External links
miRNA precursor families | |
|---|---|
| 1-100 | |
| 101-200 | |
| 201-300 | |
| 301-400 | |
| 401+ | |
| Other | |
| mir-367 | |
|---|---|
| Identifiers | |
| Symbol | mir-367 |
| Rfam | RF00735 |
| miRBase family | MIPF0000162 |
| Other data | |
| RNA type | microRNA |
| Domain(s) | Eukaryota; |
| PDB structures | PDBe |
In molecular biology mir-367 microRNA is a short RNA molecule. MicroRNAs function to regulate the expression levels of other genes by several mechanisms.
miR302/367 cluster, together with Hdac2 inhibition, reprograms human and mouse fibroblasts to iPS cells, faster and more efficient than the custom viral infection (OSKM) strategy. Expression of miR367 is essential for Oct4 expression and miR302/367-mediated reprogramming. [1]
The Let-7 microRNA precursor was identified from a study of developmental timing in C. elegans, and was later shown to be part of a much larger class of non-coding RNAs termed microRNAs. miR-98 microRNA precursor from human is a let-7 family member. Let-7 miRNAs have now been predicted or experimentally confirmed in a wide range of species (MIPF0000002). miRNAs are initially transcribed in long transcripts called primary miRNAs (pri-miRNAs), which are processed in the nucleus by Drosha and Pasha to hairpin structures of about 70 nucleotide. These precursors (pre-miRNAs) are exported to the cytoplasm by exportin5, where they are subsequently processed by the enzyme Dicer to a ~22 nucleotide mature miRNA. The involvement of Dicer in miRNA processing demonstrates a relationship with the phenomenon of RNA interference.

The miR-9 microRNA, is a short non-coding RNA gene involved in gene regulation. The mature ~21nt miRNAs are processed from hairpin precursor sequences by the Dicer enzyme. The dominant mature miRNA sequence is processed from the 5' arm of the mir-9 precursor, and from the 3' arm of the mir-79 precursor. The mature products are thought to have regulatory roles through complementarity to mRNA. In vertebrates, miR-9 is highly expressed in the brain, and is suggested to regulate neuronal differentiation. A number of specific targets of miR-9 have been proposed, including the transcription factor REST and its partner CoREST.
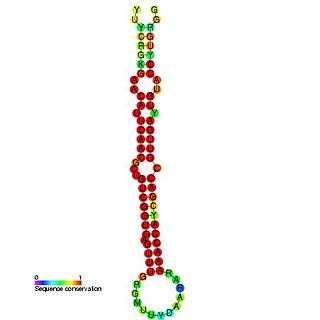
In molecular biology miR-181 microRNA precursor is a small non-coding RNA molecule. MicroRNAs (miRNAs) are transcribed as ~70 nucleotide precursors and subsequently processed by the RNase-III type enzyme Dicer to give a ~22 nucleotide mature product. In this case the mature sequence comes from the 5' arm of the precursor. They target and modulate protein expression by inhibiting translation and / or inducing degradation of target messenger RNAs. This new class of genes has recently been shown to play a central role in malignant transformation. miRNA are downregulated in many tumors and thus appear to function as tumor suppressor genes. The mature products miR-181a, miR-181b, miR-181c or miR-181d are thought to have regulatory roles at posttranscriptional level, through complementarity to target mRNAs. miR-181 which has been predicted or experimentally confirmed in a wide number of vertebrate species as rat, zebrafish, and in the pufferfish.

