
Gavialinae is a subfamily of large semiaquatic crocodilian reptiles, resembling crocodiles, but with much thinner snouts. Gavialinae is one of the two major subfamilies within the family Gavialidae - the other being the subfamily Tomistominae, which contains the false gharial and extinct relatives.

Gavialosuchus is an extinct genus of gavialoid crocodylian from the early Miocene of Europe. Currently only one species is recognized, as a few other species of Gavialosuchus have since been reclassified to other genera.
Ocepesuchus is an extinct genus of gavialoid crocodilian, related to modern gharials. Ocepesuchus is the oldest known crocodilian of Africa, and is known only from a single species, O. eoafricanus. It lived in Morocco during the late Maastrichtian age of the Late Cretaceous.

Harpacochampsa is a poorly known Early Miocene crocodilian from the Bullock Creek lagerstätte of the Northern Territory, Australia. The current specimen consists of a partial skull and fragments of a long, slender snout reminiscent of that of a false gharial, demonstrating that it was a piscivore in life.
Dollosuchoides, colloquially known as the Crocodile of Maransart, is an extinct monospecific genus of gavialoid crocodilian, traditionally regarded as a member of the subfamily Tomistominae. Fossils have been found in the Brussel Formation of Maransart, Belgium and date back to the middle Eocene.

Eogavialis is an extinct genus of eusuchian crocodylomorph, usually regarded as a gavialoid crocodylian. It superficially resembles Tomistoma schlegelii, the extant false gharial, and consequently material from the genus was originally referred to Tomistoma. Indeed, it was not until 1982 that the name Eogavialis was constructed after it was realised that the specimens were from a more basal form.

Eothoracosaurus is an extinct monospecific genus of eusuchian crocodylomorphs found in Eastern United States which existed during the Late Cretaceous period. Eothoracosaurus is considered to belong to an informally named clade called the "thoracosaurs", named after the closely related Thoracosaurus. Thoracosaurs in general were traditionally thought to be related to the modern false gharial, largely because the nasal bones contact the premaxillae, but phylogenetic work starting in the 1990s instead supported affinities within gavialoid exclusive of such forms. Even more recent phylogenetic studies suggest that thoracosaurs might instead be non-crocodilian eusuchians.
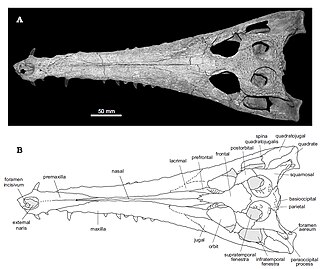
Eosuchus is an extinct genus of eusuchian crocodylomorph, traditionally regarded as a gavialoid crocodilian. It might have been among the most basal of all gavialoids, lying crownward of all other known members of the superfamily, including earlier putative members such as Thoracosaurus and Eothoracosaurus. Fossils have been found from France as well as eastern North America in Maryland, Virginia, and New Jersey. The strata from which specimens have been found date back to the late Paleocene and early Eocene epochs.

Gryposuchus is an extinct genus of gavialid crocodilian. Fossils have been found from Argentina, Colombia, Venezuela, Brazil and the Peruvian Amazon. The genus existed during the Miocene epoch. One recently described species, G. croizati, grew to an estimated length of 10 metres (33 ft). Gryposuchus is the type genus of the subfamily Gryposuchinae, although a 2018 study indicates that Gryposuchinae and Gryposuchus might be paraphyletic and rather an evolutionary grade towards the gharial.
Ikanogavialis is an extinct genus of gavialid crocodilian. Fossils have been found in the Urumaco Formation in Urumaco, Venezuela and the Solimões Formation of Brazil. The strata from which remains are found are late Miocene in age, rather than Pliocene as was once thought. A possible member of this genus survived into the Late Holocene on Muyua or Woodlark Island in Papua New Guinea.
Maroccosuchus zennaroi is an extinct gavialoid crocodylian from the Early Eocene of Morocco, traditionally regarded as a member of the subfamily Tomistominae.
Paratomistoma is an extinct monospecific genus of gavialoid crocodylian. It is based on the holotype specimen CGM 42188, a partial posterior skull and lower jaw discovered at Wadi Hitan, Egypt, in Middle Eocene-age rocks of the Gehannam Formation. The skull is unfused but considered morphologically mature. Paratomistoma was named in 2000 by Christopher Brochu and Philip Gingerich; the type species is P. courti in honor of Nicholas Court, who found CGM 42188. They performed a phylogenetic analysis and found Paratomistoma to be a derived member of Tomistominae, related to the false gharial. It may have been a marine or coastal crocodilian.

Piscogavialis is an extinct monospecific genus of gryposuchine gavialid crocodylian. The only species yet known is P. jugaliperforatus. Fossils of Piscogavialis have been found from the Mio-Pliocene Pisco Formation of the Sacaco Basin in southern Peru in 1998, where it coexisted with the much smaller gavialid Sacacosuchus.
Siquisiquesuchus is an extinct genus of gavialid crocodilian. It is known from cranial remains and a few postcranial bones found in Miocene-age rocks of the Castillo Formation in northwestern Venezuela.

Thecachampsa is an extinct genus of gavialoid crocodylian, traditionally regarded as a member of the subfamily Tomistominae. Fossils have been found from the eastern United States in deposits of Miocene age. Those named in the 19th century were distinguished primarily by the shape of their teeth, and have since been combined with T. antiquus. More recently erected species were reassigned from other genera, although their assignment to Thecachampsa has since been questioned.
Gryposuchinae is an extinct subfamily of gavialid crocodylians. Gryposuchines lived mainly in the Miocene of South America. However, "Ikanogavialis" papuensis may have survived more recently, into the Late Pleistocene/Holocene. Most were long-snouted coastal forms. The group was named in 2007 and includes genera such as Gryposuchus and Aktiogavialis, although a 2018 study indicates that the group might be paraphyletic and rather an evolutionary grade towards the gharial.

Gavialoidea is one of three superfamilies of crocodylians, the other two being Alligatoroidea and Crocodyloidea. Although many extinct species are known, only the gharial Gavialis gangeticus and the false gharial Tomistoma schlegelii are alive today, with Hanyusuchus having become extinct in the last few centuries.

Tomistominae is a subfamily of crocodylians that includes one living species, the false gharial. Many more extinct species are known, extending the range of the subfamily back to the Eocene epoch. In contrast to the false gharial, which is a freshwater species that lives only in southeast Asia, extinct tomistomines had a global distribution and lived in estuaries and along coastlines.
The San Sebastián Formation is a geologic formation in Puerto Rico. It preserves fossils dating back to the Oligocene period.
Sacacosuchus is an extinct monospecific genus of marine gavialid that lived along the coast of the south-east Pacific from approximately 19 to 6.3 million years ago. Its fossils have been found in the Chilcatay and Pisco Formations of Peru, where it coexisted with the much larger Piscogavialis. Based on its skull, Sacacosuchus was most likely a generalist feeder with an estimated total body length of 4.32 m (14.2 ft). Its extinction is thought to have been caused by a combination of factors including falling sea levels and global cooling.














