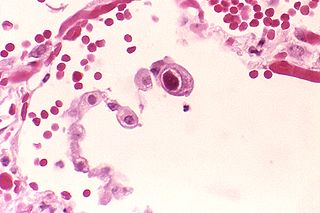
Cytomegalovirus (CMV) is a genus of viruses in the order Herpesvirales, in the family Herpesviridae, in the subfamily Betaherpesvirinae. Humans and other primates serve as natural hosts. The 11 species in this genus include human betaherpesvirus 5, which is the species that infects humans. Diseases associated with HHV-5 include mononucleosis and pneumonia, and congenital CMV in infants can lead to deafness and ambulatory problems.
Classical swine fever (CSF) or hog cholera is a highly contagious disease of swine. It has been mentioned as a potential bioweapon.
Aviadenoviruses are adenoviruses that affect birds—particularly chickens, ducks, geese, turkeys and pheasants. There are 15 species in this genus. Viruses in this genus cause specific disease syndromes such as Quail Bronchitis (QB), Egg Drop Syndrome (EDS), Haemorrhagic Enteritis (HE), Pheasant Marble Spleen Disease (MSD), and Inclusion Body Hepatitis (IBH). Avian adenoviruses have a worldwide distribution and it is common to find multiple species on a single farm. The most common serogroups are serogroup 1, 2 and 3.
Aujeszky's disease, usually called pseudorabies in the United States, is a viral disease in swine that is endemic in most parts of the world. It is caused by Suid herpesvirus 1 (SuHV-1). Aujeszky's disease is considered to be the most economically important viral disease of swine in areas where classical swine fever has been eradicated. Other mammals, such as cattle, sheep, goats, cats, dogs, and raccoons, are also susceptible. The disease is usually fatal in these animal species.
Equid alphaherpesvirus 4, formerly Equine herpesvirus 4 (EHV-4) is a virus of the family Herpesviridae that cause rhinopneumonitis in horses. It is the most important viral cause of respiratory infection in foals. Like other herpes viruses, EHV-4 causes a lifelong latent infection in affected animals. These horses are usually the source for new infection for foals over two months old, weanlings, and yearlings. Symptoms include fever, loss of appetite, and discharge from the nose. Most infected animals recover in one to three weeks, but death can occur in environments with overcrowding and other stress factors. There are several vaccines available.
Equid alphaherpesvirus 1, formerly Equine herpesvirus 1 (EHV-1), is a virus of the family Herpesviridae that causes abortion, respiratory disease and occasionally neonatal mortality in horses. Initial spread of EHV-1 by a newly introduced horse through direct and indirect contact can lead to abortion and perinatal infection in up to 70 percent of a previously unexposed herd. Abortion usually occurs in the last four months of gestation, two to four weeks after infection of the mare. Perinatal infection can lead to pneumonia and death. Encephalitis can occur in affected animals, leading to ataxia, paralysis, and death. There is a vaccine available, however its efficacy is questionable. The virus varies in severity from sub-clinical to very severe. Most horses have been infected with EHV-1, but the virus can become latent and persist without ever causing signs of infection. In 2006, an outbreak of EHV-1 among stables in Florida resulted in the institution of quarantine measures. The outbreak was determined to have originated in horses imported from Europe via New York, before being shipped to Florida.

Feline viral rhinotracheitis (FVR) is an upper respiratory or pulmonary infection of cats caused by Felid alphaherpesvirus 1 (FeHV-1), of the family Herpesviridae. It is also commonly referred to as feline influenza, feline coryza, and feline pneumonia but, as these terms describe other very distinct collections of respiratory symptoms, they are misnomers for the condition. Viral respiratory diseases in cats can be serious, especially in catteries and kennels. Causing one-half of the respiratory diseases in cats, FVR is the most important of these diseases and is found worldwide. The other important cause of feline respiratory disease is feline calicivirus.

