Related Research Articles
The Greenback Party was an American political party with an anti-monopoly ideology which was active from 1874 to 1889. The party ran candidates in three presidential elections, in 1876, 1880 and 1884, before it faded away.

The 1936 United States House of Representatives elections were elections for the United States House of Representatives to elect members to serve in the 75th United States Congress. They were held for the most part on November 3, 1936, while Maine held theirs on September 14. They coincided with President Franklin D. Roosevelt's landslide re-election. Roosevelt's Democratic Party gained twelve net seats from the Republican Party, bringing them above a three-fourths majority. This was the largest majority since Reconstruction, as the last time a party won so decisively was in 1866. To date, this was the last time that any party held three-quarters of all House seats, as well as the last time that a party won more than 300 House seats.
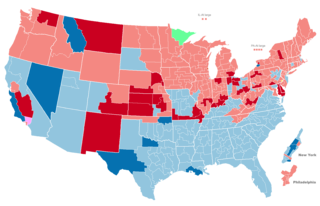
The 1918 United States House of Representatives elections were elections for the United States House of Representatives to elect members to serve in the 66th United States Congress. They were held for the most part on November 5, 1918, while Maine held theirs on September 9. They occurred in the middle of President Woodrow Wilson's second term.

1916 United States House of Representatives elections were elections for the United States House of Representatives to elect members to serve in the 65th United States Congress. They were held for the most part on November 7, 1916, while Maine held theirs on September 11. They coincided with the re-election of President Woodrow Wilson.

1914 United States House of Representatives elections were elections for the United States House of Representatives to elect members to serve in the 64th United States Congress. They were held for the most part on November 3, 1914, while Maine held theirs on September 14. They were held in the middle of President Woodrow Wilson's first term.
The 1910 United States House of Representatives elections were held for the most part on November 8, 1910, while Maine and Vermont held theirs early in September, in the middle of President William Howard Taft's term. Elections were held for all 391 seats of the United States House of Representatives, representing 46 states, to the 62nd United States Congress.

The 1892 United States House of Representatives elections were held for the most part on November 8, 1892, with Oregon, Maine, and Vermont holding theirs early in either June or September. They coincided with the election of Grover Cleveland as president for the second, non-continuous, time, defeating incumbent Benjamin Harrison. Elections were held for 356 seats of the United States House of Representatives, representing 44 states, to serve in the 53rd United States Congress. They were the first elections after reapportionment following the 1890 United States census, increasing the size of the House. Special elections were also held throughout the year.

The 1888 United States House of Representatives elections were held for the most part on November 6, 1888, with three states holding theirs early between June and September. They occurred at the same time as the election of President Benjamin Harrison. Elections were initially held for 325 seats of the United States House of Representatives, representing 38 states, to serve in the 51st United States Congress. Six new states would later join the union and increase the House to 332 seats. Special elections were also held throughout the year.
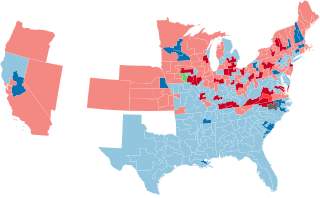
The 1886 United States House of Representatives elections were held for the most part on November 2, 1886, with three states holding theirs early between June and September. They occurred in the middle of President Grover Cleveland's first term. Elections were held for 325 seats of the United States House of Representatives, representing 38 states, to serve in the 50th United States Congress. Special elections were also held throughout the year.

The 1884 United States House of Representatives elections were held for the most part on November 4, 1884, with four states holding theirs early between June and October. They coincided with the election of President Grover Cleveland. Elections were held for 325 seats of the United States House of Representatives, representing 38 states, to serve in the 49th United States Congress. Special elections were also held throughout the year.

The 1882 United States House of Representatives elections were held for the most part on November 7, 1882, with five states holding theirs early between June and October. They occurred during President Chester A. Arthur's term. Elections were held for 325 seats of the United States House of Representatives, representing 38 states, to serve in the 48th United States Congress. They were the first elections after reapportionment following the 1880 United States census, increasing the size of the House. Special elections were also held throughout the year.

