
Victoria Island is a large island in the Canadian Arctic Archipelago that straddles the boundary between Nunavut and the Northwest Territories of Canada. It is the eighth largest island in the world, and at 217,291 km2 (83,897 sq mi) in area, it is Canada's second largest island. It is nearly double the size of Newfoundland (111,390 km2 [43,008 sq mi]), and is slightly larger than the island of Great Britain (209,331 km2 [80,823 sq mi]) but smaller than Honshu (225,800 km2 [87,182 sq mi]). It contains the world's largest island within an island within an island. The western third of the island belongs to the Inuvik Region in the Northwest Territories; the remainder is part of Nunavut's Kitikmeot Region.

The Gulf of Saint Lawrence is the outlet of the North American Great Lakes via the Saint Lawrence River into the Atlantic Ocean. The gulf is a semienclosed sea, covering an area of about 226,000 square kilometres (87,000 sq mi) and containing about 34,500 cubic kilometres (8,300 cu mi) of water, which results in an average depth of 152 metres (499 ft).

The Arctic Archipelago, also known as the Canadian Arctic Archipelago, is a group of islands north of the Canadian mainland.

Palmer Land is the portion of the Antarctic Peninsula, Antarctica that lies south of a line joining Cape Jeremy and Cape Agassiz. This application of Palmer Land is consistent with the 1964 agreement between US-ACAN and UK-APC, in which the name Antarctic Peninsula was approved for the major peninsula of Antarctica, and the names Graham Land and Palmer Land for the northern and southern portions, respectively. The line dividing them is roughly 69 degrees south.

The Wordie Ice Shelf was a confluent glacier projecting as an ice shelf into the SE part of Marguerite Bay between Cape Berteaux and Mount Edgell, along the western coast of Antarctic Peninsula.

Coronation Gulf lies between Victoria Island and mainland Nunavut in Canada. To the northwest it connects with Dolphin and Union Strait and thence the Beaufort Sea and Arctic Ocean; to the northeast it connects with Dease Strait and thence Queen Maud Gulf.

James Ross Strait, an arm of the Arctic Ocean, is a channel between King William Island and the Boothia Peninsula in the Canadian territory of Nunavut. 180 km (110 mi) long, and 48 km (30 mi) to 64 km (40 mi) wide, it connects M'Clintock Channel to the Rae Strait to the south. Islands in the channel include the Clarence Islands, Tennent Islands, Beverley Island, and Matty Island.
Bjerkø Peninsula is a broad ice-covered peninsula of Antarctica, forming the west shore of MacKenzie Bay. Norwegian whalers explored this area in January and February 1931, naming the cape at the end of this peninsula for gunner Reidar Bjerkø of the whale catcher Bouvet II, from whose deck the coast was sketched on January 19. Since Sir Douglas Mawson probably saw this cape from a great distance as early as December 26, 1929, the Australian name of Cape Darnley has been retained for the cape, while the Norwegian name has been applied to the peninsula.
Chantrey Inlet (Tariunnuaq) is a bay on the Arctic coast of Canada. It marks the southeast "corner" where the generally east–west coast turns sharply north. To the west is the Adelaide Peninsula and to the east is mainland. King William Island shelters it to the northwest. If King William Island were not an island then Chantry Inlet, Rae Strait, Wellington Strait and James Ross Strait would be a single large bay. To the west the Simpson Strait separates King William Island from the Adelaide Peninsula. Its mouth is marked by Point Ogle on the west and Cape Britannia on the east. West of Point Ogle is Barrow Bay, Starvation Cove and Point Richardson. The Back River enters from the south. Near its mouth is a weather station on the Hayes River. Montreal Island is contained within the Inlet. It is 100 mi (160 km) long and 50 mi (80 km) wide at its mouth.

The headland of Cape St. Mary's is located at the southern tip of the south-western arm of the Avalon Peninsula of the island of Newfoundland in the Canadian province of Newfoundland and Labrador.

The Franklin Strait is an Arctic waterway in Northern Canada's territory of Nunavut. It is located between southeastern Prince of Wales Island and the Boothia Peninsula.
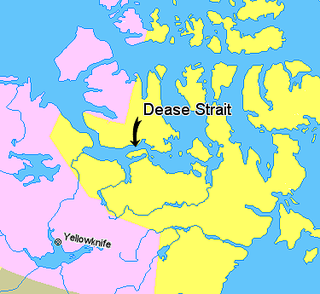
The Kent Peninsula is a large peninsula, almost totally surrounded by water, in Nunavut's northern Canadian Arctic mainland. Were it not for a 5-mile isthmus at the southeast corner it would be a long island parallel to the coast. From the isthmus it extends 105 mi (169 km) westward into the Coronation Gulf. To the south, Melville Sound separates it from the mainland. To the north is Dease Strait and then Victoria Island. To the west is Coronation Gulf and to the east, Queen Maud Gulf. Cape Flinders marks the western tip of the peninsula, Cape Franklin is at the northwestern point, and Cape Alexander marks the northeastern point.
The Henry Kater Peninsula is a peninsula on northern Baffin Island, in Nunavut, Canada. It protrudes in an eastern direction into Davis Strait. It's bounded to the north by Arctic Harbour. Further north lies Clyde Inlet. Home Bay borders the peninsula to the south.
The Wollaston Peninsula is a west-pointing peninsula located on southwestern Victoria Island, Canada. It is bordered by Prince Albert Sound to the north, Amundsen Gulf to the west and Dolphin and Union Strait to the south. Most of the peninsula lies in Nunavut's Kitikmeot Region but a smaller portion lies within the Northwest Territories's Inuvik Region. The peninsula is 225 km (140 mi) long, and between 97 and 113 km wide. Its westernmost point is Cape Baring.

The Banks Peninsula is located on the mainland of Canada's Nunavut territory. There are no communities on the peninsula, though the hamlet of Bathurst Inlet is located close-by, to the south, across the waterway of Bathurst Inlet. The peninsula has an irregular coastline, including a portion bounded by Arctic Sound. Point Wollaston is the northern most geographic feature.
Rymer Point is a cape in the Canadian Arctic territory of Nunavut. It is located on southwestern Victoria Island's Wollaston Peninsula, facing the Dolphin and Union Strait. Clouston Bay is situated along the north shoreline. Nuvuk Point is on the southwest side, jutting into Simpson Bay.
Cape Hewitt is a peninsula on eastern Baffin Island, Qikiqtaaluk Region, Nunavut, Canada. Located on Baffin Bay near Clyde Inlet, the closest settlement is Clyde River, 39.6 kilometres (24.6 mi) away.
Cape Aston is a large peninsula on eastern Baffin Island, Qikiqtaaluk Region, Nunavut, Canada. Located on Baffin Bay just south of Clyde Inlet, the closest settlement is Clyde River. The cape includes an ice-derived delta.

Jeremiah's Gutter was a canal located on the border of Orleans and Eastham, Massachusetts, the first canal to cut across the peninsula of Cape Cod. It connected Cape Cod Bay in the west to the Atlantic Ocean in the east. It was active for over 100 years, although it gradually fell out of use and was replaced by the Cape Cod Canal.
Wordie Bay is a bay which lies between Cape Berteaux and Mount Guernsey, to the west of the Wordie Ice Shelf, on the Fallières Coast of the Antarctic Peninsula. It was named by the UK Antarctic Place-names Committee in 1999 in association with the Wordie Ice Shelf.
















