
The Cache River National Wildlife Refuge is a 68,993 acre (223 km2) (2014) wildlife refuge in the state of Arkansas managed by the United States Fish and Wildlife Service (FWS). The refuge is one of the Ramsar wetlands of international importance under the Ramsar Convention signed in 1971. It is one of the most important wintering area for ducks and the largest remaining tract of contiguous bottomland hardwood forest on the North American continent. In 2005, a possible sighting of the ivory-billed woodpecker, thought to be extinct, brought attention to the refuge.

The Felsenthal National Wildlife Refuge (NWR) is a 76,000 acre national wildlife refuge located in south-central Arkansas in Ashley, Bradley, and Union counties. Felsenthal NWR is one of three refuges forming an administrative complex, which also includes Pond Creek NWR to the northwest and Overflow NWR to the east.
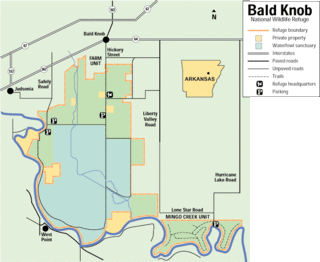
The Bald Knob National Wildlife Refuge is a 15,022 acres (60.79 km2) (2014) wildlife refuge located in White County, Arkansas about two miles south of the town of Bald Knob. The refuge is managed by the United States Fish and Wildlife Service. The refuge features large numbers of migratory waterfowl and bald eagles during the winter months.

Big Lake National Wildlife Refuge is an 11,047-acre (45 km²) National Wildlife Refuge located in Mississippi County, Arkansas, managed by the United States Fish and Wildlife Service. It is situated 2 miles (3.2 km) east of Manila, Arkansas, and consists mostly of a shallow lake, swamp, and bottomland hardwood forests. The preservation of habitat for waterfowl in an intensely agricultural region is the primary purpose of the refuge. 6,400 acres (20 km²) of Big Lake is classified as a National Natural Landmark and 2,144 acres (8 km²) are classified as wilderness.

The White River National Wildlife Refuge is a 160,756 acres (650.56 km2) wildlife refuge located in Desha, Monroe, Phillips, and Arkansas counties in the U.S. state of Arkansas. The refuge is managed by the United States Fish and Wildlife Service. White River NWR borders on Cache River National Wildlife Refuge at its northern boundary. In 1974, the White River Sugarberry Natural Area was designated as a National Natural Landmark by the National Park Service.

Fort Peck Lake, or Lake Fort Peck, is a major reservoir in Montana, formed by the Fort Peck Dam on the Missouri River. The lake lies in the eastern prairie region of Montana approximately 140 miles (230 km) east of Great Falls and 120 miles (190 km) north of Billings, reaching into portions of six counties.
The Charles M. Russell National Wildlife Refuge is a National Wildlife Refuge in the U.S. state of Montana on the Missouri River. The refuge surrounds Fort Peck Reservoir and is 915,814 acres (3,706.17 km2) in size. It is the second-largest National Wildlife Refuge in the lower 48 states of the United States, and the largest in Montana. Created in 1936, it was originally called the Fort Peck Game Range. It was renamed in 1963 after Montana artist Charles M. Russell, a famous painter of the American West. In 1976, the "range" was made a "refuge".

Boyer Chute National Wildlife Refuge, created in 1992, is a National Wildlife Refuge (NWR) located along the banks of the Missouri River in the U.S. state of Nebraska. The 4,040-acre (1,630 ha) refuge preserves an area that had been cultivated and neglected before the early 1990s. Channelization projects along the Missouri River to improve flood control and navigation resulted in the closing off a side branch of the river, known since the early 19th century as Boyer Chute. Between 1820 and 1937 the Missouri River had migrated 3 mi (4.8 km) eastward and the area of the chute had originally been on the east bank of the river; today, the chute is west of the main channel of the Missouri. In 1937, the Army Corps of Engineers began to rechannel portions of the Missouri River, cutting off the chute to flowing water. Overgrowth and cultivation took over the lands now preserved in the refuge. Restoration of the area commenced in 1993; this included planting 9,100 native plants and trees and restoring the inflow to the chute from the main channel of the Missouri River.

