
An integrated circuit (IC), also known as a microchip or simply chip, is a small electronic device made up of multiple interconnected electronic components such as transistors, resistors, and capacitors. These components are etched onto a small piece of semiconductor material, usually silicon. Integrated circuits are used in a wide range of electronic devices, including computers, smartphones, and televisions, to perform various functions such as processing and storing information. They have greatly impacted the field of electronics by enabling device miniaturization and enhanced functionality.

In microelectronics, a dual in-line package is an electronic component package with a rectangular housing and two parallel rows of electrical connecting pins. The package may be through-hole mounted to a printed circuit board (PCB) or inserted in a socket. The dual-inline format was invented by Don Forbes, Rex Rice and Bryant Rogers at Fairchild R&D in 1964, when the restricted number of leads available on circular transistor-style packages became a limitation in the use of integrated circuits. Increasingly complex circuits required more signal and power supply leads ; eventually microprocessors and similar complex devices required more leads than could be put on a DIP package, leading to development of higher-density chip carriers. Furthermore, square and rectangular packages made it easier to route printed-circuit traces beneath the packages.

PC Card is a parallel peripheral interface for laptop computers and PDAs. The PCMCIA originally introduced the 16-bit ISA-based PCMCIA Card in 1990, but renamed it to PC Card in March 1995 to avoid confusion with the name of the organization. The CardBus PC Card was introduced as a 32-bit version of the original PC Card, based on the PCI specification. The card slots are backward compatible for the original 16-bit card, older slots are not forward compatible with newer cards.

A ball grid array (BGA) is a type of surface-mount packaging used for integrated circuits. BGA packages are used to permanently mount devices such as microprocessors. A BGA can provide more interconnection pins than can be put on a dual in-line or flat package. The whole bottom surface of the device can be used, instead of just the perimeter. The traces connecting the package's leads to the wires or balls which connect the die to package are also on average shorter than with a perimeter-only type, leading to better performance at high speeds.
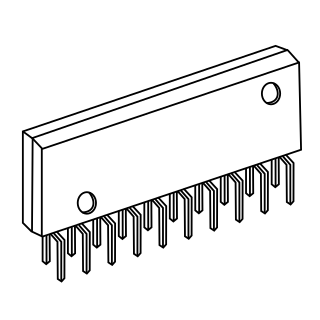
The zig-zag in-line package (ZIP) is a packaging technology for integrated circuits. It was intended as a replacement for dual in-line packaging. A ZIP is an integrated circuit encapsulated in a slab of plastic with 16, 20, 28 or 40 pins, measuring about 3 mm x 30 mm x 10 mm. The package's pins protrude in two rows from one of the long edges. The two rows are staggered by 1.27 mm (0.05"), giving them a zig-zag appearance, and allowing them to be spaced more closely than a rectangular grid would allow. The pins are inserted into holes in a printed circuit board, with the packages standing at right-angles to the board, allowing them to be placed closer together than DIPs of the same size. ZIPs have now been superseded by surface-mount packages such as the thin small-outline packages (TSOPs), but are still in use. The quad in-line package uses a similar staggered semiconductor package design, but on two sides instead of one.

Integrated circuit packaging is the final stage of semiconductor device fabrication, in which the die is encapsulated in a supporting case that prevents physical damage and corrosion. The case, known as a "package", supports the electrical contacts which connect the device to a circuit board.

The land grid array (LGA) is a type of surface-mount packaging for integrated circuits (ICs) that is notable for having the pins on the socket — as opposed to pins on the integrated circuit, known as a pin grid array (PGA). An LGA can be electrically connected to a printed circuit board (PCB) either by the use of a socket or by soldering directly to the board.