Duck plague is a worldwide disease caused by Anatid alphaherpesvirus 1 (AnHV-1) of the family Herpesviridae that causes acute disease with high mortality rates in flocks of ducks, geese, and swans. It is spread both vertically and horizontally—through contaminated water and direct contact. Migratory waterfowl are a major factor in the spread of this disease as they are often asymptomatic carriers of disease. The incubation period is three to seven days. Birds as young as one week old can be infected. DEV is not zoonotic.
Bovine gammaherpesvirus 4 (BoHV-4) is a member of the Herpesviridae family. It is part of the subfamily Gammaherpesvirinae and genus Rhadinovirus. Infection is normally sub-clinical but can cause reproductive disease in cattle such as endometritis, vulvovaginitis and mastitis. Transmission is both vertical and horizontal. It can also be indirectly spread by fomites. Distribution is worldwide and the virus infects a range of ruminants, including bison, buffalo, sheep and goats.

Cardiovirus A is a member of the Picornaviridae family. Infection with the virus causes encephalomyocarditis and reproductive disease in pigs. Although a variety of mammals may host the virus, pigs are classed as the domestic host as they are most easily infected. It is thought to be spread by rodents.
Porcine adenovirus is a virus in the family Adenoviridae. It causes mild gastrointestinal diseases in pigs and is thought to contribute to multifactorial porcine respiratory diseases complexes. Several strains of the virus can be found worldwide, and transmission occurs horizontally by the fecal-oral route.
Porcine intestinal spirochaetosis is a notifiable pig disease caused by certain spirochetal bacteria (Brachyspira hyodysenteriae and Brachyspira pilosicoli. Infection causes mild gastrointestinal signs in young pigs and can also be transmitted as intestinal spirochetosis in humans, as it is a zoonosis.

Actinobacillus suis is a beta-haemolytic, Gram-negative bacterium of the family Pasteurellaceae. The bacterium has many strains and is the pathogen responsible for actinobacillosis in pigs of all ages. It can also infect wild birds, domestic ruminants, dogs, cats, and horses. The organism can be found in the respiratory tract and tonsils of both infected and healthy pigs that act as carriers. Transmission is via the respiratory tract and piglets are usually infected early on in life. Herds with a high health status are more at risk and outbreaks can be explosive.
Blue eye disease is caused by La Piedad Michoacán Mexico virus (LPMV), the only member virus of the species Porcine orthorubulavirus in the Paramyxoviridae family. Synonyms for the disease include "Blue Eye Syndrome" and "Porcine Paramyxovirus Blue Eye Disease", and "La Piedad Michoacán Paramyxovirus Infection".
Porcine epidemic diarrhea is a condition caused by the porcine epidemic diarrhea virus that leads to severe gastrointestinal disease in pigs.
Proboscivirus is a genus of viruses in the order Herpesvirales, in the family Herpesviridae, in the subfamily Betaherpesvirinae. Elephants serve as natural hosts. EEHV1 is apathogenic for African elephants but causes fatal haemorrhagic disease in Asian elephants. The name "Proboscivirus" comes from the Greek word προβοσκίς or "proboscis" meaning "the elephant trunk," for which the virus accordingly uses as its means of contraction and transmission to enter the elephant's body.
Macavirus is a genus of viruses in the order Herpesvirales, in the family Herpesviridae, in the subfamily Gammaherpesvirinae. Mammals serve as natural hosts. There are nine species in this genus. Diseases associated with this genus include: inapparent infection in their reservoir hosts, but fatal lymphoproliferative disease when they infect MCF-susceptible hosts, including cattle, deer, bison, water buffalo and pigs.
Ictalurid herpesvirus 1 (IcHV-1) is a species of virus in the genus Ictalurivirus, family Alloherpesviridae, and order Herpesvirales. It causes disease in channel catfish and blue catfish, and can cause significant economic loss in catfish farms. The disease is endemic in the USA and there are reports of the virus in Honduras and Russia.
Human betaherpesvirus 6A (HHV-6A) is a species of virus in the genus Roseolovirus, subfamily Betaherpesvirinae, family Herpesviridae, and order Herpesvirales.
Human betaherpesvirus 6B (HHV-6B) is a species of virus in the genus Roseolovirus, subfamily Betaherpesvirinae, family Herpesviridae, and order Herpesvirales.





