
Australosuchus is an extinct monospecific genus of crocodylian belonging to the subfamily Mekosuchinae. The type and only known species Australosuchus clarkae lived during the Late Oligocene and the Early Miocene in the Lake Eyre Basin of South Australia. It was described in 1991 by Paul Willis and Ralph Molnar from fossil material discovered at Lake Palankarinna.

Toyotamaphimeia is a genus of extinct gavialid crocodylian which lived in Japan and Taiwan during the Middle Pleistocene. A specimen recovered in 1964 at Osaka University during the construction of a new science building has been dated to around 430–380 thousand years old based on the stratum in which it was found. Toyotamaphimeia was a fairly large crocodylian measuring approximately 6.3–7.3 metres (21–24 ft) long. Two species are named, T. machikanensis from Japan and T. taiwanicus from Taiwan, both originally described as members of the genus Tomistoma.

Harpacochampsa is a poorly known Early Miocene crocodilian from the Bullock Creek lagerstätte of the Northern Territory, Australia. The current specimen consists of a partial skull and fragments of a long, slender snout reminiscent of that of a false gharial, demonstrating that it was a piscivore in life.

Langstonia is an extinct genus of notosuchian crocodylomorph of the family Sebecidae. It lived in the middle Miocene, in the "Monkey Beds" of the Colombian Villavieja Formation. Langstonia was named in 2007 by Alfredo Paolillo and Omar Linares for fossils originally described by Langston in 1965 as Sebecus huilensis. Thus, the type species is L. huilensis.
Eogavialis is an extinct genus of eusuchian crocodylomorph, usually regarded as a gavialoid crocodylian. It superficially resembles Tomistoma schlegelii, the extant false gharial, and consequently material from the genus was originally referred to Tomistoma. Indeed, it was not until 1982 that the name Eogavialis was constructed after it was realised that the specimens were from a more basal form.

Eothoracosaurus is an extinct monospecific genus of eusuchian crocodylomorphs found in Eastern United States which existed during the Late Cretaceous period. Eothoracosaurus is considered to belong to an informally named clade called the "thoracosaurs", named after the closely related Thoracosaurus. Thoracosaurs in general were traditionally thought to be related to the modern false gharial, largely because the nasal bones contact the premaxillae, but phylogenetic work starting in the 1990s instead supported affinities within gavialoid exclusive of such forms. Even more recent phylogenetic studies suggest that thoracosaurs might instead be non-crocodilian eusuchians.
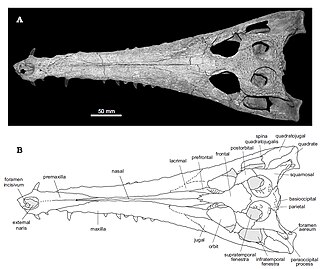
Eosuchus is an extinct genus of eusuchian crocodylomorph, traditionally regarded as a gavialoid crocodilian. It might have been among the most basal of all gavialoids, lying crownward of all other known members of the superfamily, including earlier putative members such as Thoracosaurus and Eothoracosaurus. Fossils have been found from France as well as eastern North America in Maryland, Virginia, and New Jersey. The strata from which specimens have been found date back to the late Paleocene and early Eocene epochs.

Euthecodon is an extinct genus of long-snouted crocodile. It was common throughout much of Africa during the Neogene, with fossils being especially common in Kenya, Ethiopia, and Libya. Although superficially resembling that of gharials, the long snout was a trait developed independently from that of other crocodilians and suggests a diet of primarily fish. Euthecodon coexisted with a wide range of other crocodiles in the areas it inhabited before eventually going extinct during the Pleistocene.

Gryposuchus is an extinct genus of gavialid crocodilian. Fossils have been found from Argentina, Colombia, Venezuela, Brazil and the Peruvian Amazon. The genus existed during the Miocene epoch. One recently described species, G. croizati, grew to an estimated length of 10 metres (33 ft). Gryposuchus is the type genus of the subfamily Gryposuchinae, although a 2018 study indicates that Gryposuchinae and Gryposuchus might be paraphyletic and rather an evolutionary grade towards the gharial.

Piscogavialis is an extinct monospecific genus of gryposuchine gavialid crocodylian. The only species yet known is P. jugaliperforatus. Fossils of Piscogavialis have been found from the Mio-Pliocene Pisco Formation of the Sacaco Basin in southern Peru in 1998, where it coexisted with the much smaller gavialid Sacacosuchus.
Siquisiquesuchus is an extinct genus of gavialid crocodilian. It is known from cranial remains and a few postcranial bones found in Miocene-age rocks of the Castillo Formation in northwestern Venezuela.
Gryposuchinae is an extinct subfamily of gavialid crocodylians. Gryposuchines lived mainly in the Miocene of South America. However, "Ikanogavialis" papuensis may have survived more recently, into the Late Pleistocene/Holocene. Most were long-snouted coastal forms. The group was named in 2007 and includes genera such as Gryposuchus and Aktiogavialis, although a 2018 study indicates that the group might be paraphyletic and rather an evolutionary grade towards the gharial.

