
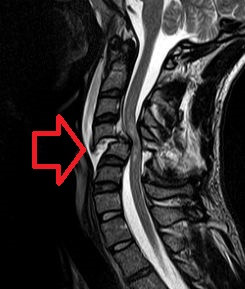
Foix–Alajouanine syndrome, also called subacute ascending necrotizing myelitis, is a disease caused by an arteriovenous malformation of the spinal cord. In particular, most cases involve dural arteriovenous malformations that present in the lower thoracic or lumbar spinal cord. The condition is named after Charles Foix and Théophile Alajouanine who first described the condition in 1926.

Syringomyelia is a generic term referring to a disorder in which a cyst or cavity forms within the spinal cord. Often, syringomyelia is used as a generic term before an etiology is determined. This cyst, called a syrinx, can expand and elongate over time, destroying the spinal cord. The damage may result in loss of feeling, paralysis, weakness, and stiffness in the back, shoulders, and extremities. Syringomyelia may also cause a loss of the ability to feel extremes of hot or cold, especially in the hands. It may also lead to a cape-like bilateral loss of pain and temperature sensation along the upper chest and arms. The combination of symptoms varies from one patient to another depending on the location of the syrinx within the spinal cord, as well as its extent.

Transverse myelitis (TM) is a rare neurological condition wherein the spinal cord is inflamed. The adjective transverse implies that the spinal inflammation (myelitis) extends horizontally throughout the cross section of the spinal cord; the terms partial transverse myelitis and partial myelitis are sometimes used to specify inflammation that affects only part of the width of the spinal cord. TM is characterized by weakness and numbness of the limbs, deficits in sensation and motor skills, dysfunctional urethral and anal sphincter activities, and dysfunction of the autonomic nervous system that can lead to episodes of high blood pressure. Signs and symptoms vary according to the affected level of the spinal cord. The underlying cause of TM is unknown. The spinal cord inflammation seen in TM has been associated with various infections, immune system disorders, or damage to nerve fibers, by loss of myelin. As opposed to leukomyelitis which affects only the white matter, it affects the entire cross-section of the spinal cord. Decreased electrical conductivity in the nervous system can result.

Tetraplegia, also known as quadriplegia, is defined as the dysfunction or loss of motor and/or sensory function in the cervical area of the spinal cord. A loss of motor function can present as either weakness or paralysis leading to partial or total loss of function in the arms, legs, trunk, and pelvis; paraplegia is similar but affects the thoracic, lumbar, and sacral segments of the spinal cord and arm function is retained. The paralysis may be flaccid or spastic. A loss of sensory function can present as an impairment or complete inability to sense light touch, pressure, heat, pinprick/pain, and proprioception. In these types of spinal cord injury, it is common to have a loss of both sensation and motor control.
Myelitis is inflammation of the spinal cord which can disrupt the normal responses from the brain to the rest of the body, and from the rest of the body to the brain. Inflammation in the spinal cord can cause the myelin and axon to be damaged resulting in symptoms such as paralysis and sensory loss. Myelitis is classified to several categories depending on the area or the cause of the lesion; however, any inflammatory attack on the spinal cord is often referred to as transverse myelitis.
Spinal tumors are neoplasms located in either the vertebral column or the spinal cord. There are three main types of spinal tumors classified based on their location: extradural and intradural. Extradural tumors are located outside the dura mater lining and are most commonly metastatic. Intradural tumors are located inside the dura mater lining and are further subdivided into intramedullary and extramedullary tumors. Intradural-intramedullary tumors are located within the dura and spinal cord parenchyma, while intradural-extramedullary tumors are located within the dura but outside the spinal cord parenchyma. The most common presenting symptom of spinal tumors is nocturnal back pain. Other common symptoms include muscle weakness, sensory loss, and difficulty walking. Loss of bowel and bladder control may occur during the later stages of the disease.
A spinal cord injury (SCI) is damage to the spinal cord that causes temporary or permanent changes in its function. Symptoms may include loss of muscle function, sensation, or autonomic function in the parts of the body served by the spinal cord below the level of the injury. Injury can occur at any level of the spinal cord and can be complete, with a total loss of sensation and muscle function at lower sacral segments, or incomplete, meaning some nervous signals are able to travel past the injured area of the cord up to the Sacral S4-5 spinal cord segments. Depending on the location and severity of damage, the symptoms vary, from numbness to paralysis, including bowel or bladder incontinence. Long term outcomes also range widely, from full recovery to permanent tetraplegia or paraplegia. Complications can include muscle atrophy, loss of voluntary motor control, spasticity, pressure sores, infections, and breathing problems.
Myelopathy describes any neurologic deficit related to the spinal cord. The most common form of myelopathy in humans, cervical spondylotic myelopathy (CSM), also called degenerative cervical myelopathy, results from narrowing of the spinal canal ultimately causing compression of the spinal cord. When due to trauma, myelopathy is known as (acute) spinal cord injury. When inflammatory, it is known as myelitis. Disease that is vascular in nature is known as vascular myelopathy.

Arachnoiditis is an inflammatory condition of the arachnoid mater or 'arachnoid', one of the membranes known as meninges that surround and protect the central nervous system. The outermost layer of the meninges is the dura mater and adheres to inner surface of the skull and vertebrae. The arachnoid is under or "deep" to the dura and is a thin membrane that adheres directly to the surface of the brain and spinal cord.
Hopkins syndrome is a neurological disorder. Its cause has not been established, but its association with asthma exacerbations has led to suspicion that the initial viral insult that causes the respiratory infection is also implicated in the subsequent paralysis. Herpes simplex virus type I DNA has been found in the cerebrospinal fluid of at least one patient diagnosed with Hopkins syndrome. In several cases, anti-viral antibody titers for echovirus, enterovirus, coxsackievirus and poliovirus types 1, 2 and 3 were specifically sought; all were negative., There is one reported case in which Mycoplasma pneumoniae infection was found in the patient.

