
Victoria Island is a large island in the Canadian Arctic Archipelago that straddles the boundary between Nunavut and the Northwest Territories of Canada. It is the eighth largest island in the world, and at 217,291 km2 (83,897 sq mi) in area, it is Canada's second largest island. It is nearly double the size of Newfoundland (111,390 km2 [43,008 sq mi]), and is slightly larger than the island of Great Britain (209,331 km2 [80,823 sq mi]) but smaller than Honshu (225,800 km2 [87,182 sq mi]). It contains the world's largest island within an island within an island. The western third of the island belongs to the Inuvik Region in the Northwest Territories; the remainder is part of Nunavut's Kitikmeot Region.

Arcadia Lakes is a small town in Richland County, South Carolina, United States. The population was 861 at the 2010 census. It is part of the Columbia, South Carolina, Metropolitan Statistical Area.
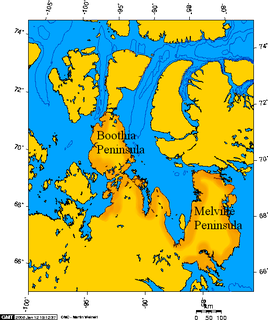
Boothia Peninsula is a large peninsula in Nunavut's northern Canadian Arctic, south of Somerset Island. The northern part, Murchison Promontory, is the northernmost point of mainland Canada.

Rivière-Ouelle is a town located in the Kamouraska Regional County Municipality within the Bas-Saint-Laurent region of Quebec. It is located on the Saint Lawrence River; the Ouelle River flows through the town. It was part of the seignory of La Bouteillerie, once owned by Charles Deschamps de Boishébert et de Raffetot. Jean-Charles Chapais, a Father of Canadian Confederation, was born here.

Northeast Glacier is a steep, heavily crevassed glacier on the west side of Hemimont Plateau, 21 km (13 mi) long and 8 km (5 mi) wide at its mouth, which flows from McLeod Hill westward and then south-westwards into Marguerite Bay between the Debenham Islands and Roman Four Promontory, on the west coast of Graham Land, Antarctica. Northeast Glacier was first surveyed in 1936 by the British Graham Land Expedition (BGLE) under John Riddoch Rymill. It was resurveyed in 1940 by members of the United States Antarctic Service (USAS), who first used the glacier as a sledging route, and so named by them because it lay on the north-eastern side of their base at Stonington Island.
The French Antarctic Expedition is any of several French expeditions in Antarctica.
The Hall Peninsula is a peninsula on the southern end of Baffin Island, in Nunavut, Canada. It lies between Frobisher Bay on the west, and the Cumberland Sound on the east between 62°40'N and 65°10'W. The Hall Peninsula is part of the Arctic Tundra biome—the world's coldest and driest biome. The Blunt Peninsula extends off the southeastern part of the Hall Peninsula.
The Barrow Point or Mutumui language, called Eibole, is a recently-extinct Australian Aboriginal language. According to Wurm and Hattori (1981), there was one speaker left at the time.

Teluk Ramunia is a town in Kota Tinggi District, Johor, Malaysia. It is a well-known bauxite mining town in the early days of Malaysia. It is a sight seeing place, good for a family picnic spot. Now it is known for Oil and Gas Fabrication industries.
The Becher Peninsula is located on southern Baffin Island in the Canadian territory of Nunavut. It is a part of the larger Hall Peninsula. Becher Peninsula is bounded by Frobisher Bay to the west, and Ward Inlet to the east.

The Back Peninsula is a cape located on eastern Bell Peninsula, Southampton Island, in the Kivalliq Region, Nunavut, Canada. Its southern shore is part of the northern boundary of Hudson Bay. Foxe Basin is to the north. There are two large bays, Gorden Bay and Junction Bay. Bowhead whale frequent the area. The Bell Peninsula's irregular coastline is marked by Seashore Point and Expectation Point.

Coolidge Springs is an unincorporated community in Imperial County, California. It is located 1 mile (1.6 km) southwest of Desert Shores, at an elevation of 180 feet below sea level.

Buford is a hamlet in central Alberta, Canada within Leduc County. It is located 2 kilometres (1.2 mi) south of Highway 39, 23 kilometres (14 mi) west of Leduc.

Nobby Nunatak is a nunatak, 270 m, standing 1 nautical mile (1.9 km) south of Lake Boeckella and 1 nautical mile (1.9 km) east of Mount Flora, at the northeast end of Antarctic Peninsula.

Flower’s Barrow is an Iron Age hillfort, built over 2500 years ago, above Worbarrow Bay in Dorset on the south coast of England.

Daħlet Qorrot Bay is a small bay found in the north of Gozo, between Qala and Nadur. The beach is rocky in Summer but in winter it's always covered with algae. In this bay you can find several boathouses which had been dug in the soft limestone. This rock is filled with fossils and this makes Dahlet Qorrot a geological hot spot.

Big Wave Bay or Tai Long Wan (大浪灣) is a bay in the Southern District of Hong Kong. It is located on the eastern coast of Hong Kong Island, south of Cape Collinson and north of Shek O.
Viera West is a census-designated place (CDP) in Brevard County, Florida, United States. The population was 6,641 at the 2010 census. It forms a part of the larger unincorporated community of Viera and is part of the Palm Bay–Melbourne–Titusville Metropolitan Statistical Area.
Veazie is an unincorporated community in King County, in the U.S. state of Washington.
National Cycle Network (NCN) Route 70 is a Sustrans National Route that runs from Walney Island in Cumbria to Sunderland. The route is fully open and signed. From end to end the route is 149 miles (240 km), but two sections are shared with other NCN routes leaving Route 70 at 128 miles (206 km).
















