
In Norse mythology, Bifröst, also called Bilröst, is a burning rainbow bridge that reaches between Midgard (Earth) and Asgard, the realm of the gods. The bridge is attested as Bilröst in the Poetic Edda, compiled in the 13th century from earlier traditional sources; as Bifröst in the Prose Edda, written in the 13th century by Snorri Sturluson; and in the poetry of skalds. Both the Poetic Edda and the Prose Edda alternately refer to the bridge as Ásbrú.

Fenrir or Fenrisúlfr, also referred to as Hróðvitnir and Vánagandr, is a monstrous wolf in Norse mythology. In Old Norse texts, Fenrir plays a key role during the events of Ragnarök, where he is foretold to assist in setting the world aflame, resulting in the collapse of humanity and society, and kill the god Odin.

In Norse mythology, Geri and Freki are two wolves which are said to accompany the god Odin. They are attested in the Poetic Edda, a collection of epic poetry compiled in the 13th century from earlier traditional sources, in the Prose Edda, written in the 13th century by Snorri Sturluson, and in the poetry of skalds. The pair has been compared to similar figures found in Greek, Roman and Vedic mythology, and may also be connected to beliefs surrounding the Germanic "wolf-warrior bands", the Úlfhéðnar.

In Norse mythology, Heimdall is a god. He is the son of Odin and nine mothers. Heimdall keeps watch for invaders and the onset of Ragnarök from his dwelling Himinbjörg, where the burning rainbow bridge Bifröst meets the sky. He is attested as possessing foreknowledge and keen senses, particularly eyesight and hearing. The god and his possessions are described in enigmatic manners. For example, Heimdall is golden-toothed, "the head is called his sword," and he is "the whitest of the gods."

Hel is a female being in Norse mythology who is said to preside over an underworld realm of the same name, where she receives a portion of the dead. Hel is attested in the Poetic Edda, compiled in the 13th century from earlier traditional sources, and the Prose Edda, written in the 13th century. In addition, she is mentioned in poems recorded in Heimskringla and Egils saga that date from the 9th and 10th centuries, respectively. An episode in the Latin work Gesta Danorum, written in the 12th century by Saxo Grammaticus, is generally considered to refer to Hel, and Hel may appear on various Migration Period bracteates.

In Norse mythology, Ragnarök is a foretold series of impending events, including a great battle in which numerous great Norse mythological figures will perish ; it will entail a catastrophic series of natural disasters, including the burning of the world, and culminate in the submersion of the world underwater. After these events, the world will rise again, cleansed and fertile, the surviving and returning gods will meet, and the world will be repopulated by two human survivors, Líf and Lífþrasir. Ragnarök is an important event in Norse mythology and has been the subject of scholarly discourse and theory in the history of Germanic studies.

In Norse mythology, Skaði is a jötunn and goddess associated with bowhunting, skiing, winter, and mountains. Skaði is attested in the Poetic Edda, compiled in the 13th century from earlier traditional sources; the Prose Edda and in Heimskringla, written in the 13th century by Snorri Sturluson, and in the works of skalds.
In Norse mythology, Sæhrímnir is the creature killed and eaten every night by the Æsir and einherjar. The cook of the gods, Andhrímnir, is responsible for the slaughter of Sæhrímnir and its preparation in the cauldron Eldhrímnir. After Sæhrímnir is eaten, the beast is brought back to life again to provide sustenance for the following day. Sæhrímnir is attested in the Poetic Edda, compiled in the 13th century from earlier traditional material, and the Prose Edda, written in the 13th century by Snorri Sturluson.

In Norse mythology, Fólkvangr is a meadow or field ruled over by the goddess Freyja where half of those that die in combat go upon death, whilst the other half go to the god Odin in Valhalla. Others were also brought to Fólkvangr after their death; Egils Saga, for example, has a world-weary female character declare that she will never taste food again until she dines with Freyja. Fólkvangr is attested in the Poetic Edda, compiled in the 13th century from earlier traditional sources, and the Prose Edda, written in the 13th century by Snorri Sturluson. According to the Prose Edda, within Fólkvangr is Freyja's hall Sessrúmnir. Scholarly theories have been proposed about the implications of the location.

In Norse mythology, Óðr or Óð, sometimes anglicized as Odr or Od, is a figure associated with the major goddess Freyja. The Prose Edda and Heimskringla, written in the 13th century by Snorri Sturluson, both describe Óðr as Freyja's husband and father of her daughter Hnoss. Heimskringla adds that the couple produced another daughter, Gersemi. A number of theories have been proposed about Óðr, generally that he is a hypostasis of the deity Odin due to their similarities.