Spinal cord compression is a form of myelopathy in which the spinal cord is compressed. Causes can be bone fragments from a vertebral fracture, a tumor, abscess, ruptured intervertebral disc or other lesion.

Central cord syndrome (CCS) is the most common form of cervical spinal cord injury. It is characterized by loss of power and sensation in arms and hands. It usually results from trauma which causes damage to the neck, leading to major injury to the central corticospinal tract of the spinal cord. CCS most frequently occurs among older persons with cervical spondylosis, however, it also may occur in younger individuals.

Canine degenerative myelopathy, also known as chronic degenerative radiculomyelopathy, is an incurable, progressive disease of the canine spinal cord that is similar in many ways to amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS). Onset is typically after the age of 7 years and it is seen most frequently in the German shepherd dog, Pembroke Welsh corgi, and boxer dog, though the disorder is strongly associated with a gene mutation in SOD1 that has been found in 43 breeds as of 2008, including the wire fox terrier, Chesapeake Bay retriever, Rhodesian ridgeback, and Cardigan Welsh corgi. Progressive weakness and incoordination of the rear limbs are often the first signs seen in affected dogs, with progression over time to complete paralysis. Myelin is an insulating sheath around neurons in the spinal cord. One proposed cause of degenerative myelopathy is that the immune system attacks this sheath, breaking it down. This results in a loss of communication between nerves in lower body of the animal and the brain.
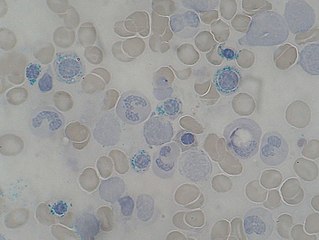
Copper deficiency, or hypocupremia, is defined either as insufficient copper to meet the needs of the body, or as a serum copper level below the normal range. Symptoms may include fatigue, decreased red blood cells, early greying of the hair, and neurological problems presenting as numbness, tingling, muscle weakness, and ataxia. The neurodegenerative syndrome of copper deficiency has been recognized for some time in ruminant animals, in which it is commonly known as "swayback". Copper deficiency can manifest in parallel with vitamin B12 and other nutritional deficiencies.
Vascular myelopathy refers to an abnormality of the spinal cord in regard to its blood supply. The blood supply is complicated and supplied by two major vessel groups: the posterior spinal arteries and the anterior spinal arteries—of which the Artery of Adamkiewicz is the largest. Both the posterior and anterior spinal arteries run the entire length of the spinal cord and receive anastomotic (conjoined) vessels in many places. The anterior spinal artery has a less efficient supply of blood and is therefore more susceptible to vascular disease. Whilst atherosclerosis of spinal arteries is rare, necrosis in the anterior artery can be caused by disease in vessels originating from the segmental arteries such as atheroma or aortic dissection.

A neurological disorder is any disorder of the nervous system. Structural, biochemical or electrical abnormalities in the brain, spinal cord or other nerves can result in a range of symptoms. Examples of symptoms include paralysis, muscle weakness, poor coordination, loss of sensation, seizures, confusion, pain, tauopathies, and altered levels of consciousness. There are many recognized neurological disorders, some relatively common, but many rare. They may be assessed by neurological examination, and studied and treated within the specialties of neurology and clinical neuropsychology.
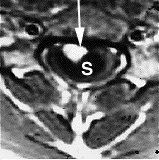
Myelomalacia is a pathological term referring to the softening of the spinal cord. Possible causes of myelomalacia include cervical myelopathy, hemorrhagic infarction, or acute injury, such as that caused by intervertebral disc extrusion.
Cobb syndrome is a rare congenital disorder characterized by visible skin lesions and spinal angiomas or arteriovenous malformations (AVMs). The skin lesions of Cobb syndrome typically are present as port wine stains or angiomas, but reports exist of angiokeratomas, angiolipomas, and lymphangioma circumscriptum. The intraspinal lesions may be angiomas or AVMs and occur at levels of the spinal cord corresponding to the affected skin dermatomes. They may in turn produce spinal cord dysfunction and weakness or paralysis.

Spinal stenosis is an abnormal narrowing of the spinal canal or neural foramen that results in pressure on the spinal cord or nerve roots. Symptoms may include pain, numbness, or weakness in the arms or legs. Symptoms are typically gradual in onset and improve with leaning forward. Severe symptoms may include loss of bladder control, loss of bowel control, or sexual dysfunction.
Spinal cord stroke is a rare type of stroke with compromised blood flow to any region of spinal cord owing to occlusion or bleeding, leading to irreversible neuronal death. It can be classified into two types, ischaemia and haemorrhage, in which the former accounts for 86% of all cases, a pattern similar to cerebral stroke. The disease is either arisen spontaneously from aortic illnesses or postoperatively. It deprives patients of motor function or sensory function, and sometimes both. Infarction usually occurs in regions perfused by anterior spinal artery, which spans the anterior two-thirds of spinal cord. Preventions of the disease include decreasing the risk factors and maintaining enough spinal cord perfusion pressure during and after the operation. The process of diagnosing the ischemic and hemorrhagic spinal cord stroke includes applying different MRI protocols and CT scan. Treatments for spinal cord stroke are mainly determined by the symptoms and the causes of the disease. For example, antiplatelet and corticosteroids might be used to reduce the risk of blood clots in ischaemic spinal stroke patients, while rapid surgical decompression is applied to minimize neurological injuries in haemorrhagic spinal stroke patients instead. Patients may spend years for rehabilitation after the spinal cord stroke.














