
Bleib bei uns, denn es will Abend werden, BWV 6, is a cantata by Johann Sebastian Bach for use in a Lutheran service. He composed it in Leipzig in 1725 for Easter Monday and first performed it on 2 April 1725.

Weinen, Klagen, Sorgen, Zagen, BWV 12, is a church cantata by Johann Sebastian Bach. He composed it in Weimar for Jubilate, the third Sunday after Easter, and led the first performance on 22 April 1714 in the Schlosskirche, the court chapel of the Schloss in Weimar.
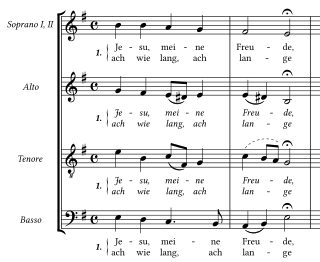
Jesu, meine Freude, BWV 227, is a motet by Johann Sebastian Bach. The longest and most musically complex of Bach's motets, it is set in eleven movements for up to five voices. It is named after the Lutheran hymn "Jesu, meine Freude" with words by Johann Franck, first published in 1653. The motet contains the six stanzas of the hymn in its odd-numbered movements. The hymn tune by Johann Crüger appears in all of these movements in different styles of chorale settings. The text of the motet's even-numbered movements is taken from the eighth chapter of the Epistle to the Romans, a passage that influenced key Lutheran teachings. The hymn, written in the first person with a focus on an emotional bond with Jesus, forms a contrasting expansion of the doctrinal biblical text. Bach set both texts alternating with and complementing each other, in a structure of symmetries on different layers.

"Ach Gott, wie manches Herzeleid" is a German hymn in 18 stanzas attributed to Martin Moller (1587). It is often catalogued as a paraphrase of the Latin "Jesu dulcis memoria", a medieval hymn attributed to Bernard of Clairvaux, but only a few lines refer directly to this song. Hymn tunes were composed for the hymn, and it is also often sung to a tune composed for "Herr Jesu Christ, meins Lebens Licht". The anonymous hymn tune of "Herr Jesu Christ, meins Lebens Licht" first appeared in Wolflein Lochamer's Lochamer-Liederbuch, printed in Nürnberg around 1455. In Leipzig in the 1720s, Johann Sebastian Bach composed settings of Lochamer's hymn based on four of his church cantatas and a sacred motet.

Jesu, nun sei gepreiset, BWV 41, is a church cantata by Johann Sebastian Bach. He composed the chorale cantata in Leipzig for New Year's Day and first performed it on 1 January 1725 as part of his second cantata cycle. It is based on the hymn by Johannes Hermann (1591).

"Christ lag in Todesbanden" is an Easter hymn by Martin Luther. Its melody is by Luther and Johann Walter. Both the text and the melody were based on earlier examples. It was published in 1524 in the Erfurt Enchiridion and in Walter's choral hymnal Eyn geystlich Gesangk Buchleyn. Various composers, including Pachelbel, Bach and Telemann, have used the hymn in their compositions.

Johann Sebastian Bach composed the church cantata Du Friedefürst, Herr Jesu Christ, BWV 116, in Leipzig for the 25th Sunday after Trinity. He led the first performance on 26 November 1724, concluding the liturgical year of 1724.

"Gelobet seist du, Jesu Christ" is a Lutheran hymn, written by Martin Luther in 1524. It was first published in 1524 in the Eyn geystlich Gesangk Buchleyn. For centuries the chorale has been the prominent hymn (Hauptlied) for Christmas Day in German speaking Lutheranism, but has also been used in different translations internationally. It has appeared in hymnals of various denominations including the Catholic Church.

Sehet, wir gehn hinauf gen Jerusalem, BWV 159, is a church cantata by Johann Sebastian Bach. He composed it in Leipzig for the Sunday Estomihi, the last Sunday before Lent, and probably first performed it on 27 February 1729. The gospel reading for the Sunday, from the Gospel of Luke, includes Jesus announcing his suffering and death in Jerusalem. The cantata's theme and Bach's music foreshadow his Passion.

Himmelskönig, sei willkommen, BWV 182, is a church cantata by Johann Sebastian Bach. He composed it in Weimar for Palm Sunday, and first performed it on 25 March 1714, which was also the feast of the Annunciation that year.

O heilges Geist- und Wasserbad, BWV 165, is a church cantata by Johann Sebastian Bach. He composed it in Weimar for Trinity Sunday and led the first performance on 16 June 1715.
Paul or Paulus Stockmann was a German academic, preacher and hymn-writer. He fought at the Battle of Lützen in 1632 and later served as court preacher to Gustavus Adolphus of Sweden, before dying of the plague in 1636.

The structure of the St John Passion, BWV 245, a sacred oratorio by Johann Sebastian Bach, is "carefully designed with a great deal of musico-theological intent". Some main aspects of the structure are shown in tables below.

"Jesu, meine Freude" is a hymn in German, written by Johann Franck in 1650, with a melody, Zahn No. 8032, by Johann Crüger. The song first appeared in Crüger's hymnal Praxis pietatis melica in 1653. The text addresses Jesus as joy and support, versus enemies and the vanity of existence. The poetry is bar form, with irregular lines from 5 to 8 syllables. The melody repeats the first line as the last, framing each of the six stanzas.

"Jesus Christus, unser Heiland, der den Tod überwand" is a hymn for Easter by Martin Luther. The text originated in 1524. Johannes Zahn listed three hymn tunes for it. Two of these, Zahn Nos. 1976 and 1977, were published in 1724. A third, Zahn No. 1978, is attributed to Luther and was first published in 1529. Variants of this melody originated up to the early 17th century.
"Herr Jesu Christ, wahr Mensch und Gott" is a Lutheran hymn by Paul Eber. It is a hymn for the dying. One of the hymn's tunes, Zahn No. 423, is also used for "Wir danken dir, Herr Jesu Christ".
"Werde munter, mein Gemüte" is a Lutheran evening hymn by Johann Rist in twelve stanzas of eight lines each, printed in 1642. The hymn was translated to English and appeared in 67 hymnals.

"Christus, der uns selig macht" is a German Lutheran Passion hymn in eight stanzas in German by Michael Weiße, written in 1531 as a translation of the Latin hymn "Patris Sapientia" to an older melody of the Bohemian Brethren.

"Liebster Jesu, wir sind hier" is a Lutheran hymn with text written by Tobias Clausnitzer in 1663, and a hymn tune, Zahn No. 3498b, based on a 1664 melody by Johann Rudolph Ahle. A prayer for illumination, it is suitable for the opening of a church service and to be sung before a sermon. The song is part of the Protestant hymnal Evangelisches Gesangbuch as EG 161. It is also part of the Catholic hymnal Gotteslob as GL 149. It is popular also in English translations such as "Blessed Jesus, at your word" by Catherine Winkworth.

Jesu, meines Glaubens Zier is a German Lutheran hymn by Gottfried Wilhelm Sacer, first published in 1661. Its hymn tune, Zahn No. 6453, was first published in 1714, in Freylinghausen's hymnal. In 1736 the hymn was adopted in Schemellis Gesangbuch, with a figured bass accompaniment which may have been contributed by Johann Sebastian Bach (BWV 472).















