Balaghat district is a district of Madhya Pradesh state in Central India. Its belongs to Jabalpur Division. Balaghat city is Administrative Headquarter of Balaghat District.

Gondia is a city and municipal council in the Indian state of Maharashtra which serves the administrative headquarters of the eponymous administrative district. Gondia is also known as Rice City due to the abundance of rice mills in the area. Gondia Airport is the only airport in the district.

The Bengal Nagpur Railway was one of the companies which pioneered development of the railways in eastern and central India. It was succeeded first by Eastern Railway and subsequently by South Eastern Railway.
Katangi is a city and a municipal council, near the city of Balaghat in Balaghat District in the Indian state of Madhya Pradesh.

Nainpur is a town and Municipal City in the Mandla district of the Indian state of Madhya Pradesh.
Nagbhir or Nagbhid is a town and a municipal council in Chandrapur district in the Indian state of Maharashtra. It Connected to NH-353D and MSH-9.
The Satpura Express was a daily express train which ran between Jabalpur Junction railway station of Jabalpur in Madhya Pradesh to another city of the same state, Balaghat Junction.

Balaghat Junction is situated on the Jabalpur–Nainpur–Gondia section of South East Central Railway, in the Indian state of Madhya Pradesh. Rail routes through the junction include routes towards Jabalpur, Gondia, Katangi on the Satpura Railway. The "10001 Satpura Express", a narrow-gauge train, was started in 1901 by the British Government and completed 100 years of service in 2001. This train used to hold the unique distinction of operating first-class service on narrow-gauge track; it was the world's fastest narrow-gauge train.
Nagpur Chhattisgarh Railway was a 49 miles (79 km) 1,000 mmmetre gauge line owned by the provincial government and operated by the state railways. The line ran from Nagpur via Tumsar - Gondia and Dongargarh to Rajnandgaon. The initial section from Nagpur to Tumsar was opened on 6 July 1880, continuing to Tirora on 21 February 1881, Gondia on 18 May 1881, Amgaon on 25 November 1881 and completed to Rajnandgaon on 16 February 1882.
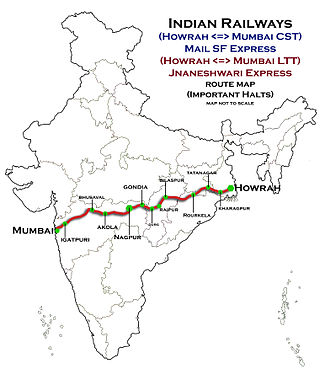
The Howrah–Nagpur–Mumbai line is a railway line in India connecting Kolkata and Mumbai via Nagpur. The 1,968-kilometre-long (1,223 mi) railway line was opened to traffic in 1900.
The Satpura Railway was a 2 ft 6 in narrow-gauge railway in the states of Madhya Pradesh and Maharashtra in central India.

The Bilaspur–Nagpur section is part of the Howrah–Nagpur–Mumbai line and connects Bilaspur in the Indian state of Chhattisgarh and Nagpur in Maharashtra. Part of one of the major trunk lines in the country, it passes through a forested plateau region interspersed with fertile valleys.
Rajnandgaon Railway Station serves Rajnandgaon in Rajnandgaon district in the Indian state of Chhattisgarh and it is the best way to reach Rajnandgaon
Balharshah railway station is a railway station serving Ballarpur town, in Chandrapur district of Maharashtra state in India. Established by the Nizam's Guaranteed State Railway, it is now under the Nagpur CR railway division of Central Railway Zone of Indian Railways. It is an important junction on New Delhi–Chennai main line of Indian Railways. It is located at 185 m above sea level and has 5 platforms. The Ballarshah–Wardha–Nagpur section was electrified in 1989.
Chanda Fort Railway Station is one of the two main railway stations serving Chandrapur city in Chandrapur district in Maharashtra state in India. It is under Nagpur SEC railway division of South East Central Railway zone of Indian Railways. It is located on Gondia–Nagbhid–Balharshah line of Indian Railways.

Nainpur Junction railway station is a railway station in Mandla District, Madhya Pradesh. Its code is NIR. It serves the town of Nainpur.
Nagbhir Junction railway station is a junction railway station on Gondia–Nagbhir–Balharshah line and Nagpur–Nagbhir line in Nagpur SEC railway division of South East Central Railway Zone of Indian Railways. It serves Nagbhid town in Chandrapur district in Maharashtra state in India. It is located at 246 m above sea level and has two platforms. 12 trains stop at this station.
Samnapur railway station is a small railway station in Balaghat district, Madhya Pradesh. Its code is SMC. It serves Samnapur village.
Lamta railway station is a small railway station in Balaghat district, Madhya Pradesh. Its code is LTA. It serves Lamta village.
Chichpalli railway station is a railway station serving Chichpalli village in Chandrapur district in Maharashtra state in India. It is under Nagpur SEC railway division of South East Central Railway Zone of Indian Railways. It is located on Gondia–Nagbhid–Balharshah line of Indian Railways.