
Tarbosaurus is a genus of large tyrannosaurid dinosaur that lived in Asia during the Late Cretaceous epoch, about 70 million years ago. It contains the single type species: Tarbosaurus bataar, which is known from the Nemegt Formation of Mongolia, with more fragmentary remains found further afield in the Subashi Formation of China. Tarbosaurus is represented by dozens of fossil specimens, including several complete skulls and skeletons. These remains have allowed studies focusing on its phylogeny, skull mechanics, and brain structure. Further fossil remains have been reported from other geologic formations of Asia, however, these remains are fragmentary and can not be confidentially assigned to Tarbosaurus or the type species.

Sarcosuchus is an extinct genus of crocodyliform and distant relative of living crocodilians that lived during the Early Cretaceous, from the late Hauterivian to the early Albian, 133 to 112 million years ago of what is now Africa and South America. The genus name comes from the Greek σάρξ (sarx) meaning flesh and σοῦχος (souchus) meaning crocodile. It was one of the largest pseudosuchians, with the largest specimen of S. imperator reaching approximately 9–9.5 metres (29.5–31.2 ft) long and weighing up to 3.45–4.3 metric tons. It is known from two species; S. imperator from the early Albian Elrhaz Formation of Niger, and S. hartti from the Late Hauterivian of northeastern Brazil. Other material is known from Morocco and Tunisia and possibly Libya and Mali.

Alectrosaurus is a genus of tyrannosauroid theropod dinosaur that lived in Asia during the Late Cretaceous period, about some 96 million years ago in what is now the Iren Dabasu Formation.

Bagaceratops is a genus of small protoceratopsid dinosaurs that lived in Asia during the Late Cretaceous, around 72 to 71 million years ago. Bagaceratops remains have been reported from the Barun Goyot Formation and Bayan Mandahu Formation. One specimen may argue the possible presence of Bagaceratops in the Djadochta Formation.

The Bayan Shireh Formation is a geological formation in Mongolia, that dates to the Cretaceous period. It was first described and established by Vasiliev et al. 1959.
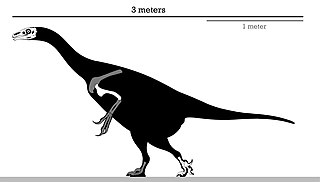
Erlikosaurus is a genus of therizinosaurid that lived in Asia during the Late Cretaceous period. The fossils, a skull and some post-cranial fragments, were found in the Bayan Shireh Formation of Mongolia in 1972, dating to around 96 million and 89 million years ago. These remains were later described by Altangerel Perle and Rinchen Barsbold in 1980, naming the new genus and species Erlikosaurus andrewsi. It represents the second therizinosaur taxon from this formation with the most complete skull among members of this peculiar family of dinosaurs.

Gobipteryx is a genus of prehistoric bird from the Campanian Age of the Late Cretaceous Period. It is not known to have any direct descendants. Like the rest of the enantiornithes clade, Gobipteryx is thought to have gone extinct near the end of the Cretaceous.

Shamosuchus is an extinct genus of neosuchian crocodyliform that lived during the Late Cretaceous (Campanian) period in what is now the Djadokhta Formation of Mongolia, approximately 75 million to 71 million years ago.

The Djadochta formation is a highly fossiliferous geological formation in Central Asia, Gobi Desert, dating from the Late Cretaceous period, about 75 million to 71 million years ago. The type locality is the Bayn Dzak locality, famously known as the Flaming Cliffs. Reptile and mammal remains are among the fossils recovered from the formation.

Charles Whitney Gilmore was an American paleontologist who gained renown in the early 20th century for his work on vertebrate fossils during his career at the United States National Museum. Gilmore named many dinosaurs in North America and Mongolia, including the Cretaceous sauropod Alamosaurus, Alectrosaurus, Archaeornithomimus, Bactrosaurus, Brachyceratops, Chirostenotes, Mongolosaurus, Parrosaurus, Pinacosaurus, Styracosaurus ovatus and Thescelosaurus.