Lake Francis Case is a large reservoir impounded by Fort Randall Dam on the Missouri River in south-central South Dakota, United States. The lake has an area of 102,000 acres (410 km2) and a maximum depth of 140 ft (43 m). Lake Francis Case has a length of approximately 107 mi (172 km) and has a shoreline of 540 mi (870 km). The lake is the eleventh-largest reservoir in the United States and is located within the counties of: Charles Mix, Gregory, Lyman, Brule, and Buffalo. The lake stretches from Pickstown, South Dakota upstream to Big Bend Dam.

The Little River is a tributary of the Red River, with a total length of 217 miles (349 km), 130 miles (210 km) within the Choctaw Indian Reservation in southeastern Oklahoma and 87 miles (140 km) in southwestern Arkansas in the United States. Via the Red, it is part of the watershed of the Mississippi River. Six large reservoirs impound the Little River and its tributaries. The drainage basin of the river totals 4,204 square miles (10,890 km2), 2,204 square miles (5,710 km2) in Oklahoma and 2,036 square miles (5,270 km2) in Arkansas. The Little River and its upper tributaries are popular for recreational canoeing and kayaking.

John Redmond Reservoir is a reservoir on the Neosho River in eastern Kansas. Built and managed by the U.S. Army Corps of Engineers, it is used for flood control, recreation, water supply, and wildlife management. It borders the Flint Hills National Wildlife Refuge to the northwest.

Straddling the headwaters of the Minnesota River in west-central Minnesota, Big Stone National Wildlife Refuge is within the heart of the tallgrass prairie's historic range. Today, less than one-percent of tallgrass prairie remains.
The Great River National Wildlife Refuge protects approximately 11,600 acres (47 km2) along 120 miles (190 km) of the Mississippi River, stretching north of St. Louis, Missouri. Three separate units are located in the floodplain, on both the Illinois and Missouri sides of the river.

The Summer Lake Wildlife Area is a 29.6-square-mile (77 km2) wildlife refuge located on the northwestern edge of the Great Basin drainage in south-central Oregon. It is administered by the Oregon Department of Fish and Wildlife. The refuge is an important stop for waterfowl traveling along the Pacific Flyway during their spring and fall migrations. The Summer Lake Wildlife Area also provides habitat for shorebirds and other bird species as well as wide variety of mammals and several fish species. The Ana River supplies the water for the refuge wetlands.
The Sherburne Complex is a joint land management venture of the U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service, the Louisiana Department of Wildlife and Fisheries (LDWF), and the U.S. Army Corps of Engineers that began in 1983. The area consists of 44,000 acres (180 km2), and is managed by the Louisiana Department of Wildlife and Fisheries. The complex is located in the Morganza Flood way system of the Atchafalaya Basin about 30 miles (48 km) west of Baton Rouge, Louisiana and actually extends a little south of the I-10 Atchafalaya Basin Bridge at Whiskey Bay, Louisiana. The bridge crosses the Whiskey Bay Pilot Channel. Located on the graveled LA 975, the west boundary is on the east side of the Atchafalaya River with the east boundary being the East Protection Levee. The complex stretches just north of old highway 190, and a short distance to the south of I-10. The nearest town is Krotz Springs to the north off US 190.

Kanopolis Lake is a reservoir in Ellsworth County in the Smoky Hills of central Kansas, about 31 miles southwest of Salina and a few miles southeast of the town of Kanopolis. The lake is formed by Kanopolis Dam. Completed in 1948 as a flood control and water conservation project of the United States Army Corps of Engineers, the dam impounds the Smoky Hill River.
Lake Whittington is an oxbow lake located in Bolivar County, Mississippi, and Desha County, Arkansas, United States. The Arkansas-Mississippi border follows the center of the narrow, curving lake.

John Martin Reservoir is a reservoir on the Arkansas River in Bent County in southeastern Colorado. Built and managed by the U.S. Army Corps of Engineers, it is used for flood control, irrigation, and recreation. John Martin Reservoir State Park lies on its shore.

DeSoto Lake is a lake within DeSoto National Wildlife Refuge, Harrison and Pottawattamie counties, Iowa and Washington County, Nebraska. The 811 acres (328 ha) lake has a maximum depth of 26 feet (7.9 m). Though it has the appearance of a natural lake it is man-made, created from a channel leading from the Missouri River in 1958.
