There are 89 known sequences today in the microRNA 19 (miR-19) family but it will change quickly. They are found in a large number of vertebrate species. The miR-19 microRNA precursor is a small non-coding RNA molecule that regulates gene expression. Within the human and mouse genome there are three copies of this microRNA that are processed from multiple predicted precursor hairpins:
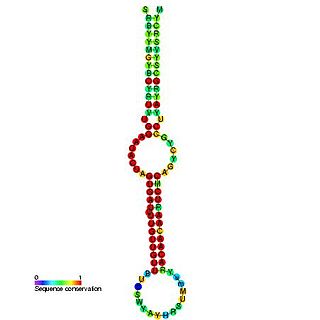
This family represents the microRNA (miRNA) precursor mir-7. This miRNA has been predicted or experimentally confirmed in a wide range of species. miRNAs are transcribed as ~70 nucleotide precursors and subsequently processed by the Dicer enzyme to give a ~22 nucleotide product. In this case the mature sequence comes from the 5' arm of the precursor. The extents of the hairpin precursors are not generally known and are estimated based on hairpin prediction. The involvement of Dicer in miRNA processing suggests a relationship with the phenomenon of RNA interference.

Induced pluripotent stem cells are a type of pluripotent stem cell that can be generated directly from a somatic cell. The iPSC technology was pioneered by Shinya Yamanaka's lab in Kyoto, Japan, who showed in 2006 that the introduction of four specific genes, collectively known as Yamanaka factors, encoding transcription factors could convert somatic cells into pluripotent stem cells. He was awarded the 2012 Nobel Prize along with Sir John Gurdon "for the discovery that mature cells can be reprogrammed to become pluripotent."

Lin-28 homolog A is a protein that in humans is encoded by the LIN28 gene.

In molecular biology, miR-137 is a short non-coding RNA molecule that functions to regulate the expression levels of other genes by various mechanisms. miR-137 is located on human chromosome 1p22 and has been implicated to act as a tumor suppressor in several cancer types including colorectal cancer, squamous cell carcinoma and melanoma via cell cycle control.

In molecular biology, mir-145 microRNA is a short RNA molecule that in humans is encoded by the MIR145 gene. MicroRNAs function to regulate the expression levels of other genes by several mechanisms.

In molecular biology, miR-184 microRNA is a short non-coding RNA molecule. MicroRNAs (miRNAs) function as posttranscriptional regulators of expression levels of other genes by several mechanisms. Several targets for miR-184 have been described, including that of mediators of neurological development, apoptosis and it has been suggested that miR-184 plays an essential role in development.
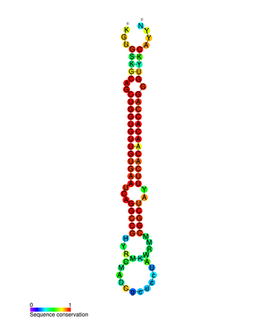
miR-138 is a family of microRNA precursors found in animals, including humans. MicroRNAs are typically transcribed as ~70 nucleotide precursors and subsequently processed by the Dicer enzyme to give a ~22 nucleotide product. The excised region or, mature product, of the miR-138 precursor is the microRNA mir-138.

miR-134 is a family of microRNA precursors found in mammals, including humans. MicroRNAs are typically transcribed as ~70 nucleotide precursors and subsequently processed by the Dicer enzyme to give a ~22 nucleotide product. The excised region or, mature product, of the miR-134 precursor is the microRNA mir-134.
In molecular biology mir-301 microRNA is a short RNA molecule. MicroRNAs function to regulate the expression levels of other genes by several mechanisms.
In molecular biology mir-339 microRNA is a short RNA molecule. MicroRNAs function to regulate the expression levels of other genes by several mechanisms. miR-339-5p expression was associated with overall survival in breast cancer.
In molecular biology mir-345 microRNA is a short RNA molecule. MicroRNAs function to regulate the expression levels of other genes by several mechanisms.
In molecular biology mir-374 microRNA is a short RNA molecule. MicroRNAs function to regulate the expression levels of other genes by several mechanisms.
In molecular biology mir-186 microRNA is a short RNA molecule. MicroRNAs function to regulate the expression levels of other genes by several mechanisms.
In molecular biology mir-396 microRNA is a short RNA molecule. MicroRNAs function to regulate the expression levels of other genes by several mechanisms.

MicroRNA 106a is a microRNA that in humans is encoded by the MIR106A gene.