The 1878–79 United States House of Representatives elections were held on various dates in various states between June 3, 1878, and September 3, 1879. Each state set its own date for its elections to the House of Representatives before or after the first session of the 46th United States Congress convened on March 18, 1879. Elections were held for all 293 seats, representing 38 states. This was the last election cycle that at least one state held its regular congressional election in an odd-numbered year.
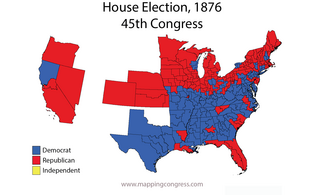
The 1876–77 United States House of Representatives elections were held on various dates in various states between June 5, 1876, and March 13, 1877. Each state set its own date for its elections to the House of Representatives before the first session of the 45th United States Congress convened on October 15, 1877. The size of the House increased to 293 seats with the addition of the new state of Colorado.

The 1858–59 United States House of Representatives elections were held on various dates in various states between June 7, 1858, and December 1, 1859. Each state set its own date for its elections to the House of Representatives. 238 representatives were elected in the new state of Oregon, the pending new state of Kansas, and the other 32 states before the first session of the 36th United States Congress convened on December 5, 1859. They were held during President James Buchanan's term.

The 1854–55 United States House of Representatives elections were held in 31 states for all 234 seats between August 4, 1854, and November 6, 1855, during President Franklin Pierce's term. Each state legislature separately set a date to elect representatives to the House of Representatives before the 34th Congress convened its first session on December 3, 1855.
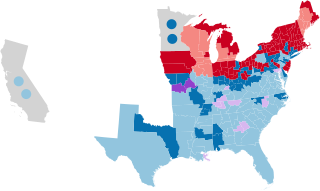
The 1856–57 United States House of Representatives elections were held on various dates in various states between August 4, 1856, and November 4, 1857. Each state set its own date for its elections to the House of Representatives. 236 representatives were elected in 31 states and the pending new state of Minnesota before the first session of the 35th United States Congress convened on December 7, 1857.

Henry Smith was a millwright, architect, builder and politician who was elected a member of the United States House of Representatives from Wisconsin from 1887 - 1889 as a member of the Union Labor Party. He also served as a Socialist member of the Wisconsin State Assembly in 1878. At different times, Smith ran for office on the Socialist, Greenback, Democratic and Union Labor tickets.
Labor Party was the name or partial name of a number of United States political parties which were organized during the 1870s and 1880s.

The 1880 Greenback Party National Convention convened in Chicago from June 9 to June 11 to select presidential and vice presidential nominees and write a party platform for the Greenback Party in the United States presidential election 1880. Delegates chose James B. Weaver of Iowa for President and Barzillai J. Chambers of Texas for Vice President.
References
- ↑ "Party Divisions of the House of Representatives* 1789–Present". Office of the Historian, United States House of Representatives. Retrieved August 17, 2015.
- 1 2 "Congress Profiles 88th Congress (1963–1965)". Office of the Historian, United States House of Representatives. Retrieved August 18, 2015.
- 1 2 "Congress Profiles 96th Congress (1979–1981)". Office of the Historian, United States House of Representatives. Retrieved August 18, 2015.
- 1 2 "Congress Profiles 99th Congress (1985–1987)". Office of the Historian, United States House of Representatives. Retrieved August 18, 2015.
- 1 2 "Congress Profiles 101st Congress (1989–1991)". Office of the Historian, United States House of Representatives. Retrieved August 18, 2015.
- 1 2 "Congress Profiles 104th Congress (1995–1997)". Office of the Historian, United States House of Representatives. Retrieved August 18, 2015.
- 1 2 "Congress Profiles 105th Congress (1997–1999)". Office of the Historian, United States House of Representatives. Retrieved August 18, 2015.
- 1 2 "Congress Profiles 107th Congress (2001–2003)". Office of the Historian, United States House of Representatives. Retrieved August 18, 2015.
- 1 2 "Congress Profiles 109th Congress (2005–2007)". Office of the Historian, United States House of Representatives. Retrieved August 18, 2015.