
The Arctic National Wildlife Refuge or Arctic Refuge is a national wildlife refuge in northeastern Alaska, United States, on traditional Iñupiaq and Gwich'in lands. The refuge is 19,286,722 acres (78,050.59 km2) of the Alaska North Slope region, with a northern coastline and vast inland forest, taiga, and tundra regions. ANWR is the largest national wildlife refuge in the country, slightly larger than the Yukon Delta National Wildlife Refuge. The refuge is administered from offices in Fairbanks. ANWR is home to a diverse range of endemic mammal species; notably, it is one of the few North American locations with all three endemic American bears—the polar bear, grizzly bear, and American black bear, each of which resides predominantly in its own ecological niche. Besides the bears, other mammal species include the moose, caribou, wolves, red and Arctic fox, Canada lynx, wolverine, pine marten, American beaver, and North American river otter. Further inland, mountain goats may be seen near the slope. Hundreds of species of migratory birds visit the refuge yearly, and it is a vital, protected breeding location for them. Snow geese, eiders and snowy owls may be observed as well.

Gates of the Arctic National Park and Preserve is a national park of the United States that protects portions of the Brooks Range in northern Alaska. The park is the northernmost national park in the United States, situated entirely north of the Arctic Circle. The area of the park and preserve is the second largest in the U.S. at 8,472,506 acres ; the National Park portion is the second largest in the U.S., after the National Park portion of Wrangell–St. Elias National Park and Preserve.

Kobuk Valley National Park is a national park of the United States in the Arctic region of northwestern Alaska, located about 25 miles (40 km) north of the Arctic Circle. The park was designated in 1980 by the Alaska National Interest Lands Conservation Act to preserve the 100 ft (30 m) high Great Kobuk Sand Dunes and the surrounding area which includes caribou migration routes. Park visitors must bring all their own gear for backcountry camping, hiking, backpacking, boating, and dog sledding. No designated trails or roads exist in the park, which at 1,750,716 acres, is slightly larger than the state of Delaware. Kobuk Valley is one of eight national parks in Alaska, the state with the second most national parks, surpassed only by California which has nine. The park is managed by the National Park Service.

The Kodiak National Wildlife Refuge is a United States National Wildlife Refuge in the Kodiak Archipelago in southwestern Alaska, United States.

Selawik National Wildlife Refuge in northwest Alaska in the Waring Mountains was officially established in 1980 with the passage of the Alaska National Interest Lands Conservation Act (ANILCA).

The Chugach National Forest is a 6,908,540-acre (27,958 km2) United States National Forest in south central Alaska. Covering portions of Prince William Sound, the Kenai Peninsula and the Copper River Delta, it was formed in 1907 from part of a larger forest reserve. The Chugach includes extensive shorelines, glaciers, forests and rivers, much of which is untouched by roads or trails. It hosts numerous bird, mammal and marine species, including extensive shorebird habitat and a bald eagle population larger than the contiguous 48 states combined. Human industry in the forest includes extensive tourism and some mining and oil and gas operations.

Wood-Tikchik State Park is a state park in the U.S. state of Alaska north of Dillingham. Over 1,600,000 acres (650,000 ha) (6,500 km2) in area—about the size of the state of Delaware—, comprising more than half of all state park land in Alaska and 15% of the total state park land in the country. Despite being the largest state park in the nation, the park had no staff whatsoever for its first five years, and even now at times only a single ranger is in charge of patrolling the entire park, usually by aircraft.

The National Wilderness Preservation System (NWPS) of the United States protects federally managed wilderness areas designated for preservation in their natural condition. Activity on formally designated wilderness areas is coordinated by the National Wilderness Preservation System. Wilderness areas are managed by four federal land management agencies: the National Park Service, the U.S. Forest Service, the U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service, and the Bureau of Land Management.

The Yukon Delta National Wildlife Refuge is a United States National Wildlife Refuge covering about 19.16 million acres (77,500 km2) in southwestern Alaska. It is the second-largest National Wildlife Refuge in the country, only slightly smaller than the Arctic National Wildlife Refuge. It is a coastal plain extending to the Bering Sea, covering the delta created by the Yukon and Kuskokwim rivers. The delta includes extensive wetlands near sea level that are often inundated by Bering Sea tides. It is bordered on the east by Wood-Tikchik State Park, the largest state park in the United States. The refuge is administered from offices in Bethel.

Southwest Alaska is a region of the U.S. state of Alaska. The area is not exactly defined by any governmental administrative region(s); nor does it always have a clear geographic boundary.

