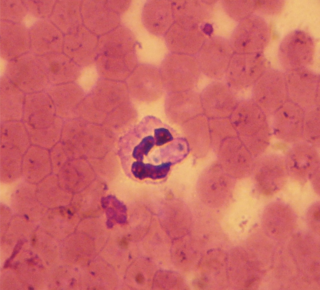
Hepatozoon is a genus of Apicomplexa alveolates which incorporates over 300 species obligate intraerythrocytic parasites. Species have been described from all groups of tetrapod vertebrates, as well as a wide range of haematophagous arthropods, which serve as both the vectors and definitive hosts of the parasite. By far the most biodiverse and prevalent of all haemogregarines, the genus is distinguished by its unique reciprocal trophic lifecycle which lacks the salivary transmission between hosts commonly associated with other apicomplexans. While particularly prevalent in amphibians and reptiles, the genus is more well known in veterinary circles for causing a tick-borne disease called hepatozoonosis in some mammals.
Giovanolaia is a subgenus of the genus Plasmodium created by Corradetti et al. in 1963. The parasites within this subgenus infect birds.
Novyella is a subgenus of the genus Plasmodium - all of which are parasites. The subgenus was created in 1963 by Corradetti et al.. Species in this subgenus infect birds. It unites the avian malaria parasites with small erythrocytic meronts and elongated gametocytes.
Plasmodium egerniae is a parasite of the genus Plasmodium subgenus Sauramoeba.
Plasmodium gundersi is a parasite of the genus Plasmodium subgenus Giovannolaia.
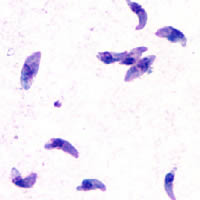
The Eucoccidiorida are an order of microscopic, spore-forming, single-celled parasites belonging to the apicomplexan class Conoidasida. Protozoans of this order include parasites of humans, and both domesticated and wild animals including birds. Among these parasites are the Toxoplasma gondii that cause toxoplasmosis and Isospora belli, which results in isosporiasis.

Haemoproteus is a genus of alveolates that are parasitic in birds, reptiles and amphibians. Its name is derived from Greek: Haima, "blood", and Proteus, a sea god who had the power of assuming different shapes. The name Haemoproteus was first used in the description of Haemoproteus columbae in the blood of the pigeon Columba livia by Kruse in 1890. This was also the first description of this genus. Two other genera — Halteridium and Simondia — are now considered to be synonyms of Haemoproteus.

Adeleorina is a suborder of parasites in the phylum Apicomplexa.

The Haemosporida are an order of intraerythrocytic parasitic alveolates.
Plasmodium alaudae is a parasite of the genus Plasmodium.
Haemosporidiasina (Haemosporidia) is a subclass of apicomplexans described by Jacques Euzéby in 1988. The taxon is very similar to Aconoidasida.
Billbraya is a genus of parasitic alveolates in the phylum Apicomplexia. It contains a single recognised species, Billbraya australis.
Nycteria is a genus of protozoan parasites that belong to the phylum Apicomplexa. It is composed of vector-borne haemosporidian parasites that infect a wide range of mammals such as primates, rodents and bats. Its vertebrate hosts are bats. First described by Garnham and Heisch in 1953, Nycteria is mostly found in bat species where it feeds off the blood of their hosts and causes disease. Within the host, Nycteria develops into peculiar lobulated schizonts in parenchyma cells of the liver, similarly to the stages of Plasmodum falciparum in the liver. The vector of Nycteria has been hard to acquire and identify. Because of this, the life cycle of Nycteria still remains unknown and understudied. It has been suggested that this vector could be an arthropod rather than a mosquito or the vector of most haemosporidian parasites.
Garnia is a genus of parasitic alveolates belonging to the phylum Apicomplexia.

The Haemoproteidae are a family of parasitic alveolates in the phylum Apicomplexa.
Dactylosoma is a genus of parasitic alveolates of the phylum Apicomplexia.

Hemolivia is a genus of the phylum Apicomplexia.
Papernaia is a subgenus of the genus Plasmodium, all of which are parasitic protozoa. The subgenus was created in 2010 by Landau et al

Alain Chabaud was a French parasitologist, mainly a specialist of nematodes and sporozoa. He was the Director of the Laboratoire de Zoologie (Vers) in the Muséum National d'Histoire Naturelle in Paris from 1960 to 1989. He was one of the founders of the Société Française de Parasitologie in 1962 and its president until 1975, and president of the Société zoologique de France in 1967.
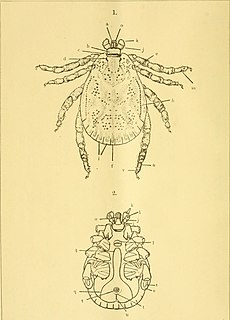
Dermacentor auratus is a hard-bodied tick of the genus Dermacentor. It is found in India, Sri Lanka, Indonesia, and Vietnam. The length from capitulum to middle festoon is 7 mm and maximum breadth at its mid length is 5 mm. Adult has highly ornate scutum, capitulum, and legs. A pair of eyes was present at the level of second coxae. Brown base color markings on the dorsal scutum is the characteristic feature.








