Related Research Articles

Transforming growth factor beta (TGF-β) is a multifunctional cytokine belonging to the transforming growth factor superfamily that includes three different mammalian isoforms and many other signaling proteins. TGFB proteins are produced by all white blood cell lineages.
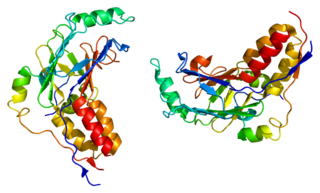
Mothers against decapentaplegic homolog 2 also known as SMAD family member 2 or SMAD2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the SMAD2 gene. MAD homolog 2 belongs to the SMAD, a family of proteins similar to the gene products of the Drosophila gene 'mothers against decapentaplegic' (Mad) and the C. elegans gene Sma. SMAD proteins are signal transducers and transcriptional modulators that mediate multiple signaling pathways.

Mothers against decapentaplegic homolog 7 or SMAD7 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the SMAD7 gene.

Transforming growth factor beta 1 or TGF-β1 is a polypeptide member of the transforming growth factor beta superfamily of cytokines. It is a secreted protein that performs many cellular functions, including the control of cell growth, cell proliferation, cell differentiation, and apoptosis. In humans, TGF-β1 is encoded by the TGFB1 gene.

Activin receptor type-1B is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ACVR1B gene.

Activin receptor type-2B is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ACVR2B gene. ACVR2B is an activin type 2 receptor.

An alveolar macrophage is a type of macrophage, a professional phagocyte, found in the pulmonary alveoli, near the pneumocytes, but separated from the wall.

Transforming growth factor-beta 2 (TGF-β2) is a secreted protein known as a cytokine that performs many cellular functions and has a vital role during embryonic development. It is an extracellular glycosylated protein. It is known to suppress the effects of interleukin dependent T-cell tumors. There are two named isoforms of this protein, created by alternative splicing of the same gene.

Betaglycan also known as Transforming growth factor beta receptor III (TGFBR3), is a cell-surface chondroitin sulfate / heparan sulfate proteoglycan >300 kDa in molecular weight. Betaglycan binds to various members of the TGF-beta superfamily of ligands via its core protein, and bFGF via its heparan sulfate chains. It is not involved directly in TGF-beta signal transduction but by binding to various member of the TGF-beta superfamily at the cell surface it acts as a reservoir of ligand for TGF-beta receptors.

The SKI protein is a nuclear proto-oncogene that is associated with tumors at high cellular concentrations. SKI has been shown to interfere with normal cellular functioning by both directly impeding expression of certain genes inside the nucleus of the cell as well as disrupting signaling proteins that activate genes.

The EGF-like domain is an evolutionary conserved protein domain, which derives its name from the epidermal growth factor where it was first described. It comprises about 30 to 40 amino-acid residues and has been found in a large number of mostly animal proteins. Most occurrences of the EGF-like domain are found in the extracellular domain of membrane-bound proteins or in proteins known to be secreted. An exception to this is the prostaglandin-endoperoxide synthase. The EGF-like domain includes 6 cysteine residues which in the epidermal growth factor have been shown to form 3 disulfide bonds. The structures of 4-disulfide EGF-domains have been solved from the laminin and integrin proteins. The main structure of EGF-like domains is a two-stranded β-sheet followed by a loop to a short C-terminal, two-stranded β-sheet. These two β-sheets are usually denoted as the major (N-terminal) and minor (C-terminal) sheets. EGF-like domains frequently occur in numerous tandem copies in proteins: these repeats typically fold together to form a single, linear solenoid domain block as a functional unit.

Transforming growth factor beta-3 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the TGFB3 gene.

Integrin beta-6 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ITGB6 gene. It is the β6 subunit of the integrin αvβ6. Integrins are αβ heterodimeric glycoproteins which span the cell’s membrane, integrating the outside and inside of the cell. Integrins bind to specific extracellular proteins in the extracellular matrix or on other cells and subsequently transduce signals intracellularly to affect cell behaviour. One α and one β subunit associate non-covalently to form 24 unique integrins found in mammals. While some β integrin subunits partner with multiple α subunits, β6 associates exclusively with the αv subunit. Thus, the function of ITGB6 is entirely associated with the integrin αvβ6.
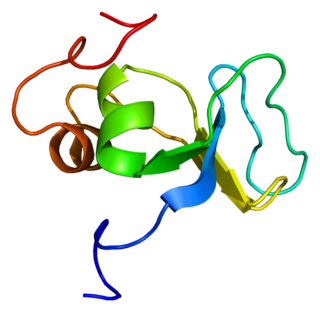
Latent-transforming growth factor beta-binding protein 1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the LTBP1 gene.

Eukaryotic translation initiation factor 3 subunit I (eIF3i) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the EIF3I gene.

Latent-transforming growth factor beta-binding protein 3 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the LTBP3 gene.

Latent-transforming growth factor beta-binding protein 2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the LTBP2 gene.

Forkhead box protein H1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the FOXH1 gene.
Transforming growth factor beta (TGF-β) is a potent cell regulatory polypeptide homodimer of 25kD. It is a multifunctional signaling molecule with more than 40 related family members. TGF-β plays a role in a wide array of cellular processes including early embryonic development, cell growth, differentiation, motility, and apoptosis.
The Transforming Growth Factor beta (TGFβ) receptors are a family of serine/threonine kinase receptors involved in TGF beta signaling pathway. These receptors bind growth factor and cytokine signaling proteins in the TGF-beta family such as TGFβs, bone morphogenetic proteins (BMPs), growth differentiation factors (GDFs), activin and inhibin, myostatin, anti-Müllerian hormone (AMH), and NODAL.
References
- ↑ Rifkin DB (March 2005). "Latent transforming growth factor-beta (TGF-beta) binding proteins: orchestrators of TGF-beta availability". J. Biol. Chem. 280 (9): 7409–12. doi: 10.1074/jbc.R400029200 . PMID 15611103.
- ↑ Todorovic V, Jurukovski V, Chen Y, Fontana L, Dabovic B, Rifkin DB (January 2005). "Latent TGF-beta binding proteins". Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 37 (1): 38–41. doi:10.1016/j.biocel.2004.03.011. PMID 15381147.