Related Research Articles

miR-218 microRNA precursor is a small non-coding RNA that regulates gene expression by antisense binding.
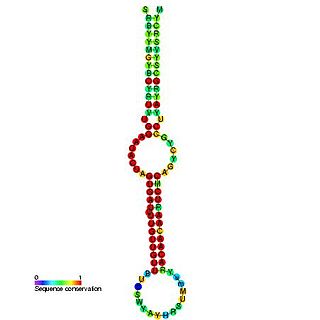
This family represents the microRNA (miRNA) precursor mir-7. This miRNA has been predicted or experimentally confirmed in a wide range of species. miRNAs are transcribed as ~70 nucleotide precursors and subsequently processed by the Dicer enzyme to give a ~22 nucleotide product. In this case the mature sequence comes from the 5' arm of the precursor. The extents of the hairpin precursors are not generally known and are estimated based on hairpin prediction. The involvement of Dicer in miRNA processing suggests a relationship with the phenomenon of RNA interference.
Triple-negative breast cancer refers to any breast cancer that does not express the genes for estrogen receptor (ER), progesterone receptor (PR) and HER2/neu. This makes it more difficult to treat since most hormone therapies target one of the three receptors, so triple-negative cancers often require combination therapies. Triple negative is sometimes used as a surrogate term for basal-like; however, more detailed classification may provide better guidance for treatment and better estimates for prognosis.

microRNA 21 also known as hsa-mir-21 or miRNA21 is a mammalian microRNA that is encoded by the MIR21 gene.

The PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway is an intracellular signaling pathway important in regulating the cell cycle. Therefore, it is directly related to cellular quiescence, proliferation, cancer, and longevity. PI3K activation phosphorylates and activates AKT, localizing it in the plasma membrane. AKT can have a number of downstream effects such as activating CREB, inhibiting p27, localizing FOXO in the cytoplasm, activating PtdIns-3ps, and activating mTOR which can affect transcription of p70 or 4EBP1. There are many known factors that enhance the PI3K/AKT pathway including EGF, shh, IGF-1, insulin, and CaM. Both leptin and insulin recruit PI3K signalling for metabolic regulation. The pathway is antagonized by various factors including PTEN, GSK3B, and HB9.

In molecular biology mir-126 is a short non-coding RNA molecule. MicroRNAs function to regulate the expression levels of other genes by several pre- and post-transcription mechanisms.

In molecular biology, mir-145 microRNA is a short RNA molecule that in humans is encoded by the MIR145 gene. MicroRNAs function to regulate the expression levels of other genes by several mechanisms.

In molecular biology, miR-184 microRNA is a short non-coding RNA molecule. MicroRNAs (miRNAs) function as posttranscriptional regulators of expression levels of other genes by several mechanisms. Several targets for miR-184 have been described, including that of mediators of neurological development, apoptosis and it has been suggested that miR-184 plays an essential role in development.

In molecular biology mir-22 microRNA is a short RNA molecule. MicroRNAs are an abundant class of molecules, approximately 22 nucleotides in length, which can post-transcriptionally regulate gene expression by binding to the 3' UTR of mRNAs expressed in a cell.

In molecular biology mir-210 microRNA is a short RNA molecule. MicroRNAs function to regulate the expression levels of other genes by several mechanisms.

miR-27 is a family of microRNA precursors found in animals, including humans. MicroRNAs are typically transcribed as ~70 nucleotide precursors and subsequently processed by the Dicer enzyme to give a ~22 nucleotide product. The excised region or, mature product, of the miR-27 precursor is the microRNA mir-27.
In molecular biology mir-365 microRNA is a short RNA molecule. MicroRNAs function to regulate the expression levels of other genes by several mechanisms.
In molecular biology mir-153 microRNA is a short RNA molecule. MicroRNAs function to regulate the expression levels of other genes by several mechanisms.
mir-612 microRNA is a short non-coding RNA molecule belonging both to the family of microRNAs and to that of small interfering RNAs (siRNAs). MicroRNAs function to regulate the expression levels of other genes by several mechanisms, whilst siRNAs are involved primarily with the RNA interference (RNAi) pathway. siRNAs have been linked through some members to the regulation of cancer cell growth, specifically in prostate adenocarcinoma.
In molecular biology mir-625 microRNA is a short RNA molecule. MicroRNAs function to regulate the expression levels of other genes by several mechanisms. Many microRNAs play important roles in cancer development and progression.

MicroRNA 7-1 is a microRNA molecule that in humans is encoded by the MIR7-1 gene.

MicroRNA 489 is a miRNA that in humans is encoded by the MIR489 gene.
MicroRNA 425 is a microRNA that in humans is encoded by the MIR425 gene.

CCR4-NOT transcription complex subunit 9 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the CNOT9 gene.
References
- ↑ Han J, Yu J, Dai Y, Li J, Guo M, Song J, Zhou X. Overexpression of miR-361-5p in triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC) inhibits migration and invasion by targeting RQCD1 and inhibiting the EGFR/PI3K/Akt pathway. Bosn J of Basic Med Sci [Internet]. 2019Feb.12 [cited 2020Apr.6];19(1):52-9. Available from: https://www.bjbms.org/ojs/index.php/bjbms/article/view/3399