
The seminal vesicles are a pair of convoluted tubular accessory glands that lie behind the urinary bladder of male mammals. They secrete fluid that partly composes the semen.

The vas deferens, with the more modern name ductus deferens, is part of the male reproductive system of many vertebrates. The ducts transport sperm from the epididymides to the ejaculatory ducts in anticipation of ejaculation. The vas deferens is a partially coiled tube which exits the abdominal cavity through the inguinal canal.

The ejaculatory ducts are paired structures in the male reproductive system. Each ejaculatory duct is formed by the union of the vas deferens with the duct of the seminal vesicle. They pass through the prostate, and open into the urethra above the seminal colliculus. During ejaculation, semen passes through the prostate gland, enters the urethra and exits the body via the urinary meatus.

The mesonephric duct, also known as the Wolffian duct, archinephric duct, Leydig's duct or nephric duct, is a paired organ that develops in the early stages of embryonic development in humans and other mammals. It is an important structure that plays a critical role in the formation of male reproductive organs. The duct is named after Caspar Friedrich Wolff, a German physiologist and embryologist who first described it in 1759.

The inguinal canal is a passage in the anterior abdominal wall on each side of the body, which in males, convey the spermatic cords and in females, the round ligament of the uterus. The inguinal canals are larger and more prominent in males.

The bile duct is a part of the biliary tract. It is formed by the union of the common hepatic duct and cystic duct. It ends by uniting with the pancreatic duct to form the hepatopancreatic ampulla. It possesses its own sphincter to enable regulation of bile flow.
An ampulla was, in Ancient Rome, a "small nearly globular flask or bottle, with two handles" (OED).

In human anatomy, the inferior epigastric artery is an artery that arises from the external iliac artery. It is accompanied by the inferior epigastric vein; inferiorly, these two inferior epigastric vessels together travel within the lateral umbilical fold The inferior epigastric artery then traverses the arcuate line of rectus sheath to enter the rectus sheath, then anastomoses with the superior epigastric artery within the rectus sheath.
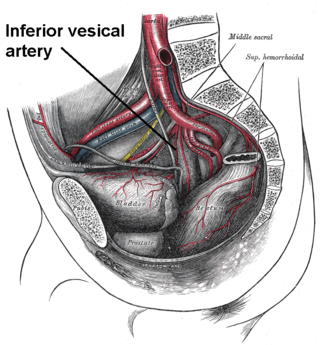
The inferior vesical artery is an artery of the pelvis which arises from the internal iliac artery and supplies parts of the urinary bladder as well as other structures of the urinary system and structures of the male reproductive system.

The superior vesical artery supplies numerous branches to the upper part of the bladder. This artery often also gives branches to the vas deferens and can provide minor collateral circulation for the testicles.
Congenital absence of the vas deferens (CAVD) is a condition in which the vasa deferentia reproductive organs fail to form properly prior to birth. It may either be unilateral (CUAVD) or bilateral (CBAVD).

The testicular artery is a branch of the abdominal aorta that supplies blood to the testicle. It is a paired artery, with one for each of the testicles.

The vesical nervous plexus arises from the forepart of the pelvic plexus. The nerves composing it are numerous, and contain a large proportion of spinal nerve fibers. They accompany the vesicle arteries, and are distributed to the sides and fundus of the bladder. Numerous filaments also pass to the seminal vesicles and vas deferens; those accompanying the vas deferens join, on the spermatic cord, with branches from the spermatic plexus.

The peritoneum of the anterior pelvic wall covers the superior surface of the bladder, and on either side of this viscus forms a depression, termed the paravesical fossa, which is limited laterally by the fold of peritoneum covering the ductus deferens.
The seminal tract is a part of the male reproductive system and consists of Seminiferous tubules, Epididymis (Appendix), Vas deferens (Ampulla) and Ejaculatory duct.

Indrella is a monotypic genus containing the single species Indrella ampulla, a tropical terrestrial air-breathing gastropod mollusk in the family Ariophantidae. It is endemic to the Western Ghats of India.
Vasectomy reversal is a term used for surgical procedures that reconnect the male reproductive tract after interruption by a vasectomy. Two procedures are possible at the time of vasectomy reversal: vasovasostomy and vasoepididymostomy. Although vasectomy is considered a permanent form of contraception, advances in microsurgery have improved the success of vasectomy reversal procedures. The procedures remain technically demanding and may not restore the pre-vasectomy condition.

PPADS (pyridoxalphosphate-6-azophenyl-2',4'-disulfonic acid) is a selective purinergic P2X antagonist. It is able to block contractions of rabbit vas deferens induced by ATP or α,β,methylene-ATP. It appears to be relatively selective for P2X receptors, having no appreciable activity at α1 adrenergic, muscarinic M2 and M3, histamine H1, and adenosine A1 receptors.
Aether Records is an Indianapolis, Indiana-based record label that reissues rare rock records from the 1960s and 1970s as well as contemporary music in a neo psychedelic style.

An organ chamber, organ bath, or isolated tissue bath, is a chamber in which isolated organs or tissues can be administered with drugs, or stimulated electrically, in order to measure their function. The tissue in the organ bath is typically oxygenated with carbogen and kept in a solution such as Tyrode's solution or lactated Ringer's solution. Historically, they have also been called gut baths.















