
Arabic is a Semitic language spoken primarily across the Arab world. Having emerged in the 1st century, it is named after the Arab people; the term "Arab" was initially used to describe those living in the Arabian Peninsula, as perceived by geographers from ancient Greece.
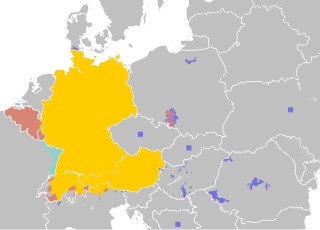
German, or more precisely High German, is a West Germanic language mainly spoken in Western Europe and Central Europe. It is the most widely spoken and official or co-official language in Germany, Austria, Switzerland, Liechtenstein, and the Italian province of South Tyrol. It is also an official language of Luxembourg and Belgium, as well as a recognized national language in Namibia. Outside Germany, it is also spoken by German communities in France (Alsace), Czech Republic, Poland, Slovakia, and Hungary (Sopron).
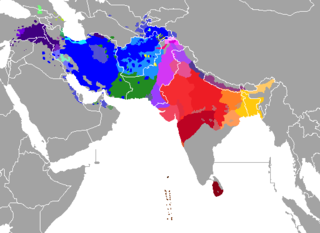
The Indo-Iranian languages constitute the largest and southeasternmost extant branch of the Indo-European language family. They include over 300 languages, spoken by around 1.5 billion speakers, predominantly in South Asia, West Asia and parts of Central Asia.

The Middle East is a geopolitical region encompassing the Arabian Peninsula, the Levant, Turkey, Egypt, Iran and Iraq. The term came into widespread usage as a replacement of the term Near East beginning in the early 20th century. The term "Middle East" has led to some confusion over its changing definitions, and being seen as too Eurocentric. The region includes the vast majority of the territories included in the closely associated definition of Western Asia, but without the South Caucasus, and additionally includes all of Egypt and all of Turkey.

Sign languages are languages that use the visual-manual modality to convey meaning, instead of spoken words. Sign languages are expressed through manual articulation in combination with non-manual markers. Sign languages are full-fledged natural languages with their own grammar and lexicon. Sign languages are not universal and are usually not mutually intelligible, although there are also similarities among different sign languages.

The United States does not have an official language at the federal level, but the most commonly used language is English, which is the de facto national language. It is also the language spoken at home by the great majority of the U.S. population. Many other languages are also spoken at home, especially Spanish, according to the American Community Survey (ACS) of the U.S. Census Bureau; these include indigenous languages originally spoken by Native Americans, Alaska Natives, Native Hawaiians, and peoples from the United States unincorporated territories, languages brought in different eras to the regions now comprising the U.S. by people from Europe, Africa, Asia, other parts of the Americas, and Oceania, as well as multiple dialects, creole languages, pidgin languages, and sign languages originating in what is now the U.S. Interlingua, an international auxiliary language, was created in the U.S.

Languages spoken in the Republic of India belong to several language families, the major ones being the Indo-Aryan languages spoken by 78.05% of Indians and the Dravidian languages spoken by 19.64% of Indians, both families together are sometimes known as Indic languages. Languages spoken by the remaining 2.31% of the population belong to the Austroasiatic, Sino–Tibetan, Tai–Kadai, and a few other minor language families and isolates. As per the People's Linguistic Survey of India, India has the second highest number of languages (780), after Papua New Guinea (840). Ethnologue lists a lower number of 456.

Japonic or Japanese–Ryukyuan, sometimes also Japanic, is a language family comprising Japanese, spoken in the main islands of Japan, and the Ryukyuan languages, spoken in the Ryukyu Islands. The family is universally accepted by linguists, and significant progress has been made in reconstructing the proto-language. The reconstruction implies a split between all dialects of Japanese and all Ryukyuan varieties, probably before the 7th century. The Hachijō language, spoken on the Izu Islands, is also included, but its position within the family is unclear.
Logba is a Kwa language spoken in the south-eastern Ghana by approximately 7,500 people. The Logba people call themselves and their language Ikpana, which means ‘defenders of truth’. Logba is different from Lukpa of Togo and Benin, which is also sometimes referred to as Logba.
The Sambalic languages are a part of the Central Luzon language family spoken by the Sambals, an ethnolinguistic group on the western coastal areas of Central Luzon and the Zambales mountain ranges.

