Transistor–transistor logic (TTL) is a logic family built from bipolar junction transistors. Its name signifies that transistors perform both the logic function and the amplifying function, as opposed to earlier resistor–transistor logic (RTL) and diode–transistor logic (DTL).
In electronics, a linear regulator is a voltage regulator used to maintain a steady voltage. The resistance of the regulator varies in accordance with both the input voltage and the load, resulting in a constant voltage output. The regulating circuit varies its resistance, continuously adjusting a voltage divider network to maintain a constant output voltage and continually dissipating the difference between the input and regulated voltages as waste heat. By contrast, a switching regulator uses an active device that switches on and off to maintain an average value of output. Because the regulated voltage of a linear regulator must always be lower than input voltage, efficiency is limited and the input voltage must be high enough to always allow the active device to reduce the voltage by some amount.

The 7400 series is a popular logic family of transistor–transistor logic (TTL) integrated circuits (ICs).

The 555 timer IC is an integrated circuit used in a variety of timer, delay, pulse generation, and oscillator applications. It is one of the most popular timing ICs due to its flexibility and price. Derivatives provide two or four timing circuits in one package. The design was first marketed in 1972 by Signetics and used bipolar junction transistors. Since then, numerous companies have made the original timers and later similar low-power CMOS timers. In 2017, it was said that over a billion 555 timers are produced annually by some estimates, and that the design was "probably the most popular integrated circuit ever made".

Solid Logic Technology (SLT) was IBM's method for hybrid packaging of electronic circuitry introduced in 1964 with the IBM System/360 series of computers. It was also used in the 1130, announced in 1965. IBM chose to design custom hybrid circuits using discrete, flip chip-mounted, glass-encapsulated transistors and diodes, with silk-screened resistors on a ceramic substrate, forming an SLT module. The circuits were either encapsulated in plastic or covered with a metal lid. Several of these SLT modules were then mounted on a small multi-layer printed circuit board to make an SLT card. Each SLT card had a socket on one edge that plugged into pins on the computer's backplane.
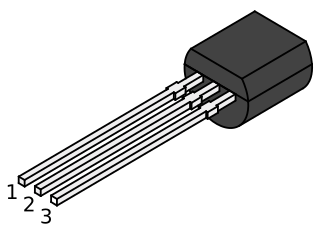
The TO-92 is a widely used style of semiconductor package mainly used for transistors. The case is often made of epoxy or plastic, and offers compact size at a very low cost.

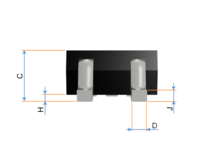
The TO-220 is a style of electronic package used for high-powered, through-hole components with 0.1 inches (2.54 mm) pin spacing. The "TO" designation stands for "transistor outline". TO-220 packages have three leads. Similar packages with two, four, five or seven leads are also manufactured. A notable characteristic is a metal tab with a hole, used to mount the case to a heatsink, allowing the component to dissipate more heat than one constructed in a TO-92 case. Common TO-220-packaged components include discrete semiconductors such as transistors and silicon-controlled rectifiers, as well as integrated circuits.
Nexperia is a semiconductor manufacturer headquartered in Nijmegen, the Netherlands. It is a subsidiary of Wingtech Technology, a Shanghai-listed company partially owned by the State-owned Assets Supervision and Administration Commission of the State Council. It has front-end factories in Hamburg, Germany, and Greater Manchester, England. It is the former Standard Products business unit of NXP Semiconductors. The company's product range includes bipolar transistors, diodes, ESD protection, TVS diodes, MOSFETs, and logic devices.

In electronics, TO-3 is a designation for a standardized metal semiconductor package used for power semiconductors, including transistors, silicon controlled rectifiers, and, integrated circuits. TO stands for "Transistor Outline" and relates to a series of technical drawings produced by JEDEC.
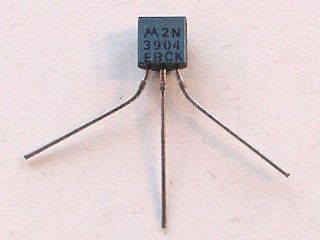
The 2N3904 is a common NPN bipolar junction transistor used for general-purpose low-power amplifying or switching applications. It is designed for low current and power, medium voltage, and can operate at moderately high speeds. It is complementary to the 2N3906 PNP transistor. Both types were registered by Motorola Semiconductor in the mid-1960s.

The 1N4148 is a standard silicon switching signal diode. It is one of the most popular and long-lived switching diodes because of its dependable specifications and low cost. Its name follows the JEDEC nomenclature. The 1N4148 is useful in switching applications up to about 100 MHz with a reverse-recovery time of no more than 4 ns.
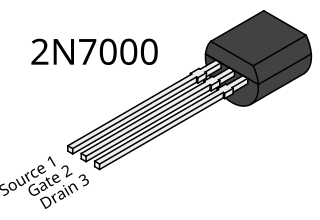
The 2N7000 is an N-channel, enhancement-mode MOSFET used for low-power switching applications.

Metal electrode leadless face (MELF) is a type of leadless cylindrical electronic surface mount device that is metallized at its ends. MELF devices are usually diodes and resistors.

78xx is a family of self-contained fixed linear voltage regulator integrated circuits. The 78xx family is commonly used in electronic circuits requiring a regulated power supply due to their ease-of-use and low cost.

Vishay Intertechnology, Inc. is an American manufacturer of discrete semiconductors and passive electronic components founded by Polish-born businessman Felix Zandman. Vishay has manufacturing plants in Israel, Asia, Europe, and the Americas where it produces rectifiers, diodes, MOSFETs, optoelectronics, selected integrated circuits, resistors, capacitors, and inductors. Vishay Intertechnology revenues for 2023 were $3.4 billion. At the end of 2023, Vishay had approximately 23,500 full-time employees.
The BZX79 series is a family of low voltage regulator diode. The diode is made in axial-lead DO-35 glass package. Regulating voltages varies from 2.4V to 75V with a total power dissipation maximum of 500 mW.

TO-252, also known as DPAK or Decawatt Package, is a semiconductor package developed by Motorola for surface mounting on circuit boards. It represents a surface-mount variant of TO-251 package, and smaller variant of the D2PAK package. It is often used for high-power MOSFETs and voltage regulators.