A sword is an edged, bladed weapon intended for manual cutting or thrusting. Its blade, longer than a knife or dagger, is attached to a hilt and can be straight or curved. A thrusting sword tends to have a straighter blade with a pointed tip. A slashing sword is more likely to be curved and to have a sharpened cutting edge on one or both sides of the blade. Many swords are designed for both thrusting and slashing. The precise definition of a sword varies by historical epoch and geographic region.

Gladius is a Latin word properly referring to the type of sword that was used by ancient Roman foot soldiers starting from the 3rd century BC and until the 3rd century AD. Linguistically, within Latin, the word also came to mean "sword", regardless of the type used.
A sabre or (American English)saber is a type of backsword with a curved blade associated with the light cavalry of the early modern and Napoleonic periods. Originally associated with Central European cavalry such as the hussars, the sabre became widespread in Western Europe during the Thirty Years' War. Lighter sabres also became popular with infantry of the early 17th century. In the 19th century, models with less curving blades became common and were also used by heavy cavalry.
This is a list of types of swords.

The kukri or khukuri is a type of knife or short sword with a distinct recurve in its blade that originated in the Indian subcontinent. It serves multiple purposes as a melee weapon and also as a regular cutting tool throughout most of South Asia. The kukri, khukri, and kukkri spellings are of Indian English origin.

Dao are single-edged Chinese swords, primarily used for slashing and chopping. They can be straight or curved. The most common form is also known as the Chinese sabre, although those with wider blades are sometimes referred to as Chinese broadswords. In China, the dao is considered one of the four traditional weapons, along with the gun, qiang (spear), and the jian, called in this group "The General of Weapons".

A blade is the sharp, cutting portion of a tool, weapon, or machine, specifically designed to puncture, chop, slice, or scrape surfaces or materials. Blades are typically made from materials that are harder than those they are intended to cut. This includes early examples made from flaked stones like flint or obsidian, evolving through the ages into metal forms like copper, bronze, and iron, and culminating in modern versions made from steel or ceramics. Serving as one of humanity's oldest tools, blades continue to have wide-ranging applications, including in combat, cooking, and various other everyday and specialized tasks.

Swordsmanship or sword fighting refers to the skills and techniques used in combat and training with any type of sword. The term is modern, and as such was mainly used to refer to smallsword fencing, but by extension it can also be applied to any martial art involving the use of a sword. The formation of the English word "swordsman" is parallel to the Latin word gladiator, a term for the professional fighters who fought against each other and a variety of other foes for the entertainment of spectators in the Roman Empire. The word gladiator itself comes from the Latin word gladius, which is a type of sword.

The English language terminology used in the classification of swords is imprecise and has varied widely over time. There is no historical dictionary for the universal names, classification, or terminology of swords; a sword was simply a single-edged or double-edged knife.

The xiphos is a double-edged, one-handed Iron Age straight shortsword used by the ancient Greeks. It was a secondary battlefield weapon for the Greek armies after the dory or javelin. The classic blade was generally about 45–60 cm (18–24 in) long, although the Spartans supposedly preferred to use blades as short as 30 cm (12 in) around the era of the Greco-Persian Wars.

The makhaira is a type of Ancient Greek bladed weapon and tool, generally a large knife or sword, similar in appearance to the modern day machete, with a single cutting edge.
The khopesh is an Egyptian sickle-shaped sword that developed from battle axes.

The falx was a weapon with a curved blade that was sharp on the inside edge used by the Thracians and Dacians. The name was later applied to a siege hook used by the Romans.
The falcata is a type of sword typical of pre-Roman Iberia. The falcata was used to great effect for warfare in the ancient Iberian Peninsula, and is firmly associated with the southern Iberian tribes, among other ancient peoples of Hispania. It was highly prized by the ancient general Hannibal, who equipped Carthaginian troops with it during the Second Punic War.

The harpē (ἅρπη) is a type of sword- or sickle-like weapon mentioned in Greek and Roman sources, and almost always in mythological contexts.

A scimitar is a single-edged sword with a convex curved blade associated with Middle Eastern, South Asian, or North African cultures. A European term, scimitar does not refer to one specific sword type, but an assortment of different Eastern curved swords inspired by types introduced to the Middle East by Central Asian ghilmans. These swords include the Persian shamshir, the Arab saif, the Indian talwar, the North African nimcha, the Turkish kilij, and the Afghan pulwar. All such swords are originally derived from earlier curved swords developed in Turkic Central Asia (Turkestan).
A single-edged sword is a class of swords with one cutting edge, such as:

The scythe sword (Sensenschwert) was a type of single-edged sword of the German Renaissance, related to the Dussack. It consisted of the blade of a scythe to which a sword hilt was attached. Like the falx or falcata of antiquity, it was thus a curved sword with the cutting edge on the inside.
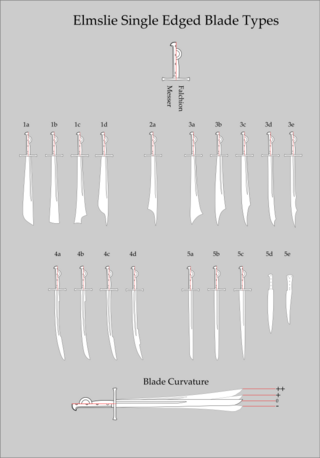
The Elmslie typology is a system for classification and description of the single edged European bladed weapons of the late medieval and early baroque period, from around 1100 to 1550. It is designed to provide classification terminology for archaeological finds of single-edged arms, as well as visual depictions in art. It includes swords which are from the Europeans Middle Ages and currently breaks them down into five main types, which each have several subtypes. Historian and bladesmith James Elmslie introduced the typology 2015, as a complement to the Oakeshott typology which covers double edged swords of the same periods.















