Related Research Articles

In molecular genetics, the three prime untranslated region (3′-UTR) is the section of messenger RNA (mRNA) that immediately follows the translation termination codon. The 3′-UTR often contains regulatory regions that post-transcriptionally influence gene expression.

Nitric oxide synthases (NOSs) are a family of enzymes catalyzing the production of nitric oxide (NO) from L-arginine. NO is an important cellular signaling molecule. It helps modulate vascular tone, insulin secretion, airway tone, and peristalsis, and is involved in angiogenesis and neural development. It may function as a retrograde neurotransmitter. Nitric oxide is mediated in mammals by the calcium-calmodulin controlled isoenzymes eNOS and nNOS. The inducible isoform, iNOS, involved in immune response, binds calmodulin at physiologically relevant concentrations, and produces NO as an immune defense mechanism, as NO is a free radical with an unpaired electron. It is the proximate cause of septic shock and may function in autoimmune disease.
The Let-7 microRNA precursor was identified from a study of developmental timing in C. elegans, and was later shown to be part of a much larger class of non-coding RNAs termed microRNAs. miR-98 microRNA precursor from human is a let-7 family member. Let-7 miRNAs have now been predicted or experimentally confirmed in a wide range of species (MIPF0000002). miRNAs are initially transcribed in long transcripts called primary miRNAs (pri-miRNAs), which are processed in the nucleus by Drosha and Pasha to hairpin structures of about 70 nucleotide. These precursors (pre-miRNAs) are exported to the cytoplasm by exportin5, where they are subsequently processed by the enzyme Dicer to a ~22 nucleotide mature miRNA. The involvement of Dicer in miRNA processing demonstrates a relationship with the phenomenon of RNA interference.

The miR-10 microRNA precursor is a short non-coding RNA gene involved in gene regulation. It is part of an RNA gene family which contains miR-10, miR-51, miR-57, miR-99 and miR-100. miR-10, miR-99 and miR-100 have now been predicted or experimentally confirmed in a wide range of species. mir-51 and mir-57 have currently only been identified in the nematode Caenorhabditis elegans.

There are 89 known sequences today in the microRNA 19 (miR-19) family but it will change quickly. They are found in a large number of vertebrate species. The miR-19 microRNA precursor is a small non-coding RNA molecule that regulates gene expression. Within the human and mouse genome there are three copies of this microRNA that are processed from multiple predicted precursor hairpins:
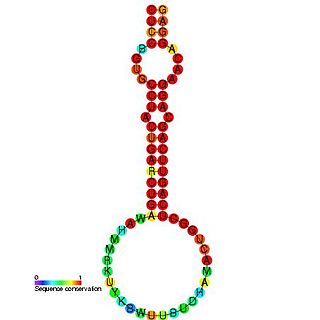
The miR-24 microRNA precursor is a small non-coding RNA molecule that regulates gene expression. microRNAs are transcribed as ~70 nucleotide precursors and subsequently processed by the Dicer enzyme to give a mature ~22 nucleotide product. In this case the mature sequence comes from the 3' arm of the precursor. The mature products are thought to have regulatory roles through complementarity to mRNA. miR-24 is conserved in various species, and is clustered with miR-23 and miR-27, on human chromosome 9 and 19. Recently, miR-24 has been shown to suppress expression of two crucial cell cycle control genes, E2F2 and Myc in hematopoietic differentiation and also to promote keratinocyte differentiation by repressing actin-cytoskeleton regulators PAK4, Tsk5 and ArhGAP19.

Endothelial NOS (eNOS), also known as nitric oxide synthase 3 (NOS3) or constitutive NOS (cNOS), is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the NOS3 gene located in the 7q35-7q36 region of chromosome 7. This enzyme is one of three isoforms that synthesize nitric oxide (NO), a small gaseous and lipophilic molecule that participates in several biological processes. The other isoforms include neuronal nitric oxide synthase (nNOS), which is constitutively expressed in specific neurons of the brain and inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS), whose expression is typically induced in inflammatory diseases. eNOS is primarily responsible for the generation of NO in the vascular endothelium, a monolayer of flat cells lining the interior surface of blood vessels, at the interface between circulating blood in the lumen and the remainder of the vessel wall. NO produced by eNOS in the vascular endothelium plays crucial roles in regulating vascular tone, cellular proliferation, leukocyte adhesion, and platelet aggregation. Therefore, a functional eNOS is essential for a healthy cardiovascular system.
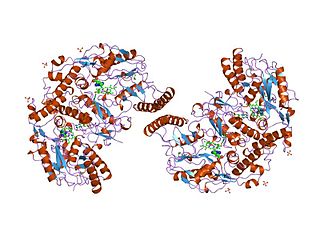
Nitric oxide synthase, inducible is an enzyme which is encoded by the NOS2 gene in humans and mice.