Crocodylus checchiai is an extinct species of crocodile from the Miocene to Pliocene of Libya and Kenya. C. checchiai was named in 1947 based on a skull from the Sahabi Formation. Remains from the lower Nawata Formation in the Turkana Basin of Kenya that were first attributed to the Nile crocodile have now been reassigned to C. checchiai, extending its geographic range. The morphology of the species, in particular the pronounced rostral boss, indicates that it may be the connecting link between African and American species of the genus Crocodylus.

Caiman wannlangstoni is an extinct species of caiman that lived in what is now the Amazon Basin and surrounding areas during the Middle and Late Miocene. Fossils of C. wannlangstoni have been found in the Pebas Formation near Iquitos in Peru and include partial skulls and isolated skull bones. Other fossils were uncovered from the Urumaco Formation in Venezuela and the Laventan Honda Group of Colombia. The species was first described in 2015. Features that in combination distinguish C. wannlangstoni from other caimans include a deep snout, a wavy upper jaw margin, a large and upward-directed narial opening, and blunt teeth at the back of the jaws. Based on the sizes of the skulls, its estimated body length is about 211 to 227 centimetres.

Gnatusuchus is an extinct genus of caiman represented by the type species Gnatusuchus pebasensis from the Middle Miocene Pebas Formation of Peru. Gnatusuchus lived about 13 million years ago (Ma) in a large wetland system called the Pebas mega-wetlands that covered over one million square kilometers of what is now the Amazon Basin.

Astorgosuchus is an extinct monospecific genus of crocodilian, closely related to true crocodiles, that lived in Pakistan during the late Oligocene period. This crocodile may have reached lengths of up to 7–8 m (23–26 ft) and is known to have preyed on many of the large mammals found in its environment. Bite marks of a large crocodile have been found on the bones of juvenile Paraceratherium, however if these were left by Astorgosuchus cannot be said with certainty. The genus contains a single species, Astorgosuchus bugtiensis, which was originally named as a species of Crocodylus in 1908 and was moved to its own genus in 2019.
Caiman brevirostris is an extinct species of caiman that lived during the Late Miocene, around 11.6 million years ago, to the end of the Miocene 5.3 million years ago in Acre and Amazonas, Brazil as well as Urumaco, Venezuela. Several specimens have been referred to the species, but only 3 of them are confidently placed in the species. C. brevirostris was originally named in 1987 on the basis of a single, incomplete rostrum with an associated mandibular ramus that had been found in Acre, Brazil. C. brevirostris is very distinct among Caiman species and caimaninae overall in that it preserves a characteristically short and robust skull that bears blunt posterior teeth that were built to break down harder foods. This was an adaption for durophagy, likely to crush shells of mollusks and clams which were common in the wetlands that C. brevirostris resided in.

Ultrastenos is an extinct genus of Australian mekosuchine crocodilian that lived during the Late Oligocene in northwestern Queensland, Australia. Following its discovery, it was speculated that Ultrastenos was a slender-snouted animal similar to modern gharials or freshwater crocodiles due to the seemingly abruptly narrowing mandible. However, a later study found that this was a missinterpretation of the fossil specimen and that Ultrastenos instead had a more generalized lower jaw. The same publication also provided evidence that the fossils of Ultrastenos belonged to the same animal previously named "Baru" huberi, adding further evidence to the idea that the animal was short snouted, contrary to the initial hypothesis. Given that "Baru" huberi was named first, the type species of Ultrastenos changed from U. willisi to U. huberi in accordance with the rules of the ICZN. Ultrastenos was a small mekosuchine, measuring upwards of 1.5 m long.

Kyhytysuka is an extinct genus of ophthalmosaurian ichthyosaur from Early Cretaceous Colombia. The animal was previously assigned to the genus Platypterygius, but given its own genus in 2021. Kyhytysuka was a mid-sized ophthalmosaurian with heterodont dentition and several adaptations suggesting that it was a macropredatory vertebrate hunter living in shallow waters. It contains a single species, Kyhytysuka sachicarum.
Eardasaurus is a genus of thalassophonean pliosaurid from the middle Jurassic Oxford Clay Formation. The animal would have measured over 4.7 m (15 ft) long and possessed a high amount of teeth relative to other pliosaurs. Its teeth show distinct ridges formed by the tooth enamel, some of which are very pronounced and similar to carinae, giving the teeth a cutting edge.


















