
Shanghai is a direct-administered municipality and the most populous urban area in China. The city is located on the Chinese shoreline on the southern estuary of the Yangtze River, with the Huangpu River flowing through it. The population of the city proper is the third largest in the world, with around 24.87 million inhabitants in 2023, while the urban area is the most populous in China, with 29.87 million residents. As of 2022, the Greater Shanghai metropolitan area was estimated to produce a gross metropolitan product (nominal) of nearly 13 trillion RMB. Shanghai is one of the world's major centers for finance, business and economics, research, science and technology, manufacturing, transportation, tourism, and culture. The Port of Shanghai is the world's busiest container port.

Yangpu is one of the 16 districts of Shanghai. It is located in the northeastern part of downtown Shanghai, bordering the Huangpu River on the east and south, Hongkou on the west, and Baoshan on the north. The southern part of Yangpu District is 4 km (2.5 mi) away from The Bund, a major tourist attraction. It is predominantly composed of residential communities, with a total area of 60.61 km2 (23.40 sq mi) and a population of 1,242,548 as of 2020. The district administers 12 subdistricts.
The China Academy of Art is one of the most prestigious top colleges of fine arts in China, and is the first national comprehensive institution of higher art education in modern China. It is recognized as the country's First-Class Discipline Construction University.

Dulwich College Shanghai Pudong (上海德威外籍人员子女学校) is a private secondary school and a school for children of foreign personnels, located in Pudong, Shanghai, China. The campus was opened in 2003, and is owned and operated by Education in Motion, a British company.
The Shanghai University of Science and Technology was a public university from 1958 to 1994 in Shanghai, China. It merged with Shanghai University of Technology, former Shanghai University, and the Shanghai Institute of Science and Technology to establish the current Shanghai University in May 1994.

Jing'an Temple is the name of an interchange station between Lines 2, 7 and 14 of the Shanghai Metro. This station is located in Jing'an District, below the historic Jing'an Temple and the Jiu Guang shopping mall. It is part of the initial section of Line 2 that opened from Zhongshan Park to Longyang Road that opened on 20 September 1999; the interchange with line 7 opened on 5 December 2009 as part of that line's initial section between Shanghai University and Huamu Road and the interchange with line 14 opened on 30 December 2021.

The Ministry of Industry and Information Technology (MIIT) is the sixth-ranked executive department of the State Council of the People's Republic of China. It is responsible for regulation and development of the postal service, Internet, wireless, broadcasting, communications, production of electronic and information goods, software industry and the promotion of the national knowledge economy.
Libraries in China have existed since the Shang dynasty. Since early in China's history, scholars have kept extensive private libraries, and imperial dynasties have constructed archives to house literary treasures and official records. The first modern libraries in China appeared in the late 19th century, and grew slowly and sporadically until encouraged through a combination of acts and government funding in the 20th century after the founding of the People's Republic of China. Notable libraries in China today include the National Library of China, the Shanghai Municipal Library, and Peking University Library.

Line 18 is a north–south Shanghai Metro line running from South Changjiang Road station in the city's Baoshan District to Hangtou station in Pudong, with a length of 36.13 km (22.45 mi). The line was originally scheduled to open by the end of 2020. However, officials announced that only the initial segment of eight stations in Pudong started test runs in September 2020. The 14.5 km (9.0 mi) southern section opened for passenger operations on December 26, 2020. The remainder of the line was opened on 30 December 2021. The line is 36.5 km (22.7 mi) long with 26 stations. The line is one of Shanghai Metro's new batch of high capacity fully automated and driverless lines along with Lines 14 and 15. The line is colored tan on system maps.

China Art Museum, Shanghai is a municipal art museum of Shanghai City. It is a public welfare institution funded by the Shanghai City Culture and Tourism Bureau.

The Power Station of Art is a municipal contemporary art museum in Huangpu, Shanghai, China. The museum is a public institution that is funded by the Shanghai City Culture and Tourism Bureau.

The Shanghai Japanese School (SJS) is a Japanese international school serving primary and junior high school levels in Shanghai. It has two campuses, one in Hongqiao and one in Pudong. The school's teachers are Japanese citizens. The school also has a senior high school component.
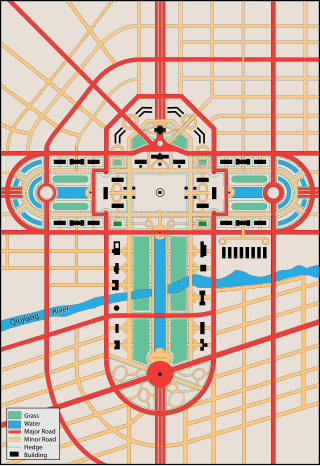
The Greater Shanghai Plan was a 1927 plan for the city of Shanghai, China, drawn up by the Nationalist Government of the Republic of China in Nanjing. It was presented at the 123rd meeting of the Shanghai City Government in July 1929 and as one of its provisions allocated 7,000 mu in the modern day Jiangwan Subdistrict of Shanghai's Yangpu District for the construction of a government headquarters and administration centre. Had it been completed, the government headquarters building would have stood close to the junction of today's Hengren Road (恒仁路) and the Qingyuan Ring Road (清源环路).

Shanghai Dianji University is a public municipal higher educational institution in Shanghai, China.

South Pudong Road is a station that is part of Line 2 and Line 14 of the Shanghai Metro. The station opened as Dongchang Road on Line 2 on September 20, 1999, and as South Pudong Road on Line 14 on December 30, 2021. Both station names were combined as one on September 21, 2024. The section between this station and Pudong Avenue is the shortest section on Line 14.

TMSR-LF1 is a 2 MWt molten salt reactor (MSR) pilot plant located in northwest China.

Shanghai Rail Transit includes all rail transit lines operating in Shanghai, mainly composed of High-volume railway system, Low-to-medium-volume railway system and Maglev system. The system was established on May 28, 1993, when Shanghai Metro Line 1 opened.

Chinese Academy of Cultural Heritage, 中国文化遗产研究院, The Chinese Academy of Cultural Heritage is an organization dedicated to the protection, preservation, and restoration of cultural heritage. It operates under the direct leadership of the State Administration of Cultural Heritage of China. The Chinese Academy of Cultural Heritage is a scientific research organization in the People's Republic of China that focuses on cultural heritage protection. It is one of the leading professional forces in the country in this field.

The Taizhou City Library, also known as Taizhou Library (台州图书馆), abbreviated as Tai Tu (台图), is a municipal-level public library located in Taizhou, Zhejiang, People's Republic of China. It is supervised by the Taizhou Municipal Bureau of Culture, Radio, Television, Tourism, and Sports, and is an affiliated unit of the latter. The library building is situated at 168 Hexie Road, Jiaojiang (Taizhou). As of 2019, the total collection of documents in the library reached 876,774 volumes, making it a nationally recognized first-grade library evaluated by the Ministry of Culture and Tourism.

The tomb of Soong Ching-ling is the mausoleum of Soong Ching-ling, the last wife of the founding father of the Republic of China, Sun Yat-sen, and the honorary chairman of the People's Republic of China. It is located next to the tomb of Soong Ching-ling's parents in the Soong Ching-ling Mausoleum in Changning district, Shanghai. The tomb of Soong Ching-ling was completed in 1981 and was declared a national major cultural relic protection unit by the State Council on February 23, 1982.


