HBx is a hepatitis B viral protein. It is 154 amino acids long and interferes with transcription, signal transduction, cell cycle progress, protein degradation, apoptosis and chromosomal stability in the host. It forms a heterodimeric complex with its cellular target protein, and this interaction dysregulates centrosome dynamics and mitotic spindle formation. It interacts with DDB1 redirecting the ubiquitin ligase activity of the CUL4-DDB1 E3 complexes, which are intimately involved in the intracellular regulation of DNA replication and repair, transcription and signal transduction.

miR-122 is a miRNA that is conserved among vertebrate species. miR-122 is not present in invertebrates, and no close paralogs of miR-122 have been detected. miR-122 is highly expressed in the liver, where it has been implicated as a regulator of fatty-acid metabolism in mouse studies. Reduced miR-122 levels are associated with hepatocellular carcinoma. miR-122 also plays an important positive role in the regulation of hepatitis C virus replication.

MiR-155 is a microRNA that in humans is encoded by the MIR155 host gene or MIR155HG. MiR-155 plays a role in various physiological and pathological processes. Exogenous molecular control in vivo of miR-155 expression may inhibit malignant growth, viral infections, and enhance the progression of cardiovascular diseases.

In molecular biology mir-126 is a short non-coding RNA molecule. MicroRNAs function to regulate the expression levels of other genes by several pre- and post-transcription mechanisms.

In molecular biology miR-132 microRNA is a short non-coding RNA molecule. MicroRNAs function to regulate the expression levels of other genes by several mechanisms, generally reducing protein levels through the cleavage of mRNAs or the repression of their translation. Several targets for miR-132 have been described, including mediators of neurological development, synaptic transmission, inflammation and angiogenesis.

In molecular biology mir-22 microRNA is a short RNA molecule. MicroRNAs are an abundant class of molecules, approximately 22 nucleotides in length, which can post-transcriptionally regulate gene expression by binding to the 3' UTR of mRNAs expressed in a cell.

In molecular biology, mir-433 is a short non-coding RNA molecule. MicroRNAs (miRNAs) function as posttranscriptional regulators of expression levels of other genes by several mechanisms. They play roles in development, metabolism and carcinogenesis.
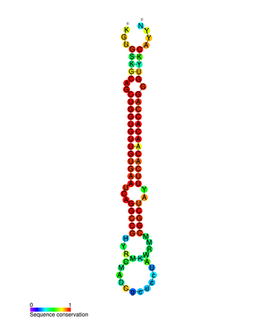
miR-138 is a family of microRNA precursors found in animals, including humans. MicroRNAs are typically transcribed as ~70 nucleotide precursors and subsequently processed by the Dicer enzyme to give a ~22 nucleotide product. The excised region or, mature product, of the miR-138 precursor is the microRNA mir-138.

MicroRNA 146a is a small non-coding RNA that in humans is encoded by the MIR146A gene.
In molecular biology mir-367 microRNA is a short RNA molecule. MicroRNAs function to regulate the expression levels of other genes by several mechanisms.

MicroRNA 494 is a microRNA sequence which is encoded in humans by the MIR494 gene.

MicroRNA 210 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the MIR210 gene.
References
- ↑ Guo Z, Shao L, Zheng L, Du Q, Li P, John B, et al. (2012). "miRNA-939 regulates human inducible nitric oxide synthase posttranscriptional gene expression in human hepatocytes". Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 109 (15): 5826–31. Bibcode:2012PNAS..109.5826G. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1118118109 . PMC 3326458 . PMID 22451906.