
Capitola is a small seaside town in Santa Cruz County, California. Capitola is located on the northern shores of Monterey Bay, on the Central Coast of California. The city had a population of 9,938 at the 2020 census. Capitola is a popular tourist destination, owing to its beaches and restaurants.

National Park Service rustic – sometimes colloquially called Parkitecture – is a style of architecture that developed in the early and middle 20th century in the United States National Park Service (NPS) through its efforts to create buildings that harmonized with the natural environment. Since its founding in 1916, the NPS sought to design and build visitor facilities without visually interrupting the natural or historic surroundings. The early results were characterized by intensive use of hand labor and a rejection of the regularity and symmetry of the industrial world, reflecting connections with the Arts and Crafts movement and American Picturesque architecture. Architects, landscape architects and engineers combined native wood and stone with convincingly native styles to create visually appealing structures that seemed to fit naturally within the majestic landscapes. Examples of the style can be found in numerous types of National Park structures, including entrance gateways, hotels and lodges, park roads and bridges, visitor centers, trail shelters, informational kiosks, and even mundane maintenance and support facilities. Many of these buildings are listed on the National Register of Historic Places.

Venetian Court is a residential seaside resort located in Capitola, California. Construction of Venetian Court, in the Mediterranean Revival, Spanish Colonial Revival, and Mission Revival architecture styles, began in 1924 and continued for several years.

Grand Canyon Village Historic District comprises the historic center of Grand Canyon Village, on the South Rim of the Grand Canyon in Grand Canyon National Park, Arizona. The district includes numerous landmark park structures, many of which are National Historic Landmarks themselves, or are listed on the National Register of Historic Places. The town design as a whole is also significant for its attention to integration with the Grand Canyon landscape, its incorporation of National Park Service Rustic design elements, and for the idiosyncratic design of park concessioner structures such as the El Tovar Hotel.

San Juan Bautista State Historic Park is a California state park encompassing the historic center of San Juan Bautista, California, United States. It preserves a significant concentration of buildings dating to California's period of Spanish and Mexican control. It includes the Mission San Juan Bautista, the Jose Castro House, and several other buildings facing the historic plaza. It became a state park in 1933 and was declared a National Historic Landmark in 1970. It is also a site on the Juan Bautista de Anza National Historic Trail.

Asilomar Conference Grounds is a conference center built for the Young Women's Christian Association (YWCA). It is located east of what was known as Moss Beach on the western tip of the Monterey Peninsula in Pacific Grove, California. Between 1913 and 1929 architect Julia Morgan designed and built 16 of the buildings on the property, of which 11 are still standing. In 1956 it became part of the State Division of Beaches and Parks of California's Department of Natural Resources, and Moss Beach was renamed Asilomar State Beach. Asilomar is a derivation of the Spanish phrase asilo al mar, meaning asylum or refuge by the sea. It is the native homeland of the Rumsen Ohlone people.

The Roosevelt Lodge Historic District comprises the area around the Roosevelt Lodge in the northern part of Yellowstone National Park, near Tower Junction. The district includes 143 buildings ranging in size from cabins to the Lodge, built beginning in 1919. The Lodge was first conceived as a field laboratory for students and educators conducting research in the park. It later became a camp for tourists, specifically designed to accommodate automobile-borne tourists. The Lodge is a simplified version of the National Park Service Rustic style.

The Highlands Historic District in Grand Teton National Park is a former private inholding within the park boundary. The inholding began as a 1914 homestead belonging to Harry and Elizabeth Sensenbach, who began in the 1920s to supplement their income by catering to automobile-borne tourists. In 1946 the property was purchased by Charles Byron, Jeanne Jenkins and Gloria Jenkins Wardell, who expanded the accommodations by one or two cabins a year in a U-shaped layout around a central lodge. The lodge and cabins are constructed in a rustic log style, considered compatible with park architecture. The Highlands was neither an auto camp, which encouraged short stays, nor a dude ranch, which provided ranch-style activities. The Highlands encouraged stays of moderate length, providing a variety of relatively sedentary amenities. It was the last private-accommodation camp to be built in the park before the Mission 66 program created concessioner-operated facilities on public lands.

Volcano House is the name of a series of historic hotels built at the edge of Kīlauea, within the grounds of Hawai'i Volcanoes National Park on the Island of Hawai'i. The original 1877 building is listed on the National Register of Historic Places and now houses the Volcano Art Center. The hotel in use today was built in 1941 and expanded in 1961.
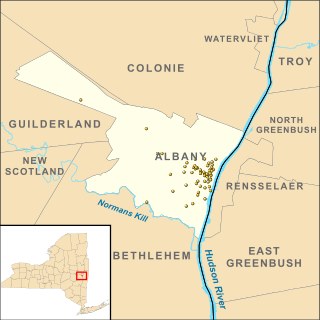
There are 73 properties listed on the National Register of Historic Places in Albany, New York, United States. Six are additionally designated as National Historic Landmarks (NHLs), the most of any city in the state after New York City. Another 14 are historic districts, for which 20 of the listings are also contributing properties. Two properties, both buildings, that had been listed in the past but have since been demolished have been delisted; one building that is also no longer extant remains listed.

