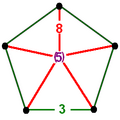
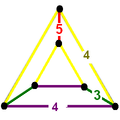
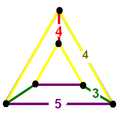
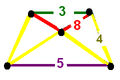
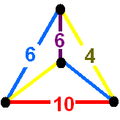
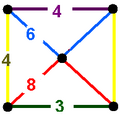
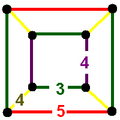
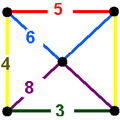
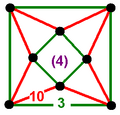
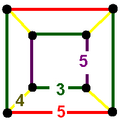
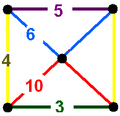
Honeycombs are divided between compact and paracompact forms defined by Coxeter groups, the first category only including finite cells and vertex figures (finite subgroups), and the second includes affine subgroups.
The nine compact Coxeter groups are listed here with their Coxeter diagrams, [1] in order of the relative volumes of their fundamental simplex domains. [2]
These 9 families generate a total of 76 unique uniform honeycombs. The full list of hyperbolic uniform honeycombs has not been proven and an unknown number of non-Wythoffian forms exist. Two known examples are cited with the {3,5,3} family below. Only two families are related as a mirror-removal halving: [5,31,1] ↔ [5,3,4,1+].
| Indexed | Fundamental
simplex
volume [2] | Witt
symbol | Coxeter
notation | Commutator
subgroup | Coxeter
diagram | Honeycombs |
|---|
| H1 | 0.0358850633 |  | [5,3,4] | [(5,3)+,4,1+]
= [5,31,1]+ |        | 15 forms, 2 regular |
|---|
| H2 | 0.0390502856 |  | [3,5,3] | [3,5,3]+ |        | 9 forms, 1 regular |
|---|
| H3 | 0.0717701267 |  | [5,31,1] | [5,31,1]+ |      | 11 forms (7 overlap with [5,3,4] family, 4 are unique) |
|---|
| H4 | 0.0857701820 |  | [(4,3,3,3)] | [(4,3,3,3)]+ |     | 9 forms |
|---|
| H5 | 0.0933255395 |  | [5,3,5] | [5,3,5]+ |        | 9 forms, 1 regular |
|---|
| H6 | 0.2052887885 |  | [(5,3,3,3)] | [(5,3,3,3)]+ |     | 9 forms |
|---|
| H7 | 0.2222287320 |  | [(4,3)[2]] | [(4,3+,4,3+)] |      | 6 forms |
|---|
| H8 | 0.3586534401 |  | [(3,4,3,5)] | [(3,4,3,5)]+ |      | 9 forms |
|---|
| H9 | 0.5021308905 |  | [(5,3)[2]] | [(5,3)[2]]+ |      | 6 forms |
|---|
There are just two radical subgroups with non-simplicial domains that can be generated by removing a set of two or more mirrors separated by all other mirrors by even-order branches. One is [(4,3,4,3*)], represented by Coxeter diagrams 


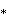 an index 6 subgroup with a trigonal trapezohedron fundamental domain ↔
an index 6 subgroup with a trigonal trapezohedron fundamental domain ↔ 





 , which can be extended by restoring one mirror as
, which can be extended by restoring one mirror as 



 . The other is [4,(3,5)*], index 120 with a dodecahedral fundamental domain.
. The other is [4,(3,5)*], index 120 with a dodecahedral fundamental domain.
There are also 23 paracompact Coxeter groups of rank 4 that produce paracompact uniform honeycombs with infinite or unbounded facets or vertex figure, including ideal vertices at infinity.
Hyperbolic paracompact group summary| Type | Coxeter groups |
|---|
| Linear graphs |        | |        | |        | |        | |        | |        |
|---|
| Tridental graphs |      | |      |
|---|
| Cyclic graphs |      | |   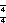  | |      | |      | |   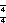   | |      | |      | |    |
|---|
| Loop-n-tail graphs |      | |      | |      |
|---|
Other paracompact Coxeter groups exists as Vinberg polytope fundamental domains, including these triangular bipyramid fundamental domains (double tetrahedra) as rank 5 graphs including parallel mirrors. Uniform honeycombs exist as all permutations of rings in these graphs, with the constraint that at least one node must be ringed across infinite order branches.
| Dimension | Rank | Graphs |
|---|
| H3 | 5 |      , ,      , ,      , ,      , ,             , ,        , ,        , ,        , ,        , ,               , ,        , ,  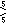      , ,  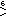      , ,        , ,        , ,             , ,      , ,      , ,      , ,      , ,      , ,      , ,      , ,  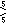    , ,  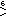    , ,      , ,      , ,     
|
|---|
[3,5,3] family
There are 9 forms, generated by ring permutations of the Coxeter group: [3,5,3] or 






One related non-wythoffian form is constructed from the {3,5,3} vertex figure with 4 (tetrahedrally arranged) vertices removed, creating pentagonal antiprisms and dodecahedra filling in the gaps, called a tetrahedrally diminished dodecahedron. [3] Another is constructed with 2 antipodal vertices removed. [4]
The bitruncated and runcinated forms (5 and 6) contain the faces of two regular skew polyhedrons: {4,10|3} and {10,4|3}.
| # | Honeycomb name
Coxeter diagram
and Schläfli
symbols | Cell counts/vertex
and positions in honeycomb | Vertex figure | Picture |
|---|
0
     | 1
      | 2
     | 3
     |
|---|
| 1 | icosahedral (ikhon)
      
t0{3,5,3} | | | | (12)

(3.3.3.3.3) |  |  |
|---|
| 2 | rectified icosahedral (rih)
      
t1{3,5,3} | (2)
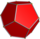
(5.5.5) | | | (3)

(3.5.3.5) | 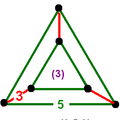 |  |
|---|
| 3 | truncated icosahedral (tih)
      
t0,1{3,5,3} | (1)

(5.5.5) | | | (3)

(5.6.6) | 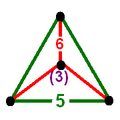 |  |
|---|
| 4 | cantellated icosahedral (srih)
      
t0,2{3,5,3} | (1)

(3.5.3.5) | (2)

(4.4.3) | | (2)

(3.5.4.5) |  |  |
|---|
| 5 | runcinated icosahedral (spiddih)
      
t0,3{3,5,3} | (1)

(3.3.3.3.3) | (5)

(4.4.3) | (5)

(4.4.3) | (1)

(3.3.3.3.3) |  |  |
|---|
| 6 | bitruncated icosahedral (dih)
      
t1,2{3,5,3} | (2)

(3.10.10) | | | (2)

(3.10.10) |  |  |
|---|
| 7 | cantitruncated icosahedral (grih)
      
t0,1,2{3,5,3} | (1)

(3.10.10) | (1)

(4.4.3) | | (2)

(4.6.10) | 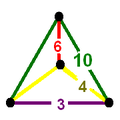 | 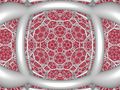 |
|---|
| 8 | runcitruncated icosahedral (prih)
      
t0,1,3{3,5,3} | (1)

(3.5.4.5) | (1)

(4.4.3) | (2)

(4.4.6) | (1)

(5.6.6) |  | 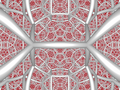 |
|---|
| 9 | omnitruncated icosahedral (gipiddih)
      
t0,1,2,3{3,5,3} | (1)

(4.6.10) | (1)

(4.4.6) | (1)

(4.4.6) | (1)

(4.6.10) |  |  |
|---|
[5,3,4] family
There are 15 forms, generated by ring permutations of the Coxeter group: [5,3,4] or 





 .
.
This family is related to the group [5,31,1] by a half symmetry [5,3,4,1+], or 



 ↔
↔ 





 , when the last mirror after the order-4 branch is inactive, or as an alternation if the third mirror is inactive
, when the last mirror after the order-4 branch is inactive, or as an alternation if the third mirror is inactive 



 ↔
↔ 





 .
.
[5,3,5] family
There are 9 forms, generated by ring permutations of the Coxeter group: [5,3,5] or 






The bitruncated and runcinated forms (29 and 30) contain the faces of two regular skew polyhedrons: {4,6|5} and {6,4|5}.
| # | Name of honeycomb
Coxeter diagram | Cells by location and count per vertex | Vertex figure | Picture |
|---|
0
     | 1
     | 2
     | 3
     |
|---|
| 25 | (Regular) Order-5 dodecahedral (pedhon)
      
t0{5,3,5} | | | | (20)

(5.5.5) |  | 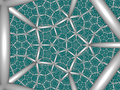 |
|---|
| 26 | rectified order-5 dodecahedral (ripped)
      
t1{5,3,5} | (2)

(3.3.3.3.3) | | | (5)

(3.5.3.5) |  |  |
|---|
| 27 | truncated order-5 dodecahedral (tipped)
      
t0,1{5,3,5} | (1)

(3.3.3.3.3) | | | (5)

(3.10.10) |  |  |
|---|
| 28 | cantellated order-5 dodecahedral (sripped)
      
t0,2{5,3,5} | (1)

(3.5.3.5) | (2)

(4.4.5) | | (2)

(3.5.4.5) |  |  |
|---|
| 29 | Runcinated order-5 dodecahedral (spidded)
      
t0,3{5,3,5} | (1)

(5.5.5) | (3)

(4.4.5) | (3)

(4.4.5) | (1)

(5.5.5) |  |  |
|---|
| 30 | bitruncated order-5 dodecahedral (diddoh)
      
t1,2{5,3,5} | (2)

(5.6.6) | | | (2)

(5.6.6) |  |  |
|---|
| 31 | cantitruncated order-5 dodecahedral (gripped)
      
t0,1,2{5,3,5} | (1)

(5.6.6) | (1)

(4.4.5) | | (2)

(4.6.10) |  |  |
|---|
| 32 | runcitruncated order-5 dodecahedral (pripped)
      
t0,1,3{5,3,5} | (1)

(3.5.4.5) | (1)

(4.4.5) | (2)

(4.4.10) | (1)

(3.10.10) |  |  |
|---|
| 33 | omnitruncated order-5 dodecahedral (gipidded)
      
t0,1,2,3{5,3,5} | (1)

(4.6.10) | (1)

(4.4.10) | (1)

(4.4.10) | (1)

(4.6.10) |  |  |
|---|
[5,31,1] family
There are 11 forms (and only 4 not shared with [5,3,4] family), generated by ring permutations of the Coxeter group: [5,31,1] or 



 . If the branch ring states match, an extended symmetry can double into the [5,3,4] family,
. If the branch ring states match, an extended symmetry can double into the [5,3,4] family, 



 ↔
↔ 





 .
.
[(4,3,3,3)] family
There are 9 forms, generated by ring permutations of the Coxeter group: 



The bitruncated and runcinated forms (41 and 42) contain the faces of two regular skew polyhedrons: {8,6|3} and {6,8|3}.
| # | Honeycomb name
Coxeter diagram | Cells by location
(and count around each vertex) | vertex figure | Picture |
|---|
0
   | 1
   | 2
    | 3
    | Alt |
|---|
| 38 | tetrahedral-cubic (gadtatdic)
   
{(3,3,3,4)} | (4)

(3.3.3) | - | (4)

(4.4.4) | (6)

(3.4.3.4) | |  |  |
|---|
| 39 | tetrahedral-octahedral (gacocaddit)
   
{(3,3,4,3)} | (12)

(3.3.3.3) | (8)

(3.3.3) | - | (8)

(3.3.3.3) | |  |  |
|---|
| 40 | cyclotruncated tetrahedral-cubic (cytitch)
   
ct{(3,3,3,4)} | (3)

(3.6.6) | (1)

(3.3.3) | (1)

(4.4.4) | (3)

(4.6.6) | | 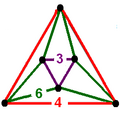 |  |
|---|
| 41 | cyclotruncated cube-tetrahedron (cyticth)
   
ct{(4,3,3,3)} | (1)

(3.3.3) | (1)

(3.3.3) | (3)

(3.8.8) | (3)

(3.8.8) | | 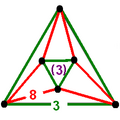 |  |
|---|
| 42 | cyclotruncated octahedral-tetrahedral (cytoth)
   
ct{(3,3,4,3)} | (4)

(3.6.6) | (4)

(3.6.6) | (1)

(3.3.3.3) | (1)

(3.3.3.3) | |  |  |
|---|
| 43 | rectified tetrahedral-cubic (ritch)
   
r{(3,3,3,4)} | (1)

(3.3.3.3) | (2)

(3.4.3.4) | (1)

(3.4.3.4) | (2)

(3.4.4.4) | |  |  |
|---|
| 44 | truncated tetrahedral-cubic (titch)
   
t{(3,3,3,4)} | (1)

(3.6.6) | (1)

(3.4.3.4) | (1)

(3.8.8) | (2)

(4.6.8) | | 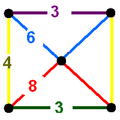 |  |
|---|
| 45 | truncated tetrahedral-octahedral (titdoh)
   
t{(3,3,4,3)} | (2)

(4.6.6) | (1)

(3.6.6) | (1)

(3.4.4.4) | (1)

(4.6.6) | | 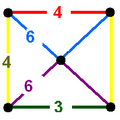 |  |
|---|
| 46 | omnitruncated tetrahedral-cubic (otitch)
   
tr{(3,3,3,4)} | (1)

(4.6.6) | (1)

(4.6.6) | (1)

(4.6.8) | (1)

(4.6.8) | |  |  |
|---|
| Nonuniform | omnisnub tetrahedral-cubic
   
sr{(3,3,3,4)} | (1)

(3.3.3.3.3) | (1)

(3.3.3.3.3) | (1)

(3.3.3.3.4) | (1)

(3.3.3.3.4) | (4)

+(3.3.3) |  |
[(4,3,4,3)] family
There are 6 forms, generated by ring permutations of the Coxeter group: 



 . There are 4 extended symmetries possible based on the symmetry of the rings:
. There are 4 extended symmetries possible based on the symmetry of the rings: 



 ,
, 



 ,
, 



 , and
, and 



 .
.
This symmetry family is also related to a radical subgroup, index 6, 


 ↔
↔ 





 , constructed by [(4,3,4,3*)], and represents a trigonal trapezohedron fundamental domain.
, constructed by [(4,3,4,3*)], and represents a trigonal trapezohedron fundamental domain.
The truncated forms (57 and 58) contain the faces of two regular skew polyhedrons: {6,6|4} and {8,8|3}.
Other non-Wythoffians
There are infinitely many known non-Wythoffian uniform compact hyperbolic honeycombs, and there may be more undiscovered ones. Two have been listed above as diminishings of the icosahedral honeycomb {3,5,3}. [6]
In 1997 Wendy Krieger discovered an infinite series of uniform hyperbolic honeycombs with pseudoicosahedral vertex figures, made from 8 cubes and 12 p-gonal prisms at a vertex for any integer p. In the case p = 4, all cells are cubes and the result is the order-5 cubic honeycomb. The case p = 2 degenerates to the Euclidean cubic honeycomb. [6]
Another four known ones are related to noncompact families. The tessellation 





 consists of truncated cubes
consists of truncated cubes 



 and infinite order-8 triangular tilings
and infinite order-8 triangular tilings 



 . However the latter intersect the sphere at infinity orthogonally, having exactly the same curvature as the hyperbolic space, and can be replaced by mirror images of the remainder of the tessellation, resulting in a compact uniform honeycomb consisting only of the truncated cubes. (So they are analogous to the hemi-faces of spherical hemipolyhedra.) [6] [7] Something similar can be done with the tessellation
. However the latter intersect the sphere at infinity orthogonally, having exactly the same curvature as the hyperbolic space, and can be replaced by mirror images of the remainder of the tessellation, resulting in a compact uniform honeycomb consisting only of the truncated cubes. (So they are analogous to the hemi-faces of spherical hemipolyhedra.) [6] [7] Something similar can be done with the tessellation 



 consisting of small rhombicuboctahedra
consisting of small rhombicuboctahedra 



 , infinite order-8 triangular tilings
, infinite order-8 triangular tilings 



 , and infinite order-8 square tilings
, and infinite order-8 square tilings 



 . The order-8 square tilings already intersect the sphere at infinity orthogonally, and if the order-8 triangular tilings are augmented with a set of triangular prisms, the surface passing through their centre points also intersects the sphere at infinity orthogonally. After replacing with mirror images, the result is a compact honeycomb containing the small rhombicuboctahedra and the triangular prisms. [8] Two more such constructions were discovered in 2023. The first one arises from the fact that
. The order-8 square tilings already intersect the sphere at infinity orthogonally, and if the order-8 triangular tilings are augmented with a set of triangular prisms, the surface passing through their centre points also intersects the sphere at infinity orthogonally. After replacing with mirror images, the result is a compact honeycomb containing the small rhombicuboctahedra and the triangular prisms. [8] Two more such constructions were discovered in 2023. The first one arises from the fact that 





 and
and 





 have the same circumradius; the former has truncated octahedra
have the same circumradius; the former has truncated octahedra 



 and order-6 square tilings
and order-6 square tilings 



 , while the latter has cuboctahedra
, while the latter has cuboctahedra 



 and order-6 square tilings
and order-6 square tilings 



 . A compact uniform honeycomb is taken by discarding the order-6 square tilings they have in common, using only the truncated octahedra and cuboctahedra. The second one arises from a similar construction involving
. A compact uniform honeycomb is taken by discarding the order-6 square tilings they have in common, using only the truncated octahedra and cuboctahedra. The second one arises from a similar construction involving 



 (which has small rhombicosidodecahedra
(which has small rhombicosidodecahedra 



 , octahedra
, octahedra 



 , and order-4 pentagonal tilings
, and order-4 pentagonal tilings 



 ) and
) and 





 (which is the prism of the order-4 pentagonal tiling, having pentagonal prisms
(which is the prism of the order-4 pentagonal tiling, having pentagonal prisms 



 and order-4 pentagonal tilings
and order-4 pentagonal tilings 



 ). These two likewise have the same circumradius, and a compact uniform honeycomb is obtained by taking only the finite cells of both, discarding the order-4 pentagonal tilings they have in common. [9]
). These two likewise have the same circumradius, and a compact uniform honeycomb is obtained by taking only the finite cells of both, discarding the order-4 pentagonal tilings they have in common. [9]
Another non-Wythoffian was discovered in 2021. It has as vertex figure a snub cube with 8 vertices removed and contains two octahedra and eight snub cubes at each vertex. [6] Subsequently Krieger found a non-Wythoffian with a snub cube as the vertex figure, containing 32 tetrahedra and 6 octahedra at each vertex, and that the truncated and rectified versions of this honeycomb are still uniform. In 2022, Richard Klitzing generalised this construction to use any snub 



 as vertex figure: the result is compact for p=4 or 5 (with a snub cube or snub dodecahedral vertex figure respectively), paracompact for p=6 (with a snub trihexagonal tiling as the vertex figure), and hypercompact for p>6. Again, the truncated and rectified versions of these honeycombs are still uniform. The cases p=3 and p=2 are spherical (they are the regular 600-cell and 16-cell, respectively). [6]
as vertex figure: the result is compact for p=4 or 5 (with a snub cube or snub dodecahedral vertex figure respectively), paracompact for p=6 (with a snub trihexagonal tiling as the vertex figure), and hypercompact for p>6. Again, the truncated and rectified versions of these honeycombs are still uniform. The cases p=3 and p=2 are spherical (they are the regular 600-cell and 16-cell, respectively). [6]
There are also other forms based on parallelepiped domains. Two known forms generalise the cubic-octahedral honeycomb, having distorted small rhombicuboctahedral vertex figures. One form has small rhombicuboctahedra, cuboctahedra, and cubes; another has small rhombicosidodecahedra, icosidodecahedra, and cubes. (The version with tetrahedral-symmetry polyhedra is the cubic-octahedral honeycomb, using cuboctahedra, octahedra, and cubes). [9]
This is the complete enumeration of the 76 Wythoffian uniform honeycombs. The alternations are listed for completeness, but most are non-uniform.
| Index | Coxeter group | Extended
symmetry | Honeycombs | Chiral
extended
symmetry | Alternation honeycombs |
|---|
| H1 | 
[4,3,5]
       | [4,3,5]
       | 15 |        | |        | |        | |        | |       
       | |        | |        | |        | |       
       | |        | |        | |        | |        | [1+,4,(3,5)+] | (2) |        (= (=      ) )
       |
|---|
| [4,3,5]+ | (1) |        |
| H2 | 
[3,5,3]
       | [3,5,3]
       | 6 |        | |        | |        | |        | |        | |
|---|
[2+[3,5,3]]
       | 5 |        | |        | [2+[3,5,3]]+ | (1) |        |
| H3 | 
[5,31,1]
     | [5,31,1]
     | 4 |      | |      | |      | |
|---|
[1[5,31,1]]=[5,3,4]
     ↔ ↔        | (7) |      | |      | |      | |      | |      | |      | [1[5,31,1]]+
=[5,3,4]+ | (1) |      |
| H4 | 
[(4,3,3,3)]
    | [(4,3,3,3)] | 6 |     | |     | |     | |     | |     | |
|---|
[2+[(4,3,3,3)]]
    | 3 |     | |     | [2+[(4,3,3,3)]]+ | (1) |     |
| H5 | 
[5,3,5]
       | [5,3,5]
       | 6 |        | |        | |        | |        | |        | |
|---|
[2+[5,3,5]]
   | 3 |        | |        | [2+[5,3,5]]+ | (1) |        |
| H6 | 
[(5,3,3,3)]
    | [(5,3,3,3)] | 6 |     | |     | |     | |     | |     | |
|---|
[2+[(5,3,3,3)]]
    | 3 |     | |     | [2+[(5,3,3,3)]]+ | (1) |     |
| H7 | 
[(3,4)[2]]
     | [(3,4)[2]] | 2 |      | |
|---|
[2+[(3,4)[2]]]
     | 1 |      | |
[2+[(3,4)[2]]]
     | 1 |      | |
[2+[(3,4)[2]]]
     | 1 |      | [2+[(3+,4)[2]]] | (1) |      |
[(2,2)+[(3,4)[2]]]
     | 1 |      | [(2,2)+[(3,4)[2]]]+ | (1) |      |
| H8 | 
[(5,3,4,3)]
     | [(5,3,4,3)] | 6 |      | |      | |      | |      | |      | |
|---|
[2+[(5,3,4,3)]]
     | 3 |      | |      | [2+[(5,3,4,3)]]+ | (1) |      |
| H9 | 
[(3,5)[2]]
     | [(3,5)[2]] | 2 |      | |
|---|
[2+[(3,5)[2]]]
     | 1 |      | |
[2+[(3,5)[2]]]
     | 1 |      | |
[2+[(3,5)[2]]]
     | 1 |      | |
[(2,2)+[(3,5)[2]]]
     | 1 |      | [(2,2)+[(3,5)[2]]]+ | (1) |      |