
Franklin County is a county along the Gulf of Mexico in the panhandle of the U.S. state of Florida. As of the 2020 census, the population was 12,451, making it the third-least populous county in Florida. The county seat is Apalachicola.

Liberty County is a county located in the state of Florida. As of the 2020 census, the population was 7,974, making it the least populous county in Florida. Its county seat is Bristol. Liberty County is one of only two dry counties in Florida.

Apalachicola is a city and the county seat of Franklin County, Florida, United States, on the shore of Apalachicola Bay, an inlet of the Gulf of Mexico. The population was 2,231 at the 2010 census.

The Chattahoochee River forms the southern half of the Alabama and Georgia border, as well as a portion of the Florida and Georgia border. It is a tributary of the Apalachicola River, a relatively short river formed by the confluence of the Chattahoochee and Flint rivers and emptying from Florida into Apalachicola Bay in the Gulf of Mexico. The Chattahoochee River is about 430 miles (690 km) long. The Chattahoochee, Flint, and Apalachicola rivers together make up the Apalachicola–Chattahoochee–Flint River Basin. The Chattahoochee makes up the largest part of the ACF's drainage basin.
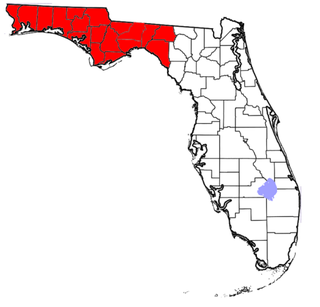
The Florida Panhandle is the northwestern part of the U.S. state of Florida. It is a salient roughly 200 miles long, bordered by Alabama on the north and the west, Georgia on the north, and the Gulf of Mexico to the south. Its eastern boundary is arbitrarily defined. It is defined by its southern culture and rural geography relative to the rest of Florida, as well as closer cultural links to French-influenced Louisiana, Mississippi, and Alabama. Its major communities include Pensacola, Navarre, Destin, Panama City Beach, and Tallahassee.

Prospect Bluff Historic Sites is located in Franklin County, Florida, on the Apalachicola River, 6 miles (9.7 km) SW of Sumatra, Florida. The site contains the ruins of two forts.

San Marcos de Apalache Historic State Park is a Florida State Park in Wakulla County, Florida organized around the historic site of a Spanish colonial fort, which was used by succeeding nations that controlled the area. The Spanish first built wooden buildings and a stockade in the late 17th and early 18th centuries here, which were destroyed by a hurricane.

The Cape St. George Light is a 72-foot (22 m) high brick lighthouse which had originally stood for 153 years on St. George Island, Florida, until toppling into the Gulf of Mexico October 22, 2005. The pieces of the lighthouse were retrieved, and in April 2008, the light's restoration was completed.

This is a list of properties and historic districts in Washington that are listed on the National Register of Historic Places. There are at least three listings in each of Washington's 39 counties.
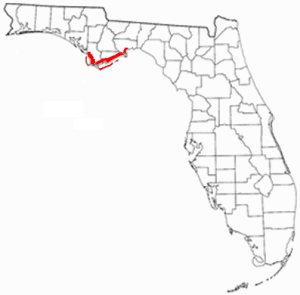
The Forgotten Coast refers to a largely untouched and uninhabited area of coastline in the panhandle of the US state of Florida. The term, also a trademark, was first used in 1992, but the Forgotten Coast's exact location is not agreed upon.

The Apalachicola Historic District is a U.S. historic district in Apalachicola, Florida. It is bounded by the Apalachicola River, Apalachicola Bay, 17th and Jefferson Streets, encompasses approximately 4600 acres (19 km2), and contains 652 historic buildings. On November 21, 1980, it was added to the U.S. National Register of Historic Places.
The Yent Mound (8FR5) is a Santa Rosa-Swift Creek culture archaeological site located on Alligator Harbor west of St. Teresa, Florida. It is on the east side of County Road 370, approximately 2.5 miles from the junction of U.S. Route 98. On May 24, 1973, it was added to the U.S. National Register of Historic Places.
The Cayson Mound and Village Site (8CA3) is a prehistoric archaeological site located near Blountstown, Florida. It is located three miles southeast of Blountstown, on the Apalachicola River. The site was occupied by peoples of the Fort Walton Culture. On March 15, 1976, it was added to the U.S. National Register of Historic Places.
The Otis Hare Archeological Site is a historic site near Bristol, Florida, at mile 73 on the east bank of the Apalachicola River. On July 26, 1989, it was added to the U.S. National Register of Historic Places.
The Yon Mound and Village Site (8LI2) is a prehistoric archaeological site located two miles west of Bristol, Florida on the east bank of the Apalachicola River. The site was occupied by peoples of the Fort Walton Culture. On December 15, 1978, it was added to the U.S. National Register of Historic Places as reference number 78000952.

The Thomas R. Pierce House is a historic house in Bushnell, Florida. It is locally significant as an outstanding example of vernacular architecture, and the only historic hotel or boarding house from this period remaining in Bushnell.

The David G. Raney House is a historic site in Apalachicola, Florida, United States, located at the southwest corner of Market Street and Avenue F. On September 22, 1972, it was added to the U.S. National Register of Historic Places.

Trinity Episcopal Church, originally known as Christ Church, is a historic house of worship in Apalachicola, Florida, United States, located at the corner of Avenue D and 6th Street. On June 30, 1972, it was added to the U.S. National Register of Historic Places.

The Big Bend of Florida, United States, is an informally-named geographic region of North Florida where the Florida Panhandle transitions to the Florida Peninsula south and east of Tallahassee. The region is known for its vast woodlands and marshlands and its low population density relative to much of the state. The area is home to the largest single spring in the United States, the Alapaha Rise, and the longest surveyed underwater cave in the United States, the 32-mile (51 km) Wakulla-Leon Sinks cave system.

Yuchi Town Site, or Yuchi Town, is a late prehistoric and historic era archaeological site showing occupation of both the Apalachicola and of Yuchi tribes. The site is located in a remote area of Fort Moore, Russell County, Alabama. The Yuchi Town Site is an example of historic Native American cultures adopting various strategies to maintain their cultural integrity in the face of European colonization and the expansion of the United States. It was declared a National Historic Landmark in 1996.



















