Lithium citrate (Li3C6H5O7) is a chemical compound of lithium and citrate that is used as a mood stabilizer in psychiatric treatment of manic states and bipolar disorder. There is extensive pharmacology of lithium, the active component of this salt.

Citric acid is an organic compound with the chemical formula HOC(CO2H)(CH2CO2H)2. It is a colorless weak organic acid. It occurs naturally in citrus fruits. In biochemistry, it is an intermediate in the citric acid cycle, which occurs in the metabolism of all aerobic organisms.
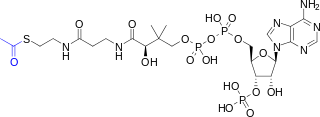
Acetyl-CoA is a molecule that participates in many biochemical reactions in protein, carbohydrate and lipid metabolism. Its main function is to deliver the acetyl group to the citric acid cycle to be oxidized for energy production. Coenzyme A consists of a β-mercaptoethylamine group linked to the vitamin pantothenic acid (B5) through an amide linkage and 3'-phosphorylated ADP. The acetyl group of acetyl-CoA is linked to the sulfhydryl substituent of the β-mercaptoethylamine group. This thioester linkage is a "high energy" bond, which is particularly reactive. Hydrolysis of the thioester bond is exergonic (−31.5 kJ/mol).

Calcium citrate is the calcium salt of citric acid. It is commonly used as a food additive (E333), usually as a preservative, but sometimes for flavor. In this sense, it is similar to sodium citrate. Calcium citrate is also found in some dietary calcium supplements. Calcium makes up 24.1% of calcium citrate (anhydrous) and 21.1% of calcium citrate (tetrahydrate) by mass. The tetrahydrate occurs in nature as the mineral Earlandite.

Propel Water is an American brand of flavored bottled water that is advertised for having antioxidants and vitamins. It is a beverage product of Gatorade and is marketed by PepsiCo.

The enzyme citrate synthase E.C. 2.3.3.1 ] exists in nearly all living cells and stands as a pace-making enzyme in the first step of the citric acid cycle. Citrate synthase is localized within eukaryotic cells in the mitochondrial matrix, but is encoded by nuclear DNA rather than mitochondrial. It is synthesized using cytoplasmic ribosomes, then transported into the mitochondrial matrix.

Caffeine citrate, sold under the brand name Cafcit among others, is a medication used to treat a lack of breathing in premature babies. Specifically it is given to babies who are born at less than 35 weeks or weigh less than 2 kilograms (4.4 lb) once other causes are ruled out. It is given by mouth or slow injection into a vein.

Ammonium ferric citrate has the formula (NH4)5[Fe(C6H4O7)2]. A distinguishing feature of this compound is that it is very soluble in water, in contrast to ferric citrate which is not very soluble.
Ovulation induction is the stimulation of ovulation by medication. It is usually used in the sense of stimulation of the development of ovarian follicles to reverse anovulation or oligoovulation.

Magnesium citrate is a magnesium preparation in salt form with citric acid in a 1:1 ratio. The name "magnesium citrate" is ambiguous and sometimes may refer to other salts such as trimagnesium citrate which has a magnesium:citrate ratio of 3:2.

Oxeladin is a cough suppressant. It is a highly potent and effective drug used to treat all types of cough of various etiologies. It is not related to opium or its derivatives, so treatment with oxeladin is free of risk of dependence or addiction. Oxeladin has none of the side effects which are present when common antitussives, such as codeine and its derivatives, are used. It may be used at every age, as well as in patients with heart disease, since it has a high level of safety and a great selectivity to act on the bulbar centre of cough.
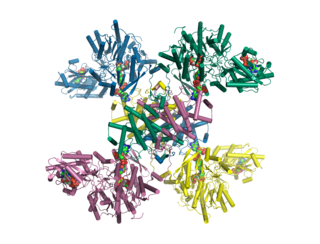
ATP citrate synthase is an enzyme that in animals represents an important step in fatty acid biosynthesis. By converting citrate to acetyl-CoA, the enzyme links carbohydrate metabolism, which yields citrate as an intermediate, with fatty acid biosynthesis, which consumes acetyl-CoA. In plants, ATP citrate lyase generates cytosolic acetyl-CoA precursors of thousands of specialized metabolites, including waxes, sterols, and polyketides.
In enzymology, a citrate (Re)-synthase (EC 2.3.3.3) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
Sodium citrate may refer to any of the sodium salts of citric acid :

Tricarboxylate transport protein, mitochondrial, also known as tricarboxylate carrier protein and citrate transport protein (CTP), is a protein that in humans is encoded by the SLC25A1 gene. SLC25A1 belongs to the mitochondrial carrier gene family SLC25. High levels of the tricarboxylate transport protein are found in the liver, pancreas and kidney. Lower or no levels are present in the brain, heart, skeletal muscle, placenta and lung.

The E. coli long-term evolution experiment (LTEE) is an ongoing study in experimental evolution led by Richard Lenski that has been tracking genetic changes in 12 initially identical populations of asexual Escherichia coli bacteria since 24 February 1988. The populations reached the milestone of 50,000 generations in February 2010. Lenski performed the 10,000th transfer of the experiment on March 13, 2017. The populations reached over 73,000 generations in early 2020, shortly before being frozen because of the COVID-19 pandemic. In September 2020, the LTEE experiment was resumed using the frozen stocks.
Alverine is a drug used for functional gastrointestinal disorders. Alverine is a smooth muscle relaxant. Smooth muscle is a type of muscle that is not under voluntary control; it is the muscle present in places such as the gut and uterus.

Tofacitinib, sold under the brand Xeljanz among others, is a medication used to treat rheumatoid arthritis, psoriatic arthritis, and ulcerative colitis.

Solute carrier family 13 (sodium-dependent citrate transporter), member 5 also known as the Na+/citrate cotransporter or mIndy is a protein that in humans is encoded by the SLC13A5 gene. It is the mammalian homolog of the fly Indy (gene).

Nitromifene is a nonsteroidal selective estrogen receptor modulator (SERM) related to triphenylethylenes like tamoxifen that was never marketed. It is a mixture of (E)- and (Z)-isomers that possess similar antiestrogenic activity. The drug was described in 1966. Along with tamoxifen, nafoxidine, and clomifene, it was one of the earliest SERMs.