Borealosuchus is an extinct genus of crocodyliforms that lived from the Late Cretaceous to the Eocene in North America. It was named by Christopher Brochu in 1997 for several species that had been assigned to Leidyosuchus. The species assigned to it are: B. sternbergii, the type species, from the Maastrichtian of Colorado, Montana, North Dakota, South Dakota, and Wyoming; B. acutidentatus, from the Paleocene of Saskatchewan; B. formidabilis, from the Paleocene of North Dakota; B. griffithi, from the Paleocene of Alberta; and B. wilsoni, from the Eocene of Wyoming. B. formidabilis is particularly well-known, represented by the remains of many individuals from the Wannagan Creek site in North Dakota. An indeterminate species is known from the Late Cretaceous Demopolis Chalk in Alabama.

Didymictis is an extinct genus of placental mammals from extinct subfamily Didymictinae within extinct family Viverravidae, that lived in North America and Europe from the late Paleocene to middle Eocene.
Gobiderma is an extinct genus of Late Cretaceous lizard whose fossils are known from the Gobi Desert in southern Mongolia. It was first discovered as a result of a joint Polish-Mongolian Paleontological Expedition, and formally named in 1984. In life, it probably resembled lizards of the genus Heloderma to a large degree, though its skull was more elongated than lizards of that genus.
The Ulan Malgait Formation is a Late Jurassic geologic formation in Mongolia. Dinosaur remains are among the fossils that have been recovered from the formation, although as of 2004 none have yet been referred to a specific genus.

Tchoiria () is a genus of neochoristoderan reptile from the Early Cretaceous of Mongolia. The name Tchoiria comes from the city of Choir which is nearby to where the holotype was found. Tchoiria is thought to have a similar diet to another neochoristoderan reptile, Champsosaurus, due to morphology of the skull. It would hunt in freshwater environments, like the living gharials, where it would prey on many different types of fish and turtles.
Wulatelong is an extinct genus of basal oviraptorid dinosaur known from the Late Cretaceous Wulansuhai Formation of Bayan Mandahu, Linhe District of Inner Mongolia, northern China. It contains a single species, Wulatelong gobiensis.

Coryphodontidae is an extinct family of pantodont mammals known from the Late Paleocene to the Middle Eocene of Eurasia and North America.
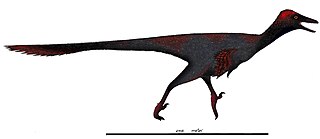
Gobivenator is an extinct genus of troodontid theropod dinosaur known from the late Campanian Djadokhta Formation of central Gobi Desert, Mongolia. It contains a single species, Gobivenator mongoliensis. G. mongoliensis is known from a single individual, which represents the most complete specimen of a Late Cretaceous troodontid currently known.
Phrynosomimus is an extinct genus of iguanian lizard from the Late Cretaceous of Mongolia belonging to the extinct family Priscagamidae. The type species Phrynosomimus asper was named in 1996. Fossils have been found in the Barun Goyot and Djadochta formations and include several complete skulls. Phrynosomimus has a short, triangular skull with bony spikes projecting from the back, stemming from the squamosal and parietal bones. These spikes give it a similar appearance to the modern horned lizard Phrynosoma and inspire its name, which means "Phrynosoma mimic." Like other priscagamids it has an acrodont dentition, meaning that its teeth grow from the margins of the jaws rather than their inner surfaces, as is the case for the pleurodont dentitions of most lizards.

Gobioolithus is an oogenus of fossil bird egg native to Mongolia. They are small, smooth-shelled, and elongated eggs that were first discovered in the 1960s and early 70s during a series of fossil-hunting expeditions in the Gobi Desert. Two oospecies have been described: Gobioolithus minor and G. major. The eggs were probably laid in colonial nesting sites on the banks of rivers and lakes.


















