Related Research Articles

Phosphatidylinositol 3,5-bisphosphate is one of the seven phosphoinositides found in eukaryotic cell membranes. In quiescent cells, the PtdIns(3,5)P2 levels, typically quantified by HPLC, are the lowest amongst the constitutively present phosphoinositides. They are approximately 3 to 5-fold lower as compared to PtdIns3P and PtdIns5P levels, and more than 100-fold lower than the abundant PtdIns4P and PtdIns(4,5)P2. PtdIns(3,5)P2 was first reported to occur in mouse fibroblasts and budding yeast S. cerevisiae in 1997. In S. cerevisiae PtdIns(3,5)P2 levels increase dramatically during hyperosmotic shock. The response to hyperosmotic challenge is not conserved in most tested mammalian cells except for differentiated 3T3L1 adipocytes.

CCAAT-enhancer-binding proteins is a family of transcription factors composed of six members, named from C/EBPα to C/EBPζ. They promote the expression of certain genes through interaction with their promoters. Once bound to DNA, C/EBPs can recruit so-called co-activators that in turn can open up chromatin structure or recruit basal transcription factors.

The miR-8 microRNA precursor, is a short non-coding RNA gene involved in gene regulation. miR-8 in Drosophila melanogaster is expressed from the 3' arm of related precursor hairpins, along with miR-200, miR-236, miR-429 and human and mouse homolog miR-141. Members of this precursor family have now been predicted or experimentally confirmed in a wide range of species. The bounds of the precursors are predicted based on conservation and base pairing and are not generally known.

mir-133 is a type of non-coding RNA called a microRNA that was first experimentally characterised in mice. Homologues have since been discovered in several other species including invertebrates such as the fruitfly Drosophila melanogaster. Each species often encodes multiple microRNAs with identical or similar mature sequence. For example, in the human genome there are three known miR-133 genes: miR-133a-1, miR-133a-2 and miR-133b found on chromosomes 18, 20 and 6 respectively. The mature sequence is excised from the 3' arm of the hairpin. miR-133 is expressed in muscle tissue and appears to repress the expression of non-muscle genes.
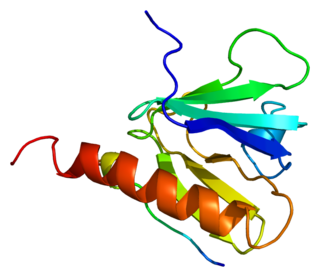
Insulin receptor substrate 1(IRS-1) is a signaling adapter protein that in humans is encoded by the IRS1 gene. It is a 131 kDa protein with amino acid sequence of 1242 residues. It contains a single pleckstrin homology (PH) domain at the N-terminus and a PTB domain ca. 40 residues downstream of this, followed by a poorly conserved C-terminus tail. Together with IRS2, IRS3 (pseudogene) and IRS4, it is homologous to the Drosophila protein chico, whose disruption extends the median lifespan of flies up to 48%. Similarly, Irs1 mutant mice experience moderate life extension and delayed age-related pathologies.

3T3-L1 is a sub clonal cell line derived from the original 3T3 Swiss albino cell line of 1962. The 3T3 original cell line was isolated from a mouse embryo and propagated for 3this specific line of 3T3 cells is used to study adipose tissuerelated diseases and dysfunctions. The 3T3-L1 Swiss sub clone line has been widely utilized, since its development, due to its affinity for lipid droplet deposition in vitro. 3T3-L1 cells have a fibroblast-like morphology, but, under appropriate conditions, the cells differentiate into an adipocyte-like phenotype, providing an exemplar model for white adipocytes. 3T3-L1 cells can be utilized to study a number of cellular and molecular mechanisms related to insulin-resistance, obesity, and diabetes in vitro. Aside from its usages, this cell line is widely developed and can be purchased for continuous propagation for numerous research studies. 3T3-L1 cells of the adipocyte morphology increase the synthesis and accumulation of triglycerides and acquire the signet ring appearance of adipose cells. These cells are also sensitive to lipogenic and lipolytic hormones, as well as drugs, including epinephrine, isoproterenol, and insulin.
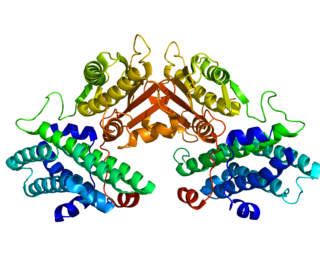
Pyruvate dehydrogenase lipoamide kinase isozyme 4, mitochondrial (PDK4) is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the PDK4 gene. It codes for an isozyme of pyruvate dehydrogenase kinase.

Mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase kinase kinase 4 (MAP4K4) – also known as hepatocyte progenitor kinase-like/germinal center kinase-like kinase (HGK) and Nck-interacting kinase (NIK) – is an enzyme, specifically a serine/threonine (S/T) kinase encoded by the MAP4K4 gene in humans.
The Akt signaling pathway or PI3K-Akt signaling pathway is a signal transduction pathway that promotes survival and growth in response to extracellular signals. Key proteins involved are PI3K and Akt.

Adipogenesis is the formation of adipocytes from stem cells. It involves 2 phases, determination, and terminal differentiation. Determination is mesenchymal stem cells committing to the adipocyte precursor cells, also known as lipoblasts or preadipocytes which lose the potential to differentiate to other types of cells such as chondrocytes, myocytes, and osteoblasts. Terminal differentiation is that preadipocytes differentiate into mature adipocytes. Adipocytes can arise either from preadipocytes resident in adipose tissue, or from bone-marrow derived progenitor cells that migrate to adipose tissue.

In molecular biology, miR-184 microRNA is a short non-coding RNA molecule. MicroRNAs (miRNAs) function as posttranscriptional regulators of expression levels of other genes by several mechanisms. Several targets for miR-184 have been described, including that of mediators of neurological development, apoptosis and it has been suggested that miR-184 plays an essential role in development.

In molecular biology mir-320 microRNA is a short RNA molecule. MicroRNAs function to regulate the expression levels of other genes by several mechanisms.
The insulin transduction pathway is a biochemical pathway by which insulin increases the uptake of glucose into fat and muscle cells and reduces the synthesis of glucose in the liver and hence is involved in maintaining glucose homeostasis. This pathway is also influenced by fed versus fasting states, stress levels, and a variety of other hormones.
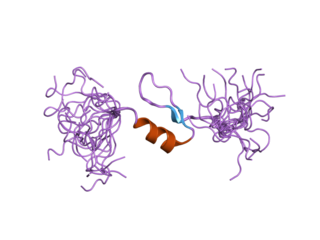
Krüppel-like factor 15 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the KLF15 gene in the Krüppel-like factor family. Its former designation KKLF stands for kidney-enriched Krüppel-like factor.

miR-33 is a family of microRNA precursors, which are processed by the Dicer enzyme to give mature microRNAs. miR-33 is found in several animal species, including humans. In some species there is a single member of this family which gives the mature product mir-33. In humans there are two members of this family called mir-33a and mir-33b, which are located in intronic regions within two protein-coding genes for Sterol regulatory element-binding proteins respectively.
In molecular biology mir-361 microRNA is a short RNA molecule. MicroRNAs function to regulate the expression levels of other genes by several mechanisms. For example, miR-361-5p might act as a suppressor in triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC) by targeting RQCD1 to inhibit the EGFR/PI3K/Akt signaling pathway.
In molecular biology mir-153 microRNA is a short RNA molecule. MicroRNAs function to regulate the expression levels of other genes by several mechanisms.

Geniposide, the glycoside form of genipin, is a bioactive iridoid glycoside that is found in a wide variety of medicinal herbs, such as Gardenia jasminoides (fruits) . Geniposide shows several pharmacological effects including neuroprotective, antidiabetic, hepatoprotective, anti-inflammatory, analgesic, antidepressant-like, cardioprotective, antioxidant, immune-regulatory, antithrombotic and antitumoral activity. These pharmacology benefits arise through the modulating action of geniposide on several proteins and genes that are associated with inflammatory and oxidative stress processes.

Phosphotyrosine interaction domain containing 1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the PID1 gene.
References
- ↑ Papaioannou MD, Lagarrigue M, Vejnar CE, Rolland AD, Kühne F, Aubry F, et al. (2011). "Loss of Dicer in Sertoli cells has a major impact on the testicular proteome of mice". Mol Cell Proteomics. 10 (4): M900587–MCP200. doi: 10.1074/mcp.M900587-MCP200 . PMC 3069350 . PMID 20467044.
- ↑ Chang CL, Au LC, Huang SW, Fai Kwok C, Ho LT, Juan CC (2011). "Insulin up-regulates heme oxygenase-1 expression in 3T3-L1 adipocytes via PI3-kinase- and PKC-dependent pathways and heme oxygenase-1-associated microRNA downregulation". Endocrinology. 152 (2): 384–93. doi: 10.1210/en.2010-0493 . PMID 21147878.