Many languages are spoken, written and signed in Norway.
The Lambas are an ethnic and linguistic group of people living in the Kéran and Doufelgou Districts (Préfecture) of the Kara Region in Northern Togo and in the Atakora and Donga Departments of Bénin, West Africa. The capital of the Kéran District is Kanté and the capital of the Doufelgou District is Niamtougou.

The Logba people live in the Volta Region of Ghana, east of the Volta Lake in the mountains of the Ghana-Togo borderland. Most Logba towns and villages are situated along the trunk road from Accra to Hohoe. They include the following settlements: Wuinta, Akusame, Adiveme, Andokɔfe, Adzakoe, Alakpeti, Klikpo, and Tota. Tota is located high in the Ghana Togo Mountains to the east of the Accra-Hohoe road. Alakpeti is the commercial centre of Logba, while Klikpo is traditionally the seat of the head of the Logba people. The Logba people are primarily subsistence farmers, producing cassava, maize, yams and forest fruits, supplemented by cash crops like cocoa, coffee and sawn mahogany logs. The Logba area is known for its scenery, which includes waterfalls, cliffs, and limestone formations, including one or two known small caves with minor speleothems.
Moken is spoken by inhabitants in southern Myanmar and Southern Thailand, who refer to themselves as Moken (people) and Mawken.

Dutch, also known as Netherlandic or Netherlandish, is a West Germanic language spoken by about 25 million people as a first language and 5 million as a second language. It is the third most widely spoken Germanic language, after its close relatives German and English. Afrikaans is a separate but somewhat mutually intelligible daughter language spoken, to some degree, by at least 16 million people, mainly in South Africa and Namibia, evolving from the Cape Dutch dialects of Southern Africa. The dialects used in Belgium and in Suriname, meanwhile, are all guided by the Dutch Language Union.
Biguina is a community or village in the commune of Bassila in the Donga Department of northwestern Benin. It is located near the border with Togo and it sits on Benin's Route Nationale 3, one of the two main north-south highways in the country.
Betanure Jewish Neo-Aramaic, the local language variety of Betanure in Iraqi Kurdistan, is among the rarest and most seriously endangered varieties of Aramaic spoken at the present time. It is also one of the most conservative of both Jewish Neo-Aramaic languages and the Northeastern Neo-Aramaic languages in particular.
The Bima language, or Bimanese is an Austronesian language spoken on the eastern half of Sumbawa Island, Indonesia, which it shares with speakers of the Sumbawa language. Bima territory includes the Sanggar Peninsula, where the extinct Papuan language Tambora was once spoken. Bima is an exonym; the autochthonous name for the territory is Mbojo and the language is referred to as Nggahi Mbojo. There are over half a million Bima speakers. Neither the Bima nor the Sumbawa people have alphabets of their own for they use the alphabets of the Bugis and the Malay language indifferently.
Pahang Malay is a Malayic language spoken in the Malaysian state of Pahang. It is regarded as the dominant Malay dialect spoken along the vast riverine systems of Pahang, but co-exists with other Malay dialects traditionally spoken in the state. Along the coastline of Pahang, Terengganu Malay is spoken in a narrow strip of sometimes discontiguous fishing villages and towns. Another dialect spoken in Tioman island is a distinct Malay variant and most closely related to Riau Archipelago Malay subdialect spoken in Natuna and Anambas islands in the South China Sea, together forming a dialect continuum between the Bornean Malay and the Mainland Peninsular/Sumatran Malay.

The Bikol languages or Bicolano languages are a group of Central Philippine languages spoken mostly in the Bicol Peninsula in the island of Luzon, the neighboring island province of Catanduanes and the island of Burias in Masbate.