A quad flat package (QFP) is a surface-mounted integrated circuit package with "gull wing" leads extending from each of the four sides. Socketing such packages is rare and through-hole mounting is not possible. Versions ranging from 32 to 304 pins with a pitch ranging from 0.4 to 1.0 mm are common. Other special variants include low-profile QFP (LQFP) and thin QFP (TQFP).
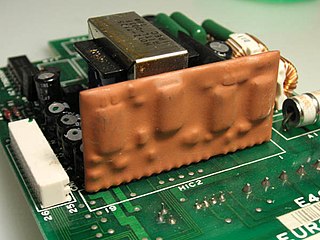
A hybrid integrated circuit (HIC), hybrid microcircuit, hybrid circuit or simply hybrid is a miniaturized electronic circuit constructed of individual devices, such as semiconductor devices and passive components, bonded to a substrate or printed circuit board (PCB). A PCB having components on a Printed wiring board (PWB) is not considered a true hybrid circuit according to the definition of MIL-PRF-38534.

A small outline integrated circuit (SOIC) is a surface-mounted integrated circuit (IC) package which occupies an area about 30–50% less than an equivalent dual in-line package (DIP), with a typical thickness being 70% less. They are generally available in the same pin-outs as their counterpart DIP ICs. The convention for naming the package is SOIC or SO followed by the number of pins. For example, a 14-pin 4011 would be housed in an SOIC-14 or SO-14 package.

A multi-chip module (MCM) is generically an electronic assembly where multiple integrated circuits, semiconductor dies and/or other discrete components are integrated, usually onto a unifying substrate, so that in use it can be treated as if it were a larger IC. Other terms for MCM packaging include "heterogeneous integration" or "hybrid integrated circuit". The advantage of using MCM packaging is it allows a manufacturer to use multiple components for modularity and/or to improve yields over a conventional monolithic IC approach.

Flat no-leads packages such as quad-flat no-leads (QFN) and dual-flat no-leads (DFN) physically and electrically connect integrated circuits to printed circuit boards. Flat no-leads, also known as micro leadframe (MLF) and SON, is a surface-mount technology, one of several package technologies that connect ICs to the surfaces of PCBs without through-holes. Flat no-lead is a near chip scale plastic encapsulated package made with a planar copper lead frame substrate. Perimeter lands on the package bottom provide electrical connections to the PCB. Flat no-lead packages usually, but not always, include an exposed thermally conductive pad to improve heat transfer out of the IC. Heat transfer can be further facilitated by metal vias in the thermal pad. The QFN package is similar to the quad-flat package (QFP), and a ball grid array (BGA).

In computing, a memory module or RAM stick is a printed circuit board on which memory integrated circuits are mounted.
Package on a package (PoP) is an integrated circuit packaging method to vertically combine ball grid array (BGA) packages for discrete logic and memory. Two or more packages are installed atop each other, i.e. stacked, with a standard interface to route signals between them. PoP allows higher component density in devices, such as mobile phones, personal digital assistants (PDA), and digital cameras, at the cost of being slightly taller. Stacks with more than 2 packages are uncommon, due to heat dissipation considerations.
A three-dimensional integrated circuit is a MOS integrated circuit (IC) manufactured by stacking as many as 16 or more ICs and interconnecting them vertically using, for instance, through-silicon vias (TSVs) or Cu-Cu connections, so that they behave as a single device to achieve performance improvements at reduced power and smaller footprint than conventional two dimensional processes. The 3D IC is one of several 3D integration schemes that exploit the z-direction to achieve electrical performance benefits in microelectronics and nanoelectronics.

In electronics, a chip carrier is one of several kinds of surface-mount technology packages for integrated circuits. Connections are made on all four edges of a square package; compared to the internal cavity for mounting the integrated circuit, the package overall size is large.
Glossary of microelectronics manufacturing terms

The Mini Small Outline Package (MSOP) is a miniaturized version of the small outline integrated circuit packaging format for integrated circuits.

The Thin Shrink Small Outline Package (TSSOP) is a rectangular surface mount plastic integrated circuit (IC) package with gull-wing leads.


















