
Millipedes are a group of arthropods that are characterised by having two pairs of jointed legs on most body segments; they are known scientifically as the class Diplopoda, the name derived from this feature. Each double-legged segment is a result of two single segments fused together. Most millipedes have very elongated cylindrical or flattened bodies with more than 20 segments, while pill millipedes are shorter and can roll into a tight ball. Although the name "millipede" derives from Latin for "thousand feet", no species was known to have 1,000 or more until the discovery in 2020 of Eumillipes persephone, which can have over 1,300 legs. There are approximately 12,000 named species classified into 16 orders and around 140 families, making Diplopoda the largest class of myriapods, an arthropod group which also includes centipedes and other multi-legged creatures.

Chilognatha is a subclass of the class Diplopoda, which includes the vast majority of extant millipedes, about 12,000 species.
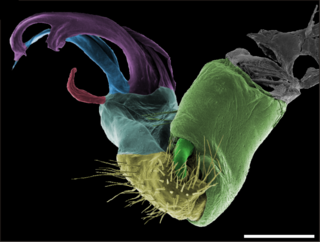
Gonopods are specialized appendages of various arthropods used in reproduction or egg-laying. In males, they facilitate the transfer of sperm from male to female during mating, and thus are a type of intromittent organ. In crustaceans and millipedes, gonopods are modified walking or swimming legs. Gonopods may be highly decorated with elaborate structures which may play roles in sperm competition, and can be used to differentiate and identify closely related species. Gonopods generally occur in one or more pairs, as opposed to the single (un-paired) reproductive organs such as the aedeagus of insects or the penis of harvestmen.

Glomerida is an order of pill-millipedes found primarily in the Northern Hemisphere. Also known as northern pill millipedes, they superficially resemble pill-bugs or woodlice, and can enroll into a protective ball. They have twelve body segments, 17 to 19 pairs of legs, and males have enlarged rear legs involved in mating. The order includes about 30 genera and at least 280 species, including Glomeris marginata, the common European pill-millipede. The order contains members in Europe, South-east Asia and the Americas from California to Guatemala. Although historically considered closely related with the similar sphaerotheriidans that also enroll, some DNA evidence suggest they may be more closely related to glomeridesmidans, a poorly known order that does not enroll.
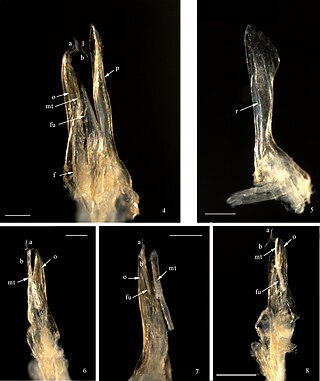
Mammamia profuga is a species of cave-dwelling millipede in the family Julidae. The only known species of the genus Mammamia, it was described in 2011 from a specimen discovered in a cave in Italy.

Polydesmida is the largest order of millipedes, with more than 5,000 species, including all the millipedes reported to produce hydrogen cyanide (HCN). This order is also the most diverse of the millipede orders in terms of morphology. Millipedes in this order are found in all regions of the world other than Antarctica.

Xystodesmidae is a family of millipedes in the suborder Leptodesmidea within the order Polydesmida. The family Xystodesmidae was created by the American biologist Orator F. Cook in 1895 and named after the genus Xystodesmus. This family includes more than 390 known species distributed among 62 genera. Many species, however, remain undescribed: for example, it is estimated that the genus Nannaria contains over 200 species, but only 25 were described as of 2006. By 2022, 78 species in Nannaria have been described.
Tridontomidae is a small family of millipedes. Its members are endemic to Guatemala. These millipedes range from 22 mm to 28 mm in length and are uniformly grayish in color; their legs and antennae are unusually long and slender. This family includes the remarkable species Aenigmopus alatus, in which adult males feature no gonopods. This millipede is the only species in the infraclass Helminthomorpha without gonopods.

