
Victoria Island is a large island in the Arctic Archipelago that straddles the boundary between Nunavut and the Northwest Territories of Canada. It is the eighth largest island in the world, and at 217,291 km2 (83,897 sq mi) in area, it is Canada's second largest island. It is nearly double the size of Newfoundland (111,390 km2 [43,008 sq mi]), and is slightly larger than the island of Great Britain (209,331 km2 [80,823 sq mi]) but smaller than Honshu (225,800 km2 [87,182 sq mi]). It contains the world's largest island within an island within an island. The western third of the island lies in the Inuvik Region of the Northwest Territories; the remainder is part of Nunavut's Kitikmeot Region.

The Arctic Archipelago, also known as the Canadian Arctic Archipelago, is an archipelago lying to the north of the Canadian continental mainland, excluding Greenland.

John Rae was a Scottish surgeon who explored parts of northern Canada.

In the Canadian Arctic Archipelago, Somerset Island is a large, uninhabited island separated by the 2 km (1.2 mi) wide Bellot Strait from the Boothia Peninsula in the Qikiqtaaluk Region of Nunavut, Canada, lying between Peel Sound and Prince Regent Inlet. It has an area of 24,786 km2 (9,570 sq mi), making it the 46th largest island in the world and Canada's twelfth largest island.

King William Island is an island in the Kitikmeot Region of Nunavut, which is part of the Arctic Archipelago. In area it is between 12,516 km2 (4,832 sq mi) and 13,111 km2 (5,062 sq mi) making it the 61st-largest island in the world and Canada's 15th-largest island. Its population, as of the 2016 census, was 1,279, all of whom live in the island's only community, Gjoa Haven.

Melville Peninsula is a large peninsula in the Canadian Arctic north of Hudson Bay. To the east is Foxe Basin and to the west the Gulf of Boothia. To the north the Fury and Hecla Strait separates it from Baffin Island. To the south Repulse Bay and Frozen Strait separate it from Southampton Island at the north end of Hudson Bay. On the southwest it is connected to the mainland by the "Rae Isthmus" named after arctic explorer Dr John Rae.
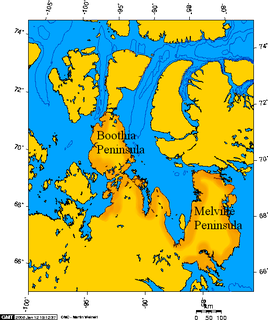
Boothia Peninsula is a large peninsula in Nunavut's northern Canadian Arctic, south of Somerset Island. The northern part, Murchison Promontory, is the northernmost point of mainland Canada.

Wales Island is one of the uninhabited Canadian arctic islands in the Qikiqtaaluk Region of Nunavut. Located 1.5 kilometres off the Melville Peninsula, the island is situated in Committee Bay within western Gulf of Boothia. It has an area of 1,137 square kilometres.

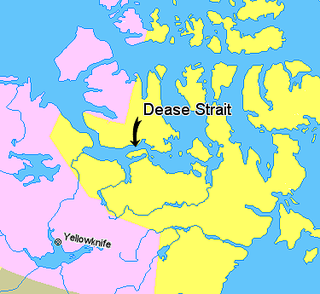
Coronation Gulf lies between Victoria Island and mainland Nunavut in Canada. To the northwest it connects with Dolphin and Union Strait and thence the Beaufort Sea and Arctic Ocean; to the northeast it connects with Dease Strait and thence Queen Maud Gulf.

The Gulf of Boothia is a body of water in Nunavut, Canada. Administratively it is divided between the Kitikmeot Region on the west and the Qikiqtaaluk Region on the east. It merges north into Prince Regent Inlet, the two forming a single bay with different names for its parts. It is surrounded by, clockwise, Baffin Island, Fury and Hecla Strait, the Melville Peninsula, the Canadian mainland, the Boothia Peninsula and perhaps Bellot Strait if the Gulf can be said to extend that far north. The south end is Committee Bay, northwest of which are the Simpson Peninsula and Pelly Bay. In addition to its connection to Prince Regent Inlet one can use an icebreaker to go east through the Fury and Hecla Strait, or, with luck, pass the Bellot Strait westward.

Prince Regent Inlet is a body of water in Nunavut, Canada between the west end of Baffin Island and Somerset Island on the west. It opens north into Lancaster Sound and to the south merges into the Gulf of Boothia. The Arctic inlet's northern portion is approximately 40 mi (64 km) wide; the southern portion is approximately 65 mi (105 km) wide. It is deep throughout and there are no islands within the inlet.

Pelly Bay is an Arctic waterway in Kitikmeot Region, Nunavut, Canada. It is located in the Gulf of Boothia. To the east, it is bounded by the Simpson Peninsula. Helen Island lies in the bay. Pelly Bay is named after Sir John Pelly, governor of the Hudson's Bay Company, that managed the British colony of Rupert's Land, that Pelly Bay was located within when it was named.
Rae Strait is a small strait in the Kitikmeot Region of Nunavut, Canada. It is located between King William Island and the Boothia Peninsula on the mainland to the east. It is named after Scottish Arctic explorer John Rae who, in 1854, was the first European to visit the area while mapping the northern coast of North America.

The Tennent Islands are an uninhabited Canadian Arctic island group in the Kitikmeot Region, Nunavut. The islands are located in Rae Strait between the Clarence Islands and Beverly Islands. Thomson Point on King William Island lies 3.5 km (2.2 mi) away, across the Humboldt Channel. Matty Island lies 3.7 km (2.3 mi) to the east, separated by the Wellington Strait. Boothia Peninsula's Oscar Bay is to the northeast.
The Simpson Strait is a natural, shallow waterway separating King William Island to the north from Adelaide Peninsula on Nunavut's mainland to the south. The strait, an arm of the Arctic Ocean, connects the Queen Maud Gulf with Rasmussen Basin's Rae Strait.
Kiillinnguyaq, formerly the Kent Peninsula, is a large Arctic peninsula, almost totally surrounded by water, in the Kitikmeot Region of Nunavut. Were it not for a 5 mi (8.0 km) isthmus at the southeast corner it would be a long island parallel to the coast. From the isthmus it extends 105 mi (169 km) westward into the Coronation Gulf. To the south, Melville Sound separates it from the mainland. To the north is Dease Strait and then Victoria Island. To the west is Coronation Gulf and to the east, Queen Maud Gulf. Cape Flinders marks the western tip of the peninsula, Cape Franklin is at the northwestern point, and Hiiqtinniq, formerly Cape Alexander marks the northeastern point.
Berlinguet Inlet is a body of water within the Qikiqtaaluk Region of Nunavut, Canada. It runs west–east at Admiralty Inlet's southern end, separated from Berlinguet Bay, which opens into the Gulf of Boothia, by a 1.5 km (0.93 mi) isthmus. Baffin Island's Brodeur Peninsula is to the north.

Committee Bay is an Arctic waterway in Kitikmeot Region, Nunavut, Canada. It forms the southeast end of the Gulf of Boothia and is bounded on the east by the Melville Peninsula, and to the northwest by the Simpson Peninsula. Wales Island lies within the bay. It was first explored by John Rae (explorer) in 1846/47.

Lord Mayor Bay is an Arctic waterway in Kitikmeot Region, Nunavut, Canada. It is located in the west of the Gulf of Boothia.
The Rae–Richardson Arctic expedition of 1848 was an early British effort to determine the fate of the lost Franklin Polar Expedition. Led overland by Sir John Richardson and John Rae, the team explored the accessible areas along Franklin's proposed route near the Mackenzie and Coppermine rivers.














