
Year 622 (DCXXII) was a common year starting on Friday of the Julian calendar, the 622nd year of the Common Era (CE) and Anno Domini (AD) designations, the 622nd year of the 1st millennium, the 22nd year of the 7th century, and the 3rd year of the 620s decade. The denomination 622 for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years.
The 620s decade ran from January 1, 620, to December 31, 629.
The 720s decade ran from January 1, 720, to December 31, 729.
The 630s decade ran from January 1, 630, to December 31, 639.
The 640s decade ran from January 1, 640, to December 31, 649.
The 650s decade ran from January 1, 650, to December 31, 659.

Year 634 (DCXXXIV) was a common year starting on Saturday of the Julian calendar. The denomination 634 for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years.
Year 636 (DCXXXVI) was a leap year starting on Monday of the Julian calendar. The denomination 636 for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years.

Year 637 (DCXXXVII) was a common year starting on Wednesday of the Julian calendar. The denomination 637 for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years.

Year 624 (DCXXIV) was a leap year starting on Sunday of the Julian calendar. The denomination 624 for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years.

The Battle of the Yarmuk was a major battle between the army of the Byzantine Empire and the Arab Muslim forces of the Rashidun Caliphate. The battle consisted of a series of engagements that lasted for six days in August 636, near the Yarmouk River, along what are now the borders of Syria–Jordan and Syria-Israel, southeast of the Sea of Galilee. The result of the battle was a decisive Muslim victory that ended Roman rule in Syria after about seven centuries. The Battle of the Yarmuk is regarded as one of the most decisive battles in military history, and it marked the first great wave of early Muslim conquests after the death of the Islamic prophet Muhammad, heralding the rapid advance of Islam into the then-Christian/Roman Levant.

ʿĀmir ibn ʿAbd Allāh ibn al-Jarrāḥ, better known as Abū ʿUbayda was a Muslim commander and one of the Companions of the Prophet. He is mostly known for being one of the ten to whom Paradise was promised. He was commander of a large section of the Rashidun Army during the time of the Rashid Caliph Umar and was on the list of Umar's appointed successors to the Caliphate, but died during the Plague of Amwas in 639 before Umar.
The Battle of Hazir or Ma'arakah al-Haadhir took place between the Byzantine army and the Rashidun army's elite cavalry, the Mobile guard. It took place in June 637, three miles east of Qinnasrin at Al-Hadher in present-day Syria.

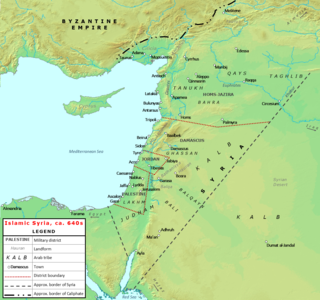
The Muslim conquest of the Levant, or Arab conquest of Syria, was a 634–638 CE invasion of Byzantine Syria by the Rashidun Caliphate. A part of the wider Arab-Byzantine Wars, the Levant was brought under Arab Muslim rule and developed into the provincial region of Bilad al-Sham. Clashes between the Arabs and Byzantines on the southern Levantine borders of the Byzantine Empire had occurred during the lifetime of Muhammad, with the Battle of Muʿtah in 629 CE. However, the actual conquest did not begin until 634, two years after Muhammad's death. It was led by the first two Rashidun caliphs who succeeded Muhammad: Abu Bakr and Umar ibn al-Khattab. During this time, Khalid ibn al-Walid was the most important leader of the Rashidun army.

The Battle of the Iron Bridge was fought between the Muslim Rashidun army and the Byzantine army in 637 AD. The battle took its name from a nearby nine-arch stone bridge spanning the Orontes River which had gates trimmed with iron. It was one of the last battles fought between the Byzantines and Rashidun Caliphate in the province of Syria. The aftermath of the battle marked the nearly complete annexation of the province into the Rashidun Caliphate with the fall of its capital, Antioch.

The siege of Damascus (634) lasted from 21 August to 19 September 634 before the city fell to the Rashidun Caliphate. Damascus was the first major city of the Eastern Roman Empire to fall in the Muslim conquest of Syria.

The siege of Jerusalem (636–637) was part of the Muslim conquest of the Levant and the result of the military efforts of the Rashidun Caliphate against the Byzantine Empire in the year 636–637/38. It began when the Rashidun army, under the command of Abu Ubayda, besieged Jerusalem beginning in November 636. After six months, Patriarch Sophronius agreed to surrender, on condition that he submit only to the caliph. In 637 or 638, Caliph Umar traveled to Jerusalem in person to receive the submission of the city. The patriarch thus surrendered to him.

The siege of Emesa was laid by the forces of Rashidun Caliphate from December 635 up until March 636. This led to the Islamic conquest of Emesa, which was a major trading city of the Byzantine Empire in the Levant.
The siege of Germanicia or Marash was led by Muslim forces of the Rashidun Caliphate during their campaigns in Anatolia in 638. The city surrendered without much bloodshed. The expedition is considered significant due to the fact that it marked the end of the military career of the Arab Muslim general Khalid ibn Walid, who was dismissed from the army a few months after his return from the expedition.
This article lists historical events that occurred between 601–700 in modern-day Lebanon or regarding its people.











