Related Research Articles
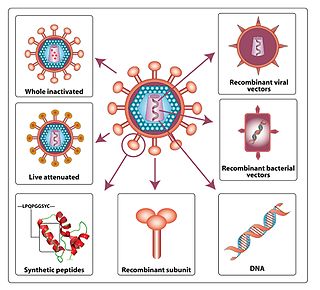
An HIV vaccine is a potential vaccine that could be either a preventive vaccine or a therapeutic vaccine, which means it would either protect individuals from being infected with HIV or treat HIV-infected individuals.
Sanofi S.A. is a French multinational pharmaceutical and healthcare company headquartered in Paris, France. Originally, the corporation was established in 1973 and merged with Synthélabo in 1999 to form Sanofi-Synthélabo. In 2004, Sanofi-Synthélabo merged with Aventis and renamed to Sanofi-Aventis, which were each the product of several previous mergers. It changed its name back to Sanofi in May 2011. The company is a component of the Euro Stoxx 50 stock market index.
Tuberculosis (TB) vaccines are vaccinations intended for the prevention of tuberculosis. Immunotherapy as a defence against TB was first proposed in 1890 by Robert Koch. Today, the only effective tuberculosis vaccine in common use is the Bacillus Calmette-Guérin (BCG) vaccine, first used on humans in 1921. About three out of every 10,000 people who get the vaccine experience side effects, which are usually minor except in severely immuno-depressed individuals. While BCG immunization provides fairly effective protection for infants and young children,, its efficacy in adults is variable, ranging from 0% to 80%. Several variables have been considered as responsible for the varying outcomes. Demand for TB immunotherapy advancement exists because the disease has become increasingly drug-resistant.
rBCG30 is a prospective vaccine against tuberculosis created by a team headed by Marcus A. Horwitz at UCLA. It is a live vaccine, consisting of BCG genetically modified to produce abundant amounts of a 30kDa antigen that has been shown to produce a strong immune response in animals and humans. The vaccine completed a Phase I double-blind randomized controlled clinical trial that demonstrated that rBCG30 was safe and immunogenic; during nine months of follow-up, rBCG30, but not BCG, induced significantly increased Antigen 85B-specific immune responses in eight immunological assays.
Minretumomab (CC49) is a mouse monoclonal antibody that was designed for the treatment of cancers that express the TAG-72 antigen. This includes breast, colon, lung, and pancreatic cancers. Apparently, it never got past Phase I clinical trials for this purpose.

A malaria vaccine is a vaccine that is used to prevent malaria. The only approved vaccine, as of 2021, is RTS,S, known by the brand name Mosquirix. In October 2021, the WHO for the first time recommended the large-scale use of a malaria vaccine for children living in areas with moderate-to-high malaria transmission. Four injections are required for full protection.

JN-International Medical Corporation (JNIMC) is a U.S.-based biopharmaceutical corporation which since 1998 has been focused on developing vaccines and diagnostics for infectious disease for developing countries. This private corporation was founded in 1998 by Dr. Jeeri R. Reddy with the help of Dr. Kelly F. Lechtenberg in a small rural town, Oakland, Nebraska. From there it grew and expanded until in the year 2000 the corporation moved to Omaha, Nebraska.
As of 2021, a vaccine against Epstein–Barr virus was not yet available. The virus establishes latent infection and causes infectious mononucleosis. There is also increasingly more evidence that EBV may be a trigger of multiple sclerosis. It is a dual-tropic virus, meaning that it infects two different host cell types — in this case, both B cells and epithelial cells. One challenge is that the Epstein–Barr virus expresses very different proteins during its lytic and its latent phases. Antiviral agents act by inhibiting viral DNA replication, but as of 2016, there was little evidence that they are effective against Epstein–Barr virus, they are expensive, they risk causing resistance to antiviral agents, and can cause unpleasant side effects.