Polyxenida is an order of millipedes readily distinguished by a unique body plan consisting of a soft, non-calcified body ornamented with tufts of bristles. These features have inspired the common names bristly millipedes or pincushion millipedes. This order includes about 148 species in four families worldwide, which represent the only living members of the subclass Penicillata.

Polyzoniida is an order of millipedes in the subterclass Colobognatha. This order contains three families and more than 70 described species. The species in this order are also known as camphor millipedes, because ozopore secretions in this order frequently have a strong camphor-like smell. Poison frogs in South America and Madagascar evidently obtain some of their poison from these millipedes.

Callipodida is an order of millipedes containing around 130 species, many characterized by crests or ridges.

Chordeumatida is a large order of millipedes containing more than 1,400 species. Also known as sausage millipedes, they are found nearly worldwide. Chordeumatida is the largest order in the superorder Nematophora, a group also known as spinning millipedes because their telsons feature spinnerets used to build nests of silk. These millipedes produce this silk to create chambers in which to molt or to lay their eggs.

Harold Frederick Loomis was an American botanist and myriapodologist known for his contributions to agronomy, plant pathology, and millipede taxonomy. He worked for the U.S. Department of Agriculture for over four decades, studying diseases of crop plants, and was a colleague of Orator F. Cook. He also made major contributions to the natural history of Central America and the West Indies, naming over 500 species of millipedes in total. He co-described with Cook the leggiest animal on earth: Illacme plenipes, with over 700 legs.
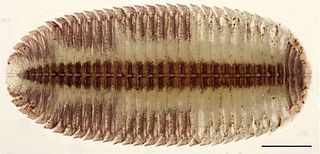
Siphonocryptida is an order of millipedes, comprising the sole family Siphonocryptidae. With only seven described species, the Siphonocryptida is the second smallest millipede order, surpassed only by Siphoniulida, with two species.

Haplodesmidae is a family of millipedes in the order Polydesmida. This family includes about 70 species. Species occur in East Asia, Southeast Asia, and Oceania, although some species have been introduced to the New world tropics.

Metopidiotrichidae is a family of millipedes in the order Chordeumatida. This family includes more than 70 species. These millipedes are found in Indochina, Australia, and on Pacific islands from New Zealand to Japan.
Speophilosomatidae is a family of millipedes belonging to the order Chordeumatida. These millipedes are found in Japan and range from 4 mm to 6 mm in length. Adult millipedes in this family are notable for being among the few in this order with only 26 segments instead of the 30 usually found in chordeumatidans. The adult males in this family are also notable for involving three leg pairs in the gonopod complex rather than the two pairs typically modified into gonopods in this order.
Peterjohnsiidae is a small family of millipedes belonging to the order Chordeumatida. The family was first described in 1987 by Jean-Paul Mauriès. These millipedes range from 3 mm to 8 mm in length and are found in Australia. Species in this family exhibit sexual dimorphism in segment number: adult males have 30 segments, but adult females have 32 segments. In adult males in this family, the gonopod complex involves three leg pairs rather than just the two usually modified into gonopods in this order.
Agenodesmus is a genus of millipedes in the family Fuhrmannodesmidae, which some authorities consider a junior synonym of Trichopolydesmidae. This genus is notable for being among the very few genera in the order Polydesmida to feature adults with only 18 segments rather than the 20 segments usually found in this order. The genus Agenodesmus contains only two species, A. reticulatus and A. nullus. The type species A. reticulatus is notable as the first polydesmidan millipede discovered with only 18 segments in adults, the smallest number recorded in the order Polydesmida. Before the discovery of A. reticulatus, polydesmidans were known to have only 19 or 20 segments in adults.
Agenodesmus reticulatus is a species of millipede in the family Fuhrmannodesmidae, which some authorities consider a junior synonym of Trichopolydesmidae. This millipede is among the very few species in the order Polydesmida to feature adults with only 18 segments rather than the 20 segments usually found in this order. This species is notable as the first polydesmidan millipede discovered with only 18 segments in adults, the smallest number recorded in the order Polydesmida. Before the discovery of A. reticulatus, polydesmidans were known to have only 19 or 20 segments in adults.

















