tumors. The prevalence of vaginal cysts is uncertain since many go unreported but it is estimated that 1 out of 200 women have a vaginal cyst. Vaginal cysts may initially be discovered during pregnancy and childbirth. These are then treated to provide an unobstructed delivery of the infant. Growths that originate from the urethra and other tissue can present as cysts of the vagina.
References
- ↑ Netter, Frank H.; Cochard, Larry R. (2002). Netter's Atlas of human embryology. Teterboro, N.J: Icon Learning Systems. p. 173. ISBN 0-914168-99-1.
- ↑ Hakin, Surahman; Sari, Yulia Margaretta; Harzif, Achmad Kemal (2020-01-01). "Secondary cervical elongatio due to large Gartner cyst: A rare case". International Journal of Surgery Case Reports. 72: 37–40. doi:10.1016/j.ijscr.2020.05.054. ISSN 2210-2612. PMC 7283091 . PMID 32506026.
- ↑ Dwyer PL, Rosamilia A (August 2006). "Congenital urogenital anomalies that are associated with the persistence of Gartner's duct: a review". Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 195 (2): 354–9. doi:10.1016/j.ajog.2005.10.815. PMID 16890546.