
Typhoid fever, also known simply as typhoid, is a disease caused by Salmonella enterica serotype Typhi bacteria, also called Salmonella typhi. Symptoms vary from mild to severe, and usually begin six to 30 days after exposure. Often there is a gradual onset of a high fever over several days. This is commonly accompanied by weakness, abdominal pain, constipation, headaches, and mild vomiting. Some people develop a skin rash with rose colored spots. In severe cases, people may experience confusion. Without treatment, symptoms may last weeks or months. Diarrhea may be severe, but is uncommon. Other people may carry it without being affected, but are still contagious. Typhoid fever is a type of enteric fever, along with paratyphoid fever. Salmonella enterica Typhi is believed to infect and replicate only within humans.

A vaccine is a biological preparation that provides active acquired immunity to a particular infectious or malignant disease. The safety and effectiveness of vaccines has been widely studied and verified. A vaccine typically contains an agent that resembles a disease-causing microorganism and is often made from weakened or killed forms of the microbe, its toxins, or one of its surface proteins. The agent stimulates the body's immune system to recognize the agent as a threat, destroy it, and recognize further and destroy any of the microorganisms associated with that agent that it may encounter in the future.

A conjugate vaccine is a type of subunit vaccine which combines a weak antigen with a strong antigen as a carrier so that the immune system has a stronger response to the weak antigen.

Meningococcal disease describes infections caused by the bacterium Neisseria meningitidis. It has a high mortality rate if untreated but is vaccine-preventable. While best known as a cause of meningitis, it can also result in sepsis, which is an even more damaging and dangerous condition. Meningitis and meningococcemia are major causes of illness, death, and disability in both developed and under-developed countries.
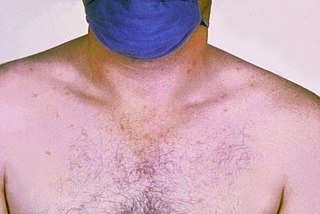
Paratyphoid fever, also known simply as paratyphoid, is a bacterial infection caused by one of three types of Salmonella enterica. Symptoms usually begin 6–30 days after exposure and are the same as those of typhoid fever. Often, a gradual onset of a high fever occurs over several days. Weakness, loss of appetite, and headaches also commonly occur. Some people develop a skin rash with rose-colored spots. Without treatment, symptoms may last weeks or months. Other people may carry the bacteria without being affected; however, they are still able to spread the disease to others. Typhoid and paratyphoid are of similar severity. Paratyphoid and typhoid fever are types of enteric fever.
An attenuated vaccine is a vaccine created by reducing the virulence of a pathogen, but still keeping it viable. Attenuation takes an infectious agent and alters it so that it becomes harmless or less virulent. These vaccines contrast to those produced by "killing" the pathogen.

Hepatitis A vaccine is a vaccine that prevents hepatitis A. It is effective in around 95% of cases and lasts for at least twenty years and possibly a person's entire life. If given, two doses are recommended beginning after the age of one. It is given by injection into a muscle. The first hepatitis A vaccine was approved in the European Union in 1991, and the United States in 1995. It is on the World Health Organization's List of Essential Medicines.

The Haemophilus influenzae type B vaccine, also known as Hib vaccine, is a vaccine used to prevent Haemophilus influenzae type b (Hib) infection. In countries that include it as a routine vaccine, rates of severe Hib infections have decreased more than 90%. It has therefore resulted in a decrease in the rate of meningitis, pneumonia, and epiglottitis.
The Vi capsular polysaccharide vaccine is a typhoid vaccine recommended by the World Health Organization for the prevention of typhoid. The vaccine was first licensed in the US in 1994 and is made from the purified Vi capsular polysaccharide from the Ty2 Salmonella Typhi strain; it is a subunit vaccine.
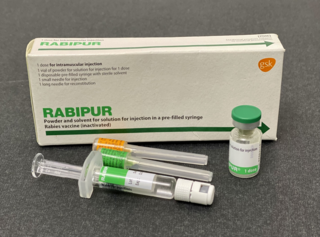
The rabies vaccine is a vaccine used to prevent rabies. There are several rabies vaccines available that are both safe and effective. Vaccinations must be administered prior to rabies virus exposure or within the latent period after exposure to prevent the disease. Transmission of rabies virus to humans typically occurs through a bite or scratch from an infectious animal, but exposure can occur through indirect contact with the saliva from an infectious individual.
NmVac4-A/C/Y/W-135 is the commercial name for a polysaccharide vaccine that protects against meningococcal meningitis caused by Neisseria meningitidis, specifically the serotypes A, C, Y, and W-135. This vaccine is part of a broader group of meningococcal vaccines. It is especially formulated for use in developing countries, aimed at protecting populations during meningitis outbreaks, particularly in high-risk regions like the African meningitis belt.

