
The history of the Falkland Islands goes back at least five hundred years, with active exploration and colonisation only taking place in the 18th century. Nonetheless, the Falkland Islands have been a matter of controversy, as they have been claimed by the French, British, Spaniards and Argentines at various points.

The Falkland Islands are located in the South Atlantic Ocean between 51°S and 53°S on a projection of the Patagonian Shelf, part of the South American continental shelf. In ancient geological time this shelf was part of Gondwana, and around 400 million years ago split from what is now Africa and drifted westwards from it. Today the islands are subjected to the Roaring Forties, winds that shape both their geography and climate.
The economy of the Falkland Islands, which first involved sealing, whaling and provisioning ships, became heavily dependent on sheep farming from the 1870s to 1980. It then diversified and now has income from tourism, commercial fishing, and servicing the fishing industry as well as agriculture. The Falkland Islands use the Falkland pound, which is backed by the British pound.

Stanley is the capital city of the Falkland Islands. It is located on the island of East Falkland, on a north-facing slope in one of the wettest parts of the islands. At the 2016 census, the city had a population of 2,460. The entire population of the Falkland Islands was 3,398 on Census Day on 9 October 2016.

The Falkland Islands wolf, also known as the warrah and occasionally as the Falkland Islands dog, Falkland Islands fox, warrah fox, or Antarctic wolf, was the only native land mammal of the Falkland Islands. This endemic canid became extinct in 1876, the first known canid to have become extinct in historical times.

West Falkland is the second largest of the Falkland Islands in the South Atlantic. It is a hilly island, separated from East Falkland by the Falkland Sound. Its area is 4,532 square kilometres, 37% of the total area of the islands. Its coastline is 1,258.7 kilometres long.

East Falkland is the largest island of the Falklands in the South Atlantic, having an area of 6,605 km2 or 54% of the total area of the Falklands. The island consists of two main land masses, of which the more southerly is known as Lafonia; it is joined by a narrow isthmus where the settlement of Goose Green is located, and it was the scene of the Battle of Goose Green during the Falklands War.

Weddell Island is one of the Falkland Islands in the South Atlantic, lying off the southwest extremity of West Falkland. It is situated 1,545 km (960 mi) west-northwest of South Georgia Island, 1,165 km (724 mi) north of Livingston Island, 606 km (377 mi) northeast of Cape Horn, 358 km (222 mi) northeast of Isla de los Estados, and 510 km (320 mi) east of the Atlantic entrance to Magellan Strait.

Lively Island is the largest of the Lively Island Group of the Falkland Islands, The island group lies east of East Falkland. Lively Island is the largest rat-free island in the Falklands, hence its importance to birdlife. The island also has a sheep farm.

Carcass Island is the largest of the West Point Island Group of the Falkland Islands.

Saunders Island is the fourth largest of the Falkland Islands, lying north west of West Falkland. The island is run as a sheep farm.
Keppel Island is one of the Falkland Islands, lying between Saunders and Pebble islands, and near Golding Island to the north of West Falkland on Keppel Sound. It has an area of 3,626 hectares and its highest point, Mt. Keppel, is 341 metres (1,119 ft) high. There is a wide, flat valley in the centre of the island with several freshwater lakes. The central valley rises steeply to the south-west, west and north. The north-east is low-lying, with a deeply indented coastline.

The Jason Islands are an archipelago in the Falkland Islands, lying to the far north-west of West Falkland. Three of the islands, Steeple Jason, Grand Jason and Clarke's Islet, are private nature reserves owned by the Wildlife Conservation Society of New York City. Other islands in the group are National Nature Reserves owned by the Falkland Islands Government.

West Point Island is one of the Falkland Islands, lying in the north-west corner of the archipelago. It has an area of 1,469 hectares (5.67 sq mi) and boasts some of the most spectacular coastal scenery in the Falklands. The island is owned by Roddy & Lily Napier and run as a sheep farm and tourist attraction.
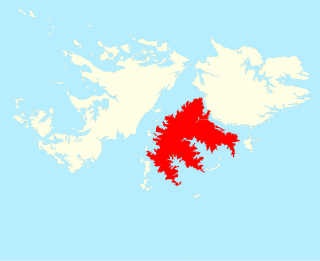
Lafonia is a peninsula forming the southern part of East Falkland, the largest of the Falkland Islands.

The Camp is the term used in the Falkland Islands to refer to any part of the islands outside the islands' only significant town, Stanley, and often the large RAF base at Mount Pleasant. It is derived from the Spanish word campo, for "countryside".

The Falkland Islands is an archipelago in the South Atlantic Ocean on the Patagonian Shelf. The principal islands are about 300 mi (480 km) east of South America's southern Patagonian coast and about 752 mi (1,210 km) from Cape Dubouzet at the northern tip of the Antarctic Peninsula, at a latitude of about 52°S. The archipelago, with an area of 4,700 sq mi (12,000 km2), comprises East Falkland, West Falkland, and 776 smaller islands. As a British overseas territory, the Falklands have internal self-governance, but the United Kingdom takes responsibility for their defence and foreign affairs. The capital and largest settlement is Stanley on East Falkland.
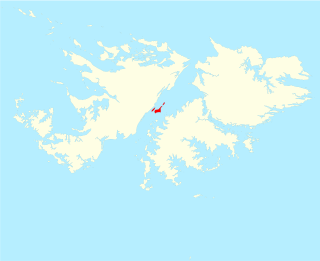
The Swan Islands are a small group of islands in the middle of Falkland Sound in the Falkland Islands, and comprising Swan Island and the smaller West Swan Island and North Swan Island.
Hummock Island is the largest of a group of islands in King George Bay in the Falkland Islands. It has a land area of 3.03 square kilometres (1.17 sq mi) and is about 4.0 miles (6.4 km) long in a north-west to south-east direction. Hummock Island is off the western coast of West Falkland, in a bay that leads to the estuary of the Chartres River. The highest point on the island is in the north-east and is 190 metres (620 ft). There are cliffs which often reach over 60 metres (200 ft) high.
Dunbar Island is part of the West Point Island Group of the Falkland Islands. It is near West Falkland, to its north, in Byron Sound. It is east of Carcass Island and Low Island and to the west of Saunders Island. It is south of Sedge Island and north of the Byron Heights and Storm Mountain.
