Germanic paganism or Germanic religion refers to the traditional, culturally significant religion of the Germanic peoples. With a chronological range of at least one thousand years in an area covering Scandinavia, the British Isles, modern Germany, and at times other parts of Europe, the beliefs and practices of Germanic paganism varied. Scholars typically assume some degree of continuity between Roman-era beliefs and those found in Norse paganism, as well as between Germanic religion and reconstructed Indo-European religion and post-conversion folklore, though the precise degree and details of this continuity are subjects of debate. Germanic religion was influenced by neighboring cultures, including that of the Celts, the Romans, and, later, by the Christian religion. Very few sources exist that were written by pagan adherents themselves; instead, most were written by outsiders and can thus present problems for reconstructing authentic Germanic beliefs and practices.

Norse cosmology is the account of the universe and its laws by the ancient North Germanic peoples. The topic encompasses concepts from Norse mythology, such as notations of time and space, cosmogony, personifications, anthropogeny, and eschatology. Like other aspects of Norse mythology, these concepts are primarily recorded from earlier oral sources in the Poetic Edda, a collection of poems compiled in the 13th century, and the Prose Edda, authored by Icelander Snorri Sturluson in the 13th century. Together these sources depict an image of Nine Worlds around a cosmic tree, Yggdrasil.
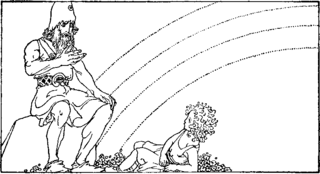
In Norse mythology, Himinbjörg is the home of the god Heimdallr. Himinbjörg is attested in the Poetic Edda, compiled from earlier traditional sources, and the Prose Edda and Heimskringla, both written in the 13th century by Snorri Sturluson. Himinbjörg is associated with Heimdallr in all sources. According to the Poetic Edda, Heimdallr dwells there as watchman for the gods and there drinks fine mead, whereas in the Prose Edda Himinbjörg is detailed as located where the burning rainbow bridge Bifröst meets heaven. Scholars have commented on the differences between the two attestations and linked the name of the mythical location to various place names.

The raven banner was a flag, possibly totemic in nature, flown by various Viking chieftains and other Scandinavian rulers during the 9th, 10th and 11th centuries. Period description simply describes it as a war banner with a raven mark on it, although no complete visual description or depiction of the raven banner is known from the time. Norse and European period artwork, however, depicts war banners as roughly triangular, with a rounded outside edge on which there hung a series of tabs or tassels, some with a resemblance to ornately carved "weather-vanes" used aboard Viking longships, indicating that some raven banners may have been constructed in a similar manner.

In Norse mythology, Sága is a goddess associated with the location Sökkvabekkr. At Sökkvabekkr, Sága and the god Odin merrily drink as cool waves flow. Both Sága and Sökkvabekkr are attested in the Poetic Edda, compiled in the 13th century from earlier traditional sources, and in the Prose Edda, written in the 13th century by Snorri Sturluson. Scholars have proposed theories about the implications of the goddess and her associated location, including that the location may be connected to the goddess Frigg's fen residence Fensalir and that Sága may be another name for Frigg.

Odin is a widely revered god in Germanic paganism. Norse mythology, the source of most surviving information about him, associates him with wisdom, healing, death, royalty, the gallows, knowledge, war, battle, victory, sorcery, poetry, frenzy, and the runic alphabet, and depicts him as the husband of the goddess Frigg. In wider Germanic mythology and paganism, the god was also known in Old English as Wōden, in Old Saxon as Uuôden, in Old Dutch as Wuodan, in Old Frisian as Wêda, and in Old High German as Wuotan, all ultimately stemming from the Proto-Germanic theonym *Wōðanaz, meaning 'lord of frenzy', or 'leader of the possessed'.

Norse, Nordic, or Scandinavian mythology, is the body of myths belonging to the North Germanic peoples, stemming from Old Norse religion and continuing after the Christianization of Scandinavia, and into the Nordic folklore of the modern period. The northernmost extension of Germanic mythology and stemming from Proto-Germanic folklore, Norse mythology consists of tales of various deities, beings, and heroes derived from numerous sources from both before and after the pagan period, including medieval manuscripts, archaeological representations, and folk tradition. The source texts mention numerous gods such as the thunder-god Thor, the raven-flanked god Odin, the goddess Freyja, and numerous other deities.

In Norse mythology, Gefjon is a goddess associated with ploughing, the Danish island of Zealand, the legendary Swedish king Gylfi, the legendary Danish king Skjöldr, foreknowledge, her oxen children, and virginity. Gefjon is attested in the Poetic Edda, compiled in the 13th century from earlier traditional sources; the Prose Edda and Heimskringla, written in the 13th century by Snorri Sturluson; in the works of skalds; and appears as a gloss for various Greco-Roman goddesses in some Old Norse translations of Latin works.
These are family trees of the Norse gods showing kin relations among gods and other beings in Nordic mythology. Each family tree gives an example of relations according to principally Eddic material however precise links vary between sources. In addition, some beings are identified by some sources and scholars.




















