
Mitchell Shire is a local government area in the Hume region of Victoria, Australia, located North of Melbourne. It covers an area of 2,862 square kilometres (1,105 sq mi) and, in April 2024, had a projected population of 61,362. Larger towns include Beveridge, Broadford, Kilmore, Seymour, Tallarook, Pyalong and Wallan. It was formed in 1994 from the amalgamation of the Shire of Pyalong, the Shire of Kilmore, most of the Shire of Broadford, and parts of the Shire of McIvor and Rural City of Seymour.

Calder Highway is a rural highway in Australia, linking Mildura and the Victoria/New South Wales border to Bendigo, in North Central Victoria. South of Bendigo, where the former highway has been upgraded to freeway-standard, Calder Freeway links to Melbourne, subsuming former alignments of Calder Highway; the Victorian Government completed the conversion to freeway standard from Melbourne to Bendigo on 20 April 2009.

Maroondah Highway is a major east–west thoroughfare in the eastern suburbs of Melbourne, and a highway connecting the north-eastern fringes of Melbourne to Mansfield, at the lower alpine region of Victoria, Australia.
Loddon Valley Highway runs roughly north-west from Bendigo to Kerang. It constitutes part of the direct route from Melbourne to the popular Murray River holiday areas around Swan Hill.

Sunraysia Highway is a 330 kilometres (205 mi) north–south rural highway in western Victoria, linking Ouyen to the north-western Ballarat suburb of Mitchell Park, and acts as a secondary route to Calder Highway, the main route between Melbourne and Mildura. It serves a number of important industries in the region such as agriculture, viticulture, food processing, winemaking and tourism. It forms an important link for these industries to markets and ports in the south of Victoria and South Australia.

Goulburn Valley Highway is a highway located in Victoria, Australia, linking Tocumwal on the Murray River through North Central Victoria to Eildon. The section north of the Hume Freeway is part of the Melbourne to Brisbane National Highway and is the main link between these two cities, as well as a major link between Victoria and inland New South Wales. It is also the most direct route between Melbourne and the major regional centre of Shepparton in Victoria.

Murray Valley Highway is a 663-kilometre (412 mi) rural highway located in Victoria, Australia, between Euston, New South Wales and Corryong, Victoria. The popular tourist route mostly follows the southern bank of the Murray River and effectively acts as the northernmost highway in Victoria. For all but the western end's last three kilometres, the highway is allocated route B400.
McIvor Highway is a short Victorian highway (44 km) linking Bendigo and Heathcote. Together with Hume Freeway and Northern Highway, it provides an alternative route between Melbourne and Bendigo. The name 'McIvor' refers to the original name of the Heathcote region, used during the Victorian gold rush.
Midland Highway is a major rural highway linking major towns in Victoria, beginning from Geelong and winding through country Victoria in a large arc through the cities of Ballarat, Bendigo and Shepparton, eventually reaching Mansfield at the foothills of the Victorian Alps.

Pyrenees Highway is a rural highway in western Victoria, Australia, linking Ararat to Elphinstone. It was named after the Pyrenees ranges, the set of low mountain ridges the road travels through.
The Tocumwal railway line is a 1,600 mm gauge railway line in Victoria, Australia. The line runs between the border town of Tocumwal in New South Wales to Southern Cross station in Melbourne. The line is used by various passenger and freight trains serving the northern suburbs of Melbourne and northern regions of Victoria.
The Deniliquin railway line is a broad-gauge railway line serving north-western Victoria, Australia. The line runs from the New South Wales town of Deniliquin into Bendigo, before turning south-south-east towards Melbourne, terminating in Docklands near the central business district. It is a major trunk line both for passenger and freight trains, with many lines branching off from it.

Burwood Highway is a major transportation link with Melbourne's eastern fringe at the foot of the Dandenong Ranges, linking the suburbs of Hawthorn and Belgrave. The highway is considered a major link for people who live in the Dandenong Ranges and acts as one of the major feeder roadway in the area along with Canterbury Road, Ferntree Gully Road, EastLink and Wellington Road.
Glenelg Highway is a rural highway in south-eastern Australia, linking the major regional centres of Mount Gambier in south-eastern South Australia with Ballarat in western Victoria.

Omeo Highway is a 163 kilometre rural highway in eastern Victoria, Australia, connecting Tallangatta on Lake Hume in north-east Victoria to Bairnsdale in East Gippsland, over parts of the Victorian Alps.

Henty Highway is a rural highway in western Victoria, Australia, linking Lascelles in the Wimmera region, to Portland on the state's soith-western coast. It was named in honour of Edward Henty, a British colonist regarded as the first permanent European settler of the Port Phillip District, in the town eventually named Portland.

Wimmera Highway is a 345 kilometre rural highway that runs predominately through the Wimmera region of western Victoria, after which the highway is named. It links the towns of Marong, Victoria, just to the west of the major regional centre of Bendigo in Victoria, and Naracoorte, in the south-eastern corner of South Australia.
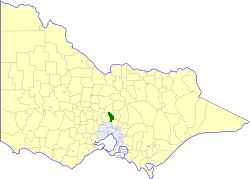
The Shire of Kilmore was a local government area about 60 kilometres (37 mi) north of Melbourne, the state capital of Victoria, Australia. The shire covered an area of 508.9 square kilometres (196.5 sq mi), and existed from 1856 until 1995.
The Heathcote railway line was a cross-country link between Bendigo and Heathcote Junction. It was partly opened in 1888 and, by 1890, it was fully operational. It was partially closed in 1958 and fully closed in 1968.
Plenty Road is a major urban arterial road through the north-eastern suburbs of Melbourne, Victoria, Australia, from the inner suburb of Preston to the township of Whittlesea, just outside the north-eastern suburban fringe of Melbourne.












