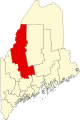
Somerset County is a county in the U.S. state of Maine, United States. As of the 2020 census, the population was 50,477. Its county seat is Skowhegan.

Brownville is a town in Piscataquis County, Maine, United States. The population was 1,139 at the 2020 census. The town includes the villages of Brownville, Knight's Landing and Brownville Junction, near which passes the 100-Mile Wilderness of the Appalachian Trail.

Jackman is a town in Somerset County, Maine, United States. The population was 783 at the 2020 census.
Vanceboro is a town in Washington County, Maine, United States. The town was named after landowner William Vance. The main village in town is located at the eastern terminus of Maine State Route 6. Vanceboro is across the St. Croix River from St. Croix, New Brunswick, Canada, to which it is connected by the Saint Croix–Vanceboro Bridge. Vanceboro is also connected to St. Croix by the Saint Croix–Vanceboro Railway Bridge, which is used by the New Brunswick Southern Railway.
Northeast Somerset is an unorganized territory in Somerset County, Maine, United States. The population was 367 at the 2020 census.

Millinocket is a town in Penobscot County, Maine, United States. The population was 4,114 at the 2020 census.

Olympic National Park is a national park of the United States located in Washington, on the Olympic Peninsula. The park has four regions: the Pacific coastline, alpine areas, the west-side temperate rainforest, and the forests of the drier east side. Within the park there are three distinct ecosystems, including subalpine forest and wildflower meadow, temperate forest, and the rugged Pacific coast.

Greenville is a town in Piscataquis County, Maine, United States. The population was 1,437 at the 2020 census. The town is centered on the lower end of Moosehead Lake, the largest body of fresh water in the state. Greenville is the historic gateway to the north country and a center for outdoor recreation in the area. Greenville High School, with 89 students, was ranked as the third best high school in Maine and one of the top 1,000 in the US in 2010.

Moosehead Lake is a deep, coldwater lake located in Piscataquis County in Northwestern Maine. It is the largest lake in Maine and the largest lake wholly within New England, the second-largest lake in New England after Lake Champlain, and the largest mountain lake in the eastern United States. Situated in the mostly undeveloped Longfellow Mountains, the lake is the source of the Kennebec River. Several rural Townships border the lake. Greenville is by far the largest town on the lake, with a small downtown area that has banks, shops, and restaurants. There are over 80 islands in the lake, the largest being Sugar Island and Deer Island to the west being the second largest.

The International Railway of Maine was a historic railroad constructed by the Canadian Pacific Railway (CPR) between Lac-Mégantic, Quebec, and Mattawamkeag, Maine, closing a key gap in the railway's transcontinental main line to the port of Saint John, New Brunswick.
The Northern Forest Canoe Trail (NFCT) is a 740-mile (1,190 km) marked canoeing trail in the northeastern United States and Canada, extending from Old Forge in the Adirondacks of New York to Fort Kent, Maine. Along the way, the trail also passes through the states and provinces of Vermont, Quebec, and New Hampshire. The trail was opened on June 3, 2006.

The Belfast & Moosehead Lake Railroad was a standard-gauge shortline railroad that operated from 1871 to 2007 over a single-track grade from Belfast to Burnham Junction in Maine.

The Moose River is an 83-mile-long (134 km) river in Maine. Its source is in Beattie, on the Canada–United States border, which runs along the height of land between the watersheds of the Kennebec River in Maine and the Chaudière River in Quebec. From there, the river runs east through Attean Pond and Wood Pond, past the town of Moose River, then through Long Pond and Brassua Lake. The Moose River empties into Moosehead Lake, the source of the Kennebec River, in Rockwood Strip. The International Railway of Maine was built along Moose River in 1889.

The West Branch Penobscot River is a 117-mile-long (188 km) tributary of the Penobscot River through the North Maine Woods in Maine. The river is also known as Abocadneticook, Kahgognamock, and Kettegwewick.

The Somerset Railroad was built to serve Kennebec River communities and later extended through timberlands to a large wooden Victorian era destination hotel on Moosehead Lake. The railway became part of the Maine Central Railroad in 1911; and a portion remained in intermittent operation by Pan Am Railways until 2013.

Harris Station Dam is a hydroelectric dam in Northeast Somerset, Somerset County, Maine. Also known as the Indian Pond Project, the dam was built from 1952 to 1954 as the largest hydroelectric dam in the state of Maine. It impounds the Kennebec River at the southern end of the natural Indian Pond, about 12 miles (19 km) downstream from Moosehead Lake.

The Maine Central Railroad Company main line extended from Portland, Maine, east to the Canada–US border with New Brunswick at the Saint Croix–Vanceboro Railway Bridge. It is the transportation artery linking Maine cities to the national railway network. Sections of the main line had been built by predecessor railroads consolidated as the Maine Central in 1862 and extended to the Canada–US border in 1882. Through the early 20th century, the main line was double track from South Portland to Royal Junction, where it split into a lower road through Brunswick and Augusta and a back road through Lewiston which converged at Waterville into single track to Bangor and points east. Westbound trains typically used the lower road with lighter grades, while eastbound trains of empty cars used the back road. This historical description does not include changes following purchase of the Maine Central Railroad by Guilford Transportation Industries in 1981 and subsequent operation as part of Pan Am Railways.

Fairfield is a town in Somerset County, Maine, United States. The population was 6,484 at the 2020 census. The town includes Fairfield Center, Fairfield village and Hinckley, and borders the city of Waterville to the south. It is home to the Good Will-Hinckley School, Lawrence High School and Kennebec Valley Community College.

Pittston Farm is a historic farm and community complex in a remote part of northern Somerset County, Maine. Located down logging roads about 20 miles (32 km) north of the village of Rockwood, the farm was developed c. 1910 by the Great Northern Paper Company to provide food and other resources to workers on logging drives in Maine's northern forests. It is believed to be the best preserved of the few such facilities established, and was listed on the National Register of Historic Places in 2000. Its surviving buildings are currently operated as a tourist establishment.
Clayton Lake is an unincorporated village in Aroostook County, Maine, United States. The community is located within the Northwest Aroostook unorganized territory, specifically T11 R14, on the north shore of its eponymous lake within the North Maine Woods in southwestern Aroostook County.