Related Research Articles
The year 1918 in science and technology involved some significant events, listed below.
The year 1829 in science and technology involved some significant events, listed below.
The year 1879 in science and technology involved some significant events, listed below.

The year 1791 in science and technology involved some significant events.
The year 1872 in science and technology involved some significant events, listed below.
The year 1818 in science and technology involved some significant events, listed below.

The year 1768 in science and technology involved some significant events.
The year 1884 in science and technology involved some significant events, listed below.
The year 1891 in science and technology involved some significant events, listed below.
The year 1848 in science and technology involved some significant events, listed below.
The year 1795 in science and technology involved some significant events.
The year 1797 in science and technology involved some significant events.
The year 1880 in science and technology included many events, some of which are listed here.
The year 1876 in science and technology involved some significant events, listed below.
The year 1868 in science and technology involved some significant events, listed below.
The year 1858 in science and technology involved some significant events, listed below.
The year 1844 in science and technology involved some significant events, listed below.

Ludwig Eduard Boltzmann was an Austrian physicist and philosopher. His greatest achievements were the development of statistical mechanics, and the statistical explanation of the second law of thermodynamics. In 1877 he provided the current definition of entropy, , where Ω is the number of microstates whose energy equals the system's energy, interpreted as a measure of the statistical disorder of a system. Max Planck named the constant kB the Boltzmann constant.

The Peirce quincuncial projection is the conformal map projection from the sphere to an unfolded square dihedron, developed by Charles Sanders Peirce in 1879. Each octant projects onto an isosceles right triangle, and these are arranged into a square. The name quincuncial refers to this arrangement: the north pole at the center and quarters of the south pole in the corners form a quincunx pattern like the pips on the five face of a traditional die. The projection has the distinctive property that it forms a seamless square tiling of the plane, conformal except at four singular points along the equator.
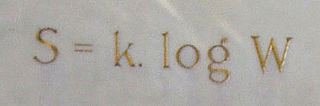
In statistical mechanics, Boltzmann's equation is a probability equation relating the entropy , also written as , of an ideal gas to the multiplicity, the number of real microstates corresponding to the gas's macrostate:
References
- ↑ Clegg, Brian (2007). The Man Who Stopped Time . Washington, DC: Joseph Henry Press. ISBN 978-0-309-10112-7.
- ↑ Peirce, C. S. (1877). "Appendix No. 15. A Quincuncial Projection of the Sphere". Report of the Superintendent of the United States Coast Survey Showing the Progress of the Survey for Fiscal Year Ending with June 1877. pp. 191–194.
- ↑ Weisstein, Eric W. (1996). "Boltzmann, Ludwig (1844–1906)". Eric Weisstein's World of Scientific Biography. Wolfram Research Products. Retrieved 2007-03-24.
- ↑ Eisenlohr, August (1877). Ein mathematisches Handbuch der alten Aegypter (Papyrus Rhind des British Museum). Leipzig: J. C. Hinrichs. Retrieved 2011-10-13.
- ↑ Mouton, Wolfgang G.; Bessell, Justin R.; Maddern, Guy J. (1998). "Looking Back to the Advent of Modern Endoscopy: 150th Birthday of Maximilian Nitze". World Journal of Surgery. 22 (12): 1256–8. doi:10.1007/s002689900555. PMID 9841754.
- ↑ U.S. patent 463,569 .
- ↑ U.S. patent 199,141 .
- ↑ U.S. patent 203,018 .
- ↑ Scientific American 17 May 1878.
- ↑ "Copley Medal | British scientific award". Encyclopedia Britannica. Retrieved 23 July 2020.