Diphtheria vaccine is a toxoid vaccine against diphtheria, an illness caused by Corynebacterium diphtheriae. Its use has resulted in a more than 90% decrease in number of cases globally between 1980 and 2000. The first dose is recommended at six weeks of age with two additional doses four weeks apart, after which it is about 95% effective during childhood. Three further doses are recommended during childhood. It is unclear if further doses later in life are needed.

A cholera vaccine is a vaccine that is effective at reducing the risk of contracting cholera. The recommended cholera vaccines are administered orally to elicit local immune responses in the gut where the intestinal cells produce antibodies against the cholera microbe. This immune response was poorly achieved with the injectable vaccines that were used until the 1970s. The first effective oral cholera vaccine was Dukoral, developed in Sweden in the 1980s. For the first six months after vaccination it provides about 85% protection, which decreases to approximately 60% during the first two years. When enough of the population is immunized, it may protect those who have not been immunized thereby increasing the total protective impact to more than 90 %.
Meningococcal vaccine refers to any vaccine used to prevent infection by Neisseria meningitidis. Different versions are effective against some or all of the following types of meningococcus: A, B, C, W-135, and Y. The vaccines are between 85 and 100% effective for at least two years. They result in a decrease in meningitis and sepsis among populations where they are widely used. They are given either by injection into a muscle or just under the skin.

Typhoid vaccines are vaccines that prevent typhoid fever. Several types are widely available: typhoid conjugate vaccine (TCV), Ty21a and Vi capsular polysaccharide vaccine (ViPS). They are about 30 to 70% effective in the first two years, depending on the specific vaccine in question. The Vi-rEPA vaccine is efficacious in children.

Yellow fever vaccine is a vaccine that protects against yellow fever. Yellow fever is a viral infection that occurs in Africa and South America. Most people begin to develop immunity within ten days of vaccination and 99% are protected within one month, and this appears to be lifelong. The vaccine can be used to control outbreaks of disease. It is given either by injection into a muscle or just under the skin.

Cocooning, also known as the Cocoon Strategy, is a vaccination strategy to protect infants and other vulnerable individuals from infectious diseases by vaccinating those in close contact with them. If the people most likely to transmit an infection are immune, their immunity creates a "cocoon" of protection around the newborn.
Tetanus vaccine, also known as tetanus toxoid (TT), is a toxoid vaccine used to prevent tetanus. During childhood, five doses are recommended, with a sixth given during adolescence.

Edward Thomas Ryan is an American microbiologist, immunologist, and physician at Harvard University and Massachusetts General Hospital. Ryan served as president of the American Society of Tropical Medicine and Hygiene from 2009 to 2010. Ryan is Professor of Immunology and Infectious Diseases at the Harvard T.H. Chan School of Public Health, Professor of Medicine at Harvard Medical School, and Director of Global Infectious Diseases at the Massachusetts General Hospital. Ryan's research and clinical focus has been on infectious diseases associated with residing in, immigrating from, or traveling through resource-limited areas. Ryan is a Fellow of the American Society of Microbiology, the American Society of Tropical Medicine and Hygiene, the American College of Physicians, and the Infectious Diseases Society of America.

A vaccine dose contains many ingredients very little of which is the active ingredient, the immunogen. A single dose may have merely nanograms of virus particles, or micrograms of bacterial polysaccharides. A vaccine injection, oral drops or nasal spray is mostly water. Other ingredients are added to boost the immune response, to ensure safety or help with storage, and a tiny amount of material is left-over from the manufacturing process. Very rarely, these materials can cause an allergic reaction in people who are very sensitive to them.
