Ebola vaccines are vaccines either approved or in development to prevent Ebola. The first vaccine to be approved in the United States was rVSV-ZEBOV in December 2019. It had been used extensively in the Kivu Ebola epidemic under a compassionate use protocol. During the early 21st century, several vaccine candidates displayed efficacy to protect nonhuman primates against lethal infection.
Owais Mohammad is an Indian immunologist, nano-technologist and a professor at the interdisciplinary biotechnology unit of the Aligarh Muslim University. Known for his studies on nanotechnology-based vaccine and drug delivery, Owais is the author of two books, Trypanothione reductase: a potential anti-leishmanial drug target and Antimicrobial properties of clove oil: clove oils as antimicrobial agent. He has also co-edited two books, Modern Phytomedicine: Turning Medicinal Plants into Drugs and Combating Fungal Infections: Problems and Remedy, and has contributed chapters. His studies have also been documented by way of a number of articles and ResearchGate, an online repository of scientific articles has listed 60 of them. He is a recipient of the Rashtriya Gaurav Award of the India International Friendship Society. The Department of Biotechnology of the Government of India awarded him the National Bioscience Award for Career Development, one of the highest Indian science awards, for his contributions to biosciences in 2007. His work has been displayed on cover pages of FEMS Immunol. Med Microbiology for all the issues of Year 2006 and Molecular Medicine in May–June issue of Year 2007.
A molecular clamp is a polypeptide used to maintain the shape of proteins in some experimental vaccines. On a virus, pre-fusion proteins on their surface provide an attractive target for an immune reaction. However, if these proteins are removed or made by recombinant technology, they lose their shape and form what is called a "post-fusion form". When part of a virus, these proteins maintain their form by forming a quaternary structure with other viral proteins. The pre-fusion state of the protein is a higher energy metastable state. The extra energy is used to overcome the activation barrier of the fusion to the cell membrane. The virus protein in combination with the clamp polypeptide is called a chimeric polypeptide.

ZF2001, trade-named Zifivax or ZF-UZ-VAC-2001, is an adjuvanted protein subunit COVID-19 vaccine developed by Anhui Zhifei Longcom in collaboration with the Institute of Microbiology at the Chinese Academy of Sciences. The vaccine candidate is in Phase III trials with 29,000 participants in China, Ecuador, Malaysia, Pakistan, and Uzbekistan.

EpiVacCorona is a peptide-based vaccine against COVID-19 developed by the VECTOR center of Virology. The lack of protective effectiveness of EpiVacCorona, which is still in use in Russia, has been reported in the scientific literature and in the media. The vaccine consists of three chemically synthesized peptides that are conjugated to a large carrier protein. This protein is a fusion product of a viral nucleocapsid protein and a bacterial MBP protein. A phase three clinical trial to show whether or not the vaccine can protect people against COVID-19 was launched in November 2020 with more than three thousand participants. The facts of the end of the trial and the result of the trial have not been made public.

The CureVac COVID-19 vaccine was a COVID-19 vaccine candidate developed by CureVac N.V. and the Coalition for Epidemic Preparedness Innovations (CEPI). The vaccine showed inadequate results in its Phase III trials with only 47% efficacy. In October 2021 CureVac abandoned further development and production plans for CVnCoV and refocused efforts on a cooperation with GlaxoSmithKline.

SCB-2019 is a protein subunit COVID-19 vaccine developed by Clover Biopharmaceuticals using an adjuvant from Dynavax technologies. Positive results of Phase I trials for the vaccine were published in The Lancet and the vaccine completed enrollment of 29,000 participants in Phase II/III trials in July 2021. In September 2021, SCB-2019 announced Phase III results showing 67% efficacy against all cases of COVID-19 and 79% efficacy against all cases of the Delta variant. Additionally, the vaccine was 84% effective against moderate cases and 100% effective against hospitalization.

The Sanofi–GSK COVID-19 vaccine code-named VAT00002 and VAT00008 is a COVID-19 vaccine candidate developed by Sanofi Pasteur and GSK.

UB-612 is a COVID-19 vaccine candidate developed by United Biomedical, Inc. Asia, Vaxxinity, and Diagnosticos da America (DASA). It is a peptide vaccine.

V-01 is a protein subunit COVID-19 vaccine candidate developed by a subsidiary of Livzon Pharmaceutical Group Inc.

COVAX-19 is the result of a collaboration between Vaxine and CinnaGen, a private company with operations in the Middle East. COVAX-19 is a recombinant protein-based COVID-19 vaccine developed by South Australian-based biotech company Vaxine. It is under clinical trial in collaboration with the Iranian company CinnaGen.
MTBVAC is a vaccine candidate against tuberculosis in humans currently in research trials. It is based on a genetically modified form of the Mycobacterium tuberculosis pathogen isolated from humans.
References
- Kaufmann SHE, McMichael AJ (2005). "Annulling a dangerous liaison: vaccination strategies against AIDS and tuberculosis". Nature Medicine. 11 (4 suppl): S33–S44. doi:10.1038/nm1221. PMC 7095892 . PMID 15812488.