The historical buildings and structures of Zion National Park represent a variety of buildings, interpretive structures, signs and infrastructure associated with the National Park Service's operations in Zion National Park, Utah. Structures vary in size and scale from the Zion Lodge to road culverts and curbs, nearly all of which were designed using native materials and regional construction techniques in an adapted version of the National Park Service Rustic style. A number of the larger structures were designed by Gilbert Stanley Underwood, while many of the smaller structures were designed or coordinated with the National Park Service Branch of Plans and Designs. The bulk of the historic structures date to the 1920s and 1930s. Most of the structures of the 1930s were built using Civilian Conservation Corps labor.

The White River Entrance to Mount Rainier National Park is a complex of buildings built between 1929 and 1931 to accommodate visitors arriving on the Yakima Park Highway, in the northeastern portion of the park. Like most of the structures in Mount Rainier, the buildings are designed in the National Park Service Rustic style, using natural stone and log materials. The historic district includes the 1933 Men's Mess Hall and Dormitory, believed to be the only surviving camp structure built by the Civilian Conservation Corps in the park.

The historical buildings and structures of Grand Teton National Park include a variety of buildings and built remains that pre-date the establishment of Grand Teton National Park, together with facilities built by the National Park Service to serve park visitors. Many of these places and structures have been placed on the National Register of Historic Places. The pre-Park Service structures include homestead cabins from the earliest settlement of Jackson Hole, working ranches that once covered the valley floor, and dude ranches or guest ranches that catered to the tourist trade that grew up in the 1920s and 1930s, before the park was expanded to encompass nearly all of Jackson Hole. Many of these were incorporated into the park to serve as Park Service personnel housing, or were razed to restore the landscape to a natural appearance. Others continued to function as inholdings under a life estate in which their former owners could continue to use and occupy the property until their death. Other buildings, built in the mountains after the initial establishment of the park in 1929, or in the valley after the park was expanded in 1950, were built by the Park Service to serve park visitors, frequently employing the National Park Service Rustic style of design.

Pleasure Point is a census-designated place (CDP) in Santa Cruz County, California. Pleasure Point sits at an elevation of 33 feet (10 m). The 2020 United States census reported Pleasure Point's population was 5,821. Prior to the 2010 census, this CDP was called Opal Cliffs.
Architects of the National Park Service are the architects and landscape architects who were employed by the National Park Service (NPS) starting in 1918 to design buildings, structures, roads, trails and other features in the United States National Parks. Many of their works are listed on the National Register of Historic Places, and a number have also been designated as National Historic Landmarks.

Murphys Grammar School is a historic school building in Murphys, California. Built in 1860, the school was the first public school in Murphys. The school was designed in a vernacular Greek Revival style, which was popular at the time of its construction; its design includes a cornice held up by square pilasters, a pedimented gable, and a cupola over the entrance with its own cornice and square pilasters. The school operated continuously from its opening until it closed in 1973; at the time of its closing, it was the longest continuously running school west of the Mississippi River.

Capitola Manufacturing Company Cotton Yarn Mill, also known as the Marshall Mill and Power Company, is a historic cotton mill complex located at Marshall, Madison County, North Carolina. The main mill building is a three-story brick building built about 1905. It was raised to three stories in 1928. It measures approximately 108 feet (33 m) by 116 feet (35 m), with a low-pitched gabled roof, and windows on three sides. Also on the property is a contributing boiler house and water tank.

The Rispin Mansion is a historic mansion, on the National Register of Historic Places, located in Capitola, California. The building was constructed in 1921 by San Franciscan Henry Allen Rispin. It was built with four stories, 22 rooms, and over 7,100 square feet (660 m2) on the grounds of what was called "Camp Capitola". Described as being "cursed," Rispin Mansion was first used as a real-estate showroom, and then, at various times, as a residence, a nunnery, a SWAT practice ground, and a ghost hunting site.

Valencia Hall, in Santa Cruz County, California near Aptos, California, was built around 1884 by F.A. Hihn. It was listed on the National Register of Historic Places in 1984.

The Stevenson House, is a historic two-story Spanish Colonial style building located at 530 Houston Street in Monterey, California. It was a boarding house called the French Hotel, built circa 1836. The Scottish author Robert Louis Stevenson lived there in 1879, writing and courting his future wife. It is now a museum and property of the Monterey State Historic Park. The building was listed on the National Register of Historic Places on January 7, 1972. The building is also listed as a California historical landmark #352.



