The Kanektok River is a 75-mile (121 km) stream in southwestern Alaska in the United States. Beginning in the Ahklun Mountains at Kagati and Pegati lakes, it flows westward into Kuskokwim Bay on the Bering Sea at the city of Quinhagak. Almost all of the river's course lies within the Togiak National Wildlife Refuge. The Quinhagak Village Corporation owns the land bordering the lowermost 17 miles (27 km) of the river.
The wildlife of Alaska is both diverse and abundant. The Alaskan Peninsula provides an important habitat for fish, mammals, reptiles, and birds. At the top of the food chain are the bears. Alaska contains about 70% of the total North American brown bear population and the majority of the grizzly bears, as well as black bears and Kodiak bears. In winter, polar bears can be found in the Kuskokwim Delta, St. Matthew Island, and at the southernmost portion of St. Lawrence Island. Other major mammals include moose and caribou, bison, wolves and wolverines, foxes, otters and beavers. Fish species are extensive, including: salmon, graylings, char, rainbow and lake trout, northern pike, halibut, pollock, and burbot. The bird population consists of hundreds of species, including: bald eagles, owls, falcons, ravens, ducks, geese, swans, and the passerines. Sea lions, seals, sea otters, and migratory whales are often found close to shore and in offshore waters. The Alaskan waters are home to two species of turtles, the leatherback sea turtle and the green sea turtle. Alaska has two species of frogs, the Columbia spotted frog and wood frog, plus two introduced species, the Pacific tree frog and the red-legged frog. The only species of toad in Alaska is the western toad. There are over 3,000 recorded species of marine macroinvertebrates inhabiting the marine waters, the most common being the various species of shrimp, crab, lobster, and sponge.

The Izembek National Wildlife Refuge is the smallest of the National Wildlife Refuges located in the U.S. state of Alaska. It lies on the northwest coastal side of central Aleutians East Borough. Almost all of the refuge was designated as wilderness in 1980 under the Alaska National Interest Lands Conservation Act (Anilca). The refuge is administered from offices in Cold Bay.
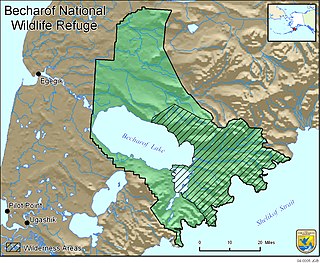
Becharof National Wildlife Refuge is a National Wildlife Refuge in the Aleutian Range of the Alaska Peninsula of southwestern Alaska. It is adjacent to Katmai National Park and Preserve. This national wildlife refuge, which covers an area of 1,200,000 acres (4,900 km2), was established in 1980 to conserve major brown bears, salmon, migratory birds, caribou, marine birds, and mammals and to comply with treaty obligations. It lies primarily in the east-central part of Lake and Peninsula Borough, but extends eastward into the mainland portion of Kodiak Island Borough. The refuge is administered from offices in King Salmon.

Kanuti National Wildlife Refuge is a national wildlife refuge in central Alaska, United States. One of 16 refuges in Alaska, it was established in 1980 when Congress passed The Alaska National Interest Lands Conservation Act (ANILCA). At 1,640,000 acres (6,600 km2), Kanuti Refuge is about the size of the state of Delaware. Located at the Arctic Circle, the refuge is a prime example of Alaska's boreal ecosystem. It is dominated by black and white spruce, with some white birch and poplars.

The Koyukuk National Wildlife Refuge is a 3,500,000-acre (14,000 km2) conservation area in Alaska. It lies within the floodplain of the Koyukuk River, in a basin that extends from the Yukon River to the Purcell Mountains and the foothills of the Brooks Range. This region of wetlands is home to fish, waterfowl, beaver and Alaskan moose, and wooded lowlands where two species of fox, bears, wolf packs, Canadian lynx and marten prowl.
The heart of Nowitna National Wildlife Refuge is a lowland basin of forests and wetlands that forms the floodplain of the meandering Nowitna River. The refuge's climate is typically marked by light precipitation, mild winds, long, hard winters and short, relatively warm, summers. The hills that circle the refuge lowlands are capped by alpine tundra.
Tetlin National Wildlife Refuge is a dynamic landscape made up of forests, wetlands, tundra, lakes, mountains and glacial rivers bounded by the snowy peaks of the Alaska Range. This upper Tanana River valley has been called the "Tetlin Passage," because it serves as a major migratory route for birds traveling to and from Canada, the lower 48 and both Central and South America. Many of these birds breed and nest on the refuge. Others pass through on their way to breeding and nesting grounds elsewhere in the state. Migrants, including ducks, geese, swans, cranes, raptors and songbirds, begin arriving in the valley in April, and continue into early June. An estimated 116 species breed on Tetlin during the short summer, when long days and warm temperatures accelerate the growth of plants, insects and other invertebrates, providing a ready source of rich foods for nesting birds.

The Ahklun Mountains are located in the northeast section of the Togiak National Wildlife Refuge in southwest Alaska. They extend southwest from the Kanektok and Narogurum Rivers to Hagemeister Strait and Kuskokwim Bay and support the only existing glaciers in western Alaska. They are the highest Alaskan mountain range west of the Alaska Range and north of the Alaska Peninsula: some summits in the range have many glaciers. To the west is the Kuskokwim River and to the east are the Bristol Bay lowlands.

The fauna of the U.S. state of California may be the most diverse in the United States. Of the lower 48 contiguous states, California has the greatest diversity in climate, terrain, and geology. The state's six life zones are the lower Sonoran (desert); upper Sonoran ; transition ; and the Canadian, Hudsonian, and Arctic zones, comprising California's highest elevations. California's diverse geography gives rise to dozens of ecosystems, each of which has its own native plants and animals. California is a huge state, the third largest in the U.S., and ranges broadly in habitats.




















