The TO-92 is a widely used style of semiconductor package mainly used for transistors. The case is often made of epoxy or plastic, and offers compact size at a very low cost.
The TO-92 is a widely used style of semiconductor package mainly used for transistors. The case is often made of epoxy or plastic, and offers compact size at a very low cost.
The JEDEC TO-92 descriptor is derived from the original full name for the package: Transistor Outline Package, Case Style 92. [1] The package is also known by the designation SOT54. By 1966 the package was being used by Motorola for their 2N3904 devices among others. [2]
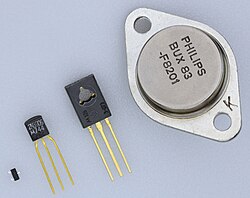
The case is molded around the transistor elements in two parts; the face is flat, usually bearing a machine-printed part number (some early examples had the part number printed on the top surface instead). The back is semi-circularly-shaped. A line of moulding flash from the injection-moulding process can be seen around the case.
The leads protrude from the bottom of the case. When looking at the face of the transistor, the leads are commonly configured from left-to-right as the emitter, base, and collector for 2N series (JEDEC) transistors, however, other configurations are possible, such as emitter, collector, and base commonly used for 2S series (Japanese) transistors or collector, base, and emitter for many of the BC series (Pro Electron) types.
If the face has a part name made up of only one letter and a few numbers, it can be either a Japanese or a Pro Electron part number. Thus, "C1234" would likely be a 2SC1234 device, but "C547" is usually short for "BC547".

The leads coming out of the case are spaced 0.05" (1.27 mm) apart. It is often convenient to bend them outward to a 0.10" (2.54 mm) spacing to make more room for wiring. [3] Units with their leads pre-bent may be ordered to fit specific board layouts, depending on the application. Otherwise, the leads may be bent manually; however, care must be taken as they can break easily, as with any other device that is manually configured.
The physical dimensions of the TO-92 housing may vary slightly depending on the manufacturer, however, the 1.27mm lead spacing must be respected.
The main disadvantage of this style of case is the lack of heat sinking.
Although TO-92 devices are mainly used in low-voltage / low-current (<30 V; <1 A) applications, high-voltage (600 Volt Vce) and high-current (5 A Ic) devices are available. Nominal maximum power dissipation is less than one watt (600 mW).
For diodes or integrated circuits with two connections (e.g. temperature sensors) the middle lead is either not connected or omitted entirely.

In the late 1960s, Ferranti introduced a smaller package with a compatible footprint, called "E-Line". [4] [5] This package was later standardized as a British Standard (but not by JEDEC) and remained in production with Ferranti Semiconductors' successor companies (Plessey, Zetex Semiconductors, Diodes Incorporated [6] ). In East Germany the E-Line package was known as the "Miniplast" package and widely used by Kombinat Mikroelektronik Erfurt.
| Standards organization | Standard | Designation for | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| TO-92 | E-Line/Miniplast | |||
| 3-lead | 2-lead | |||
| IEC | IEC 60191 [7] | A68 | ||
| DIN | DIN 41868 [8] | 10B3 [a] | ||
| EIAJ / JEITA | ED-7500A [9] [10] | SC-43A | ||
| British Standards | BS 3934 [11] | SO-94 [b] | ||
| Gosstandart | GOST 18472—88 [12] | KT-26 [c] | — | KD-129 [d] |
| Rosstandart | GOST R 57439—2017 [13] | |||
| Kombinat Mikroelektronik Erfurt | TGL 200-8380 [14] | — | — | L2 |
| TGL 11811 [7] | — | L3 | — | |
| TGL 26713/07 [7] | F2 | F3 | F4 | |
Common transistors:
Other common components: