Smith County is a county in the U.S. state of Texas. As of the 2020 census, its population was 233,479. Its county seat is Tyler. Smith County is named for James Smith, a general during the Texas Revolution.

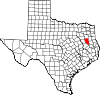
Rusk County is a county located in Texas. As of the 2020 census, its population was 52,214. Its county seat is Henderson. The county is named for Thomas Jefferson Rusk, a secretary of war of the Republic of Texas.

Gregg County is a county located in the eastern part of the U.S. state of Texas. As of the 2020 census, its population was 124,239. Its county seat is Longview. The county is named after John Gregg, a Confederate general killed in action during the American Civil War.

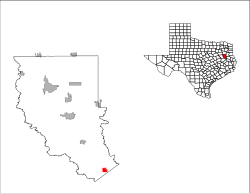
Cherokee County is a county located in the U.S. state of Texas. As of the 2020 census, its population was 50,412. The county seat is Rusk, which lies 130 miles southeast of Dallas and 160 miles north of Houston. The county was named for the Cherokee, who lived in the area before being expelled in 1839. Cherokee County comprises the Jacksonville micropolitan statistical area, which is also included in the Tyler–Jacksonville combined statistical area.

Anderson County is a county in the U.S. state of Texas. Located within East Texas, its county seat is Palestine. As of the 2020 United States census, the population of Anderson County was 57,922. Anderson County comprises the Palestine micropolitan statistical area. Anderson County was organized in 1846, and was named after Kenneth Lewis Anderson (1805-1845), the last vice president of the Republic of Texas.

Elkhart is a town the U.S. state of Texas, in Anderson County. Named for a friendly Native American who assisted the early settlers of the area, Elkhart's population was 1,287 at the 2020 U.S. census.

Palestine is a city in and the seat of Anderson County in the U.S. state of Texas. It was named after Palestine, Illinois, by preacher Daniel Parker, who had migrated from that town. It is also contested that Micham Main named Palestine after his hometown, also Palestine, Illinois, when he and his family arrived here along with the Parker family and several others.
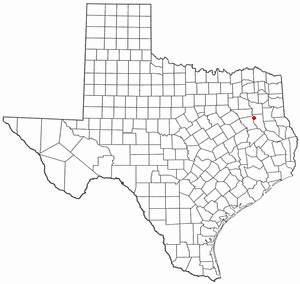
Cuney is a town located in northwestern Cherokee County, Texas, United States. With a population of 116 at the 2020 U.S. census, Cuney was the only "wet" town in Cherokee County from the mid-1980s until 2009, when voters in Rusk came out in favor of beer/wine sales. After that result, voters in Jacksonville and Frankston have since voted in favor of beer/wine sales, and Rusk voters returned to the polls to vote in favor of liquor sales.

Gallatin is a city in Cherokee County, Texas, United States, with a 2020 U.S. census-tabulated population of 321.

Jacksonville is a city located in Cherokee County, Texas, United States. The population was 13,997 at the 2020 U.S. census. It is the principal city of the Jacksonville micropolitan statistical area, which includes all of Cherokee County.

New Summerfield is a city in Cherokee County, Texas, United States. The population was 843 at the 2020 U.S. census.

Rusk is a city in and the county seat of Cherokee County, Texas, United States. At the 2020 United States census, it had a population of 5,285.
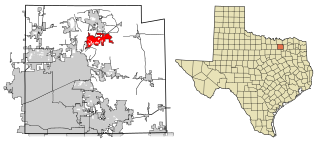
Melissa is a city in Collin County, Texas, United States. The population was 4,695 at the 2010 census, up from 1,350 at the 2000 census; in 2020, its population grew to 13,901.

Henderson is a city and the county seat of Rusk County, Texas, in Northeast Texas, United States. Its population was 13,271 at the 2020 census. Henderson is named for James Pinckney Henderson, the first governor of Texas.

Bullard is a small town in Smith and Cherokee counties in the east-central part of the U.S. state of Texas. U.S. Route 69 and Farm-to-Market Roads 2137, 2493, and 344 intersect here, about 15 miles (24 km) south of the larger city of Tyler. Its population was 3,318 at the 2020 census, up from 2,463 at the 2010 census.

Troup is a city in Smith and Cherokee counties in Texas, United States. Its population was 2,006 at the 2020 census. Troup lies in two counties in East Texas.

Kilgore is a city in Gregg and Rusk counties in the eastern part of the U.S. state of Texas. Over three-fourths of the area within city limits are located in Gregg County, the remainder in Rusk County. The population was 12,975 at the 2010 census and 13,376 at the 2020 census.

Overton is a city in Rusk and Smith counties in the U.S. state of Texas. Overton lies in two counties as well as two metropolitan areas. The Rusk County portion of the city is part of the Longview Metropolitan Statistical Area, while the Smith County portion is part of the Tyler Metropolitan Statistical Area.

Maydelle is a small unincorporated community in Cherokee County, Texas, United States. According to the Handbook of Texas, the community had a population of 250 in 2000. It is located within the Tyler-Jacksonville combined statistical area.
Lake Cherokee is an unincorporated community and census-designated place (CDP) in Gregg and Rusk counties, Texas, United States. Its population was 2,980 as of the 2020 census. Lake Cherokee is located 12 miles southeast of Gregg and northeastern Rusk counties on Cherokee Bayou. The lake is owned by the Cherokee Water Company to supply water for municipal, industrial, and recreational purposes. It has a capacity of 68,700 acre-feet. The lake impounds Cherokee Bayou. The top of the dam is at the elevation of 295 feet above the average sea level, but it has a max design of 291 feet above the